J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2010 Mar;35(2):88-95. 10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.088.
A comparison of the shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium files in simulated root canals
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Division of Dentistry, Graduate of Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. gwchoi@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2176295
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.088
Abstract
- The purpose of this study was to compare the root canal shaping ability of 4 rotary NiTi instruments in simulated root canals.
For the preparation of thirty two curved root canals, Mtwo instruments using "single length"technique, and Profile, ProTaper Universal, and K3 using crown-down technique (N = 8) were used. All canal samples were prepared by reaching an apical canal size of #30. Pre- and post-instrumentation digital images were recorded and an assessment of canal shape was determined using a computer image analysis program SigmaScan Pro (Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). The changes of the dimension of inner walls of canals, (2) the changes of the dimension of outer walls of canals, and (3) the centering ratio were measured at 7 measuring points, and then data were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Duncan's test. The results were as below;
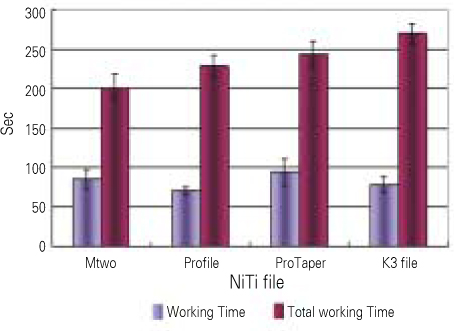
1. The root canal shaping ability of Profile was significantly faster than that of other rotary NiTi instruments (p < 0.05).
2. The deformation and fracture of all instruments used for this study were not experienced.
3. In the degree of changes of the dimension of inner walls of canals, Profile demonstrated the lowest changes of the dimension of inner walls of canals except at the measuring points of the 1 and 2 mm (p < 0.05). However, the ProTaper Universal showed the highest changes of the dimension of inner walls of canals at all measuring points (p < 0.05).
4. In the degree of changes of the dimension of outer walls of canals, Mtwo demonstrated the lowest changse of the dimension of outer walls of canals except at the measuring point of the 1 mm (p < 0.05). However, Profile exhibited the highest changes of the dimension of outer walls of canals at the measuring points of 3 and 4 mm and ProTaper Universal and K3 showed the largest changes of the dimension of outer walls of canals at the measuring points of 1, 2, 6, and 7 mm (p < 0.05).
5. In degree of centering ratio, Profile demonstrated the least centering ratio comparing with the centering ratio shown by other NiTi instruments at the measuring points of 1, 4, 5, and 6 mm.
Results
suggest that in the coronal part of canal preparation, active cutting files such as ProTaper Universal may efficiently flare the canal orifice and form a better taper, and in the apical part of the canal, files which have a better centering ability such as Profile may maintain the original canal curvature and reduce the shaping time.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
Ki-Won Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Ki-Yeol Choi, Bekir Karabucak, Jin-Woo Kim
Restor Dent Endod. 2014;39(1):7-11. doi: 10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.7.
Reference
-
1. Schilder H. Cleaning and shaping the root canal. Dent Clin North Am. 1974. 18(2):269–296.2. Schilder H, Yee F. Cohen S, Burns RC, editors. Canal debridement and disinfection. Pathways of the Pulp. 1984. 3rd ed. St Louis, MO: CV Mosby;175–204.3. Weine FS, Kelly RF, Lio PJ. The effect of preparation procedures on original canal shape and on apical foramen shape. J Endod. 1975. 1(8):255–262.
Article4. Schafer E, Tepel J, Hoppe W. Properties of endodontic hand instruments used in rotary motion. Part 2. Instrumentation of curved canals. J Endod. 1995. 21(10):493–497.
Article5. Walia H, Brantley WA, Gerstein H. An initial investigation of the bending and torsional properties of Nitinol root canal files. J Endod. 1988. 14(7):346–351.
Article6. Glossen CR, Haller RH, Dove SB, del Rio CE. A comparison of root canal preparations using Ni-Ti hand, Ni-Ti engine-driven, and K-Flex endodontic instruments. J Endod. 1995. 21(3):146–151.
Article7. Schafer E, Erler M, Dammaschke T. Comparative study on the shaping ability and cleaning efficiency of rotary Mtwo instruments. Part 1. Shaping ability in simulated curved canals. Int Endod J. 2006. 39(3):196–202.
Article8. Kosa DA, Marshall G, Baumgartner JC. An Analysis of Canal Centering Using Mechanical Instrumentation Techniques. J Endod. 1999. 25(6):441–445.
Article9. Bergmans L, Van Cleynenbreugel J, Beullens M, Wevers M, Van Meerbeek B, Lambrechts P. Progressive versus constant tapered shaft design using NiTi rotary instruments. Int Endod J. 2003. 36(4):288–295.
Article10. Schafer E, Florek H. Efficiency of rotary nickel titanium K3 instruments compared with stainless steel hand K-Flexofile. Part 1. Shaping ability in simulated curved canals. Int Endod J. 2003. 36(3):199–207.11. Peters OA. Current challenges and concepts in the preparation of root canal systems: a review. J Endod. 2004. 30(8):559–571.
Article12. Ayar LR, Love RM. Shaping ability of ProFile and K3 rotary Ni-Ti instruments when used in a variable tip sequence in simulated curved root canals. Int Endod J. 2004. 37(9):593–601.
Article13. Yang GB, Zhou XD, Zhang H, Wu HK. Shaping ability of progressive versus constant taper instruments in simulated root canals. Int Endod J. 2006. 39(10):791–799.
Article14. Yun H, Kim SK. A comparison of the shaping ability of 4 nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated root canal. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003. 95(2):228–233.
Article15. Kang MS, Kim HC, Hur B, Park JK. Comparison of shaping ability of rotary Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduates. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2006. 31(1):1–10.
Article16. Lim JJ, Kim DJ, Hwang YC, Hwangm IN, Oh WM. The change of canal configuration after instrumentation by several Nickel-Titanium files in the simulated canal with abrupt curvature. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2005. 30(4):303–311.
Article17. Lim YK, Park JK, Hur B, Kim HC. Comparison of shaping ability between single length technique and crown-down technique using Mtwo rotary file. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2007. 32(4):385–396.
Article18. Calhoun G, Montgomery S. The effects of four instrumentation techniques on root canal shape. J Endod. 1988. 14(6):273–277.
Article19. Kum KY, Spangberg L, Cha BY, et al. Shaping ability of three ProFile rotary instrumentation techniques in simulated resin root canals. J Endod. 2000. 26:719–723.
Article20. Sonntag D, Ott M, Kook K, Stachniss V. Root canal preparation with the NiTi systems K3, Mtwo and ProTaper. Aust Endod J. 2007. 33(2):73–81.
Article21. Lee BK, Kim DJ, Hwang YC, Hwang IN, Oh WM. A comparative study on the canal configuration after shaping by profile, protaper™ and K-flexofile in simulated canals with different angles of curvature. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2005. 30(4):294–302.
Article22. Schäfer E, Oitzinger M. Cutting efficiency of five different types of rotary nickel-titanium instruments. J Endod. 2008. 34(2):198–200.
Article23. Yoshimine Y, Ono M, Akamine A. The shaping effects of three nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped canals. J Endod. 2005. 31(5):373–375.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Shaping ability of nickel-titaniumrotary files
- Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
- Shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium instruments to prepare root canal at danger zone
- Influence of taper on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
- Shaping ability of Ni-Ti rotary files in combination with GT rotary Ni-Ti file