Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Apr;86(4):217-219. 10.4174/astr.2014.86.4.217.
Left paraduodenal hernia combined with acute cholecystitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. selee508@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2167130
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.86.4.217
Abstract
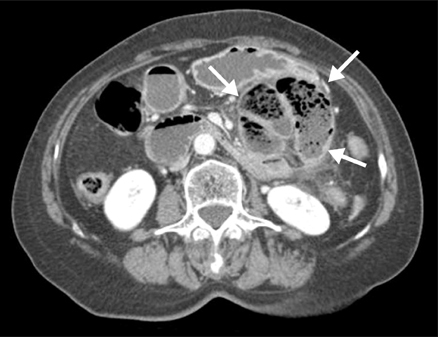
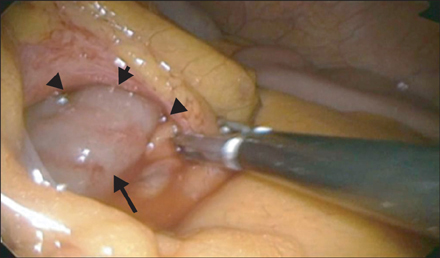
- Paraduodenal hernia is a rare congenital malformation. Management consists of reduction of the herniated intestine and repair of the defect. A 74-year-old woman presented to the Emergency Department with persistent right upper quadrant pain that began 3 hours ago. Physical examination revealed tenderness at right upper quadrant of abdomen. Computed tomography revealed multiple gallstones with gallbladder wall thickening, marked dilatation of stomach and duodenum and a sac-like mass of small bowel loops to left of ligament of Treitz suggesting acute cholecystitis and left paraduodenal hernia. Laparoscopic exploration of abdomen was performed and cholecystectomy, bowel reduction, and closure of defect with intracorporeal interrupted suturing were performed. For left paraduodenal hernia without bowel necrosis, laparoscopic reduction of incarcerated bowel and closure of hernial orifice are technically feasible and may be the surgical method of choice because of its minimal invasiveness and aesthetic advantage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berardi RS. Paraduodenal hernias. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981; 152:99–110.2. Tong RS, Sengupta S, Tjandra JJ. Left paraduodenal hernia: case report and review of the literature. ANZ J Surg. 2002; 72:69–71.3. Hirasaki S, Koide N, Shima Y, Nakagawa K, Sato A, Mizuo J, et al. Unusual variant of left paraduodenal hernia herniated into the mesocolic fossa leading to jejunal strangulation. J Gastroenterol. 1998; 33:734–738.4. Khan MA, Lo AY, Vande Maele DM. Paraduodenal hernia. Am Surg. 1998; 64:1218–1222.5. Willwerth BM, Zollinger RM Jr, Izant RJ Jr. Congenital mesocolic (paraduodenal) hernia. Embryologic basis of repair. Am J Surg. 1974; 128:358–361.6. Al-Khyatt W, Aggarwal S, Birchall J, Rowlands TE. Acute intestinal obstruction secondary to left paraduodenal hernia: a case report and literature review. World J Emerg Surg. 2013; 8:5.7. Fukunaga M, Kidokoro A, Iba T, Sugiyama K, Fukunaga T, Nagakari K, et al. Laparoscopic surgery for left paraduodenal hernia. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2004; 14:111–115.8. Jeong GA, Cho GS, Kim HC, Shin EJ, Song OP. Laparoscopic repair of paraduodenal hernia: comparison with conventional open repair. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2008; 18:611–615.