Healthc Inform Res.
2011 Mar;17(1):18-23. 10.4258/hir.2011.17.1.18.
Hospital Wireless Local Area Network-Based Tracking System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. hakjlee@radiol.snu.ac.kr
- 2Optimum Solution Co., Ltd., Korea.
- 3Department of Nursing, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2166591
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2011.17.1.18
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to develop a prototype wireless local area network (LAN)-based tracking system and evaluate its efficacy.
METHODS
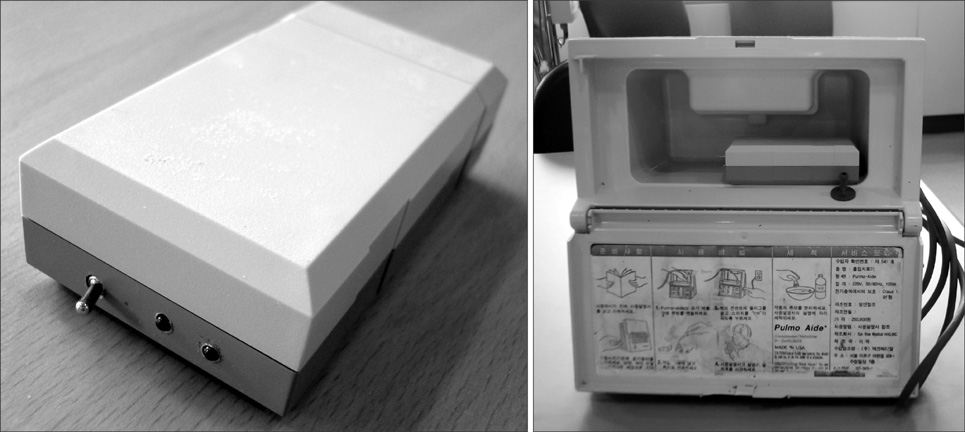
A wireless LAN-based tracking system was developed with a personal digital assistant (PDA) having a simple text messaging function and a prototype stand-alone tracking device. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the tracking system was performed in two ways. Twenty-five messages were sent to nurses by direct communication and 46 messages were sent by the wireless system. Thirty cases by nurses and 30 cases by the wireless system to locate hospital equipment were performed. The time required to transfer messages and to locate equipment was measured and analyzed with a Mann-Whitney test and a paired t-test, respectively.
RESULTS
The mean time required to transfer messages by direct communication and by the wireless system were 37.92 +/- 19.19 seconds and 30.65 +/- 9.80 seconds, respectively which were not statistically different (p = 0.108). The mean time required to locate equipment by the nurses and by the wireless system was 234.00 +/- 59.99 and 23.97 +/- 6.17 seconds, respectively which was statistically different (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
The wireless LAN-based tracking system can save time for nurses to communicate and to check for the location of equipment in wards which allows nurses to spend more time and attention to patient care and safety.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Development of Mobile Platform Integrated with Existing Electronic Medical Records
YoungAh Kim, Sung Soo Kim, Simon Kang, Kyungduk Kim, Jun Kim
Healthc Inform Res. 2014;20(3):231-235. doi: 10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.231.
Reference
-
1. Heslop L, Howard A, Fernando J, Rothfield A, Wallace L. Wireless communications in acute health-care. J Telemed Telecare. 2003. 9:187–193.
Article2. Bird SB, Zarum RS, Renzi FP. Emergency medicine resident patient care documentation using a hand-held computerized device. Acad Emerg Med. 2001. 8:1200–1203.
Article3. Eastes L. Use of the personal digital assistant for point-of-care trauma documentation. J Emerg Nurs. 2001. 27:516–518.
Article4. Traherne R, Diston A. Wireless technologies in health care. Med Device Technol. 2005. 16:35–37.5. Yoshihiro A, Nakata N, Harada J, Tada S. Wireless local area networking for linking a PC reporting system and PACS: clinical feasibility in emergency reporting. Radiographics. 2002. 22:721–728.
Article6. Breslin S, Greskovich W, Turisco F. Wireless technology improves nursing workflow and communications. Comput Inform Nurs. 2004. 22:275–281.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Electromagnetic Interference of Wireless Local Area Network on Electrocardiogram Monitoring System: A Case Report
- A Study on a Low Power Telemetry System for Infant Incubators
- A Study on the Implementation of Medical Telemetry Systems Using Wireless Public Data Network Medical Telemetry System
- The Implementation of Homecare Nursing Network System Using Wireless Network
- Development of a Home Care Nursing Network System for Low Income and Vulnerable Health People by Utilizing Wire-Wireless Network and Mobile Computing