Healthc Inform Res.
2010 Mar;16(1):52-59. 10.4258/hir.2010.16.1.52.
Knowledge Structure of Korean Medical Informatics: A Social Network Analysis of Articles in Journal and Proceedings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Biomedical Knowledge Engineering Laboratory, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. hgkim@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2166566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2010.16.1.52
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
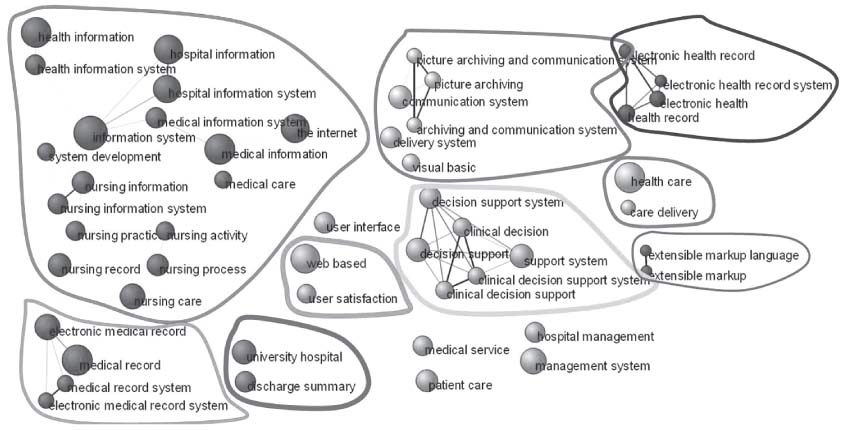
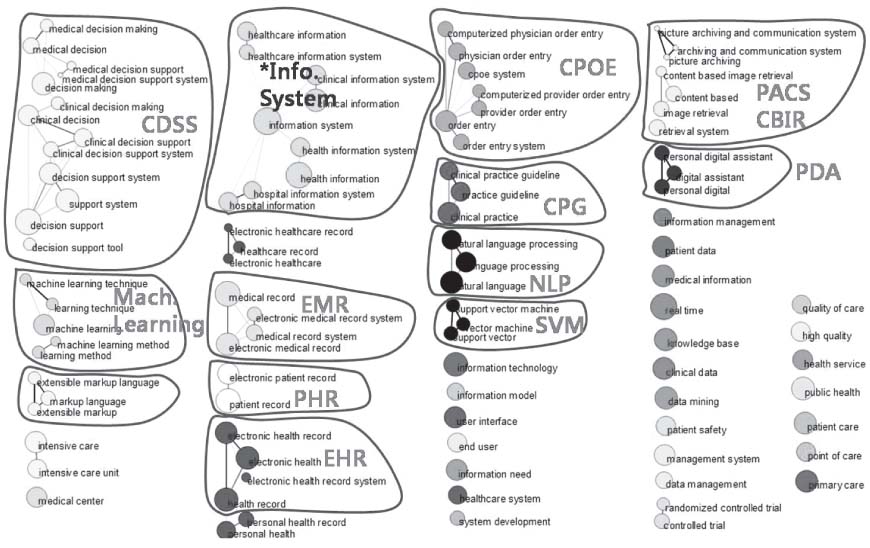
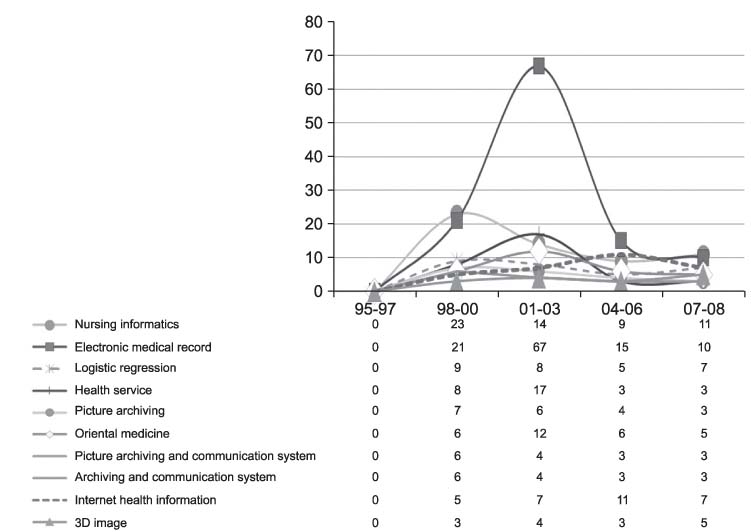
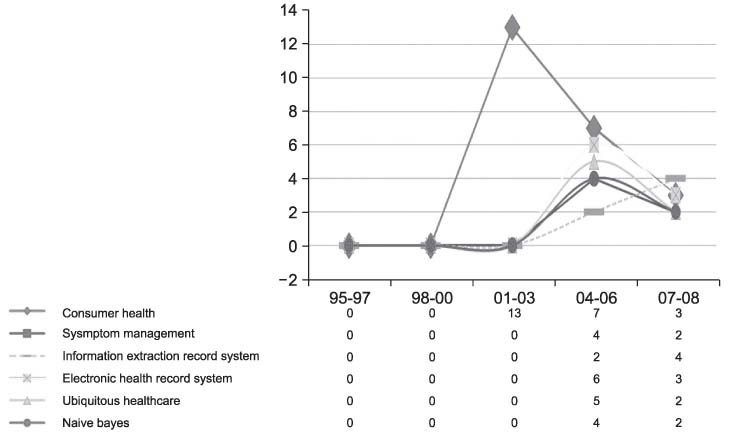
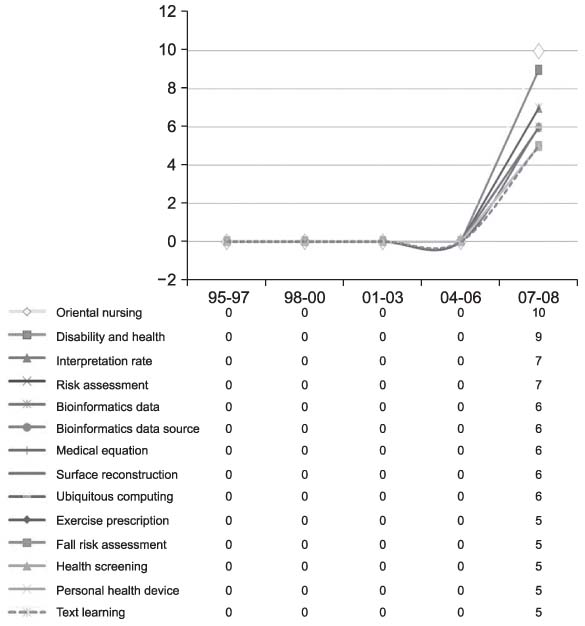
This study aimed at exploring the knowledge structure of Korean medical informatics. METHODS: We utilized the keywords, as the main variables, of the research papers that were presented in the journal and symposia of the Korean Society of Medical Informatics, and we used, as cases, the English titles and abstracts of the papers (n = 915) published from 1995 through 2008. N-grams (bigram to 5-gram) were extracted from the corpora using the BiKE Text Analyzer, and their cooccurrence networks were generated via a cosine correlation coefficient, and then the networks were analyzed and visualized using Pajek. RESULTS: With the hub and authority measures, the most important research topics in Korean medical informatics were identified. Newly emerging topics by three-year period units were observed as research trends. CONCLUSIONS: This study provides a systematic overview on the knowledge structure of Korean medical informatics.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Application of Social Network Analysis to Health Care Sectors
Hae Lan Jang, Young Sung Lee, Ji-Young An
Healthc Inform Res. 2012;18(1):44-56. doi: 10.4258/hir.2012.18.1.44.Social Network Analysis of Elders' Health Literacy and their Use of Online Health Information
Haeran Jang, Ji-Young An
Healthc Inform Res. 2014;20(3):216-225. doi: 10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.216.
Reference
-
1. Hasman A, Haux R. Modeling in biomedical informatics: an exploratory analysis part 1. Methods Inf Med. 2006. 45:638–642.
Article2. Hasman A, Haux R. Modeling in biomedical informatics: an exploratory analysis part 2. Int J Med Inform. 2007. 76:96–102.3. Maojo V, Kulikowski CA. Bioinformatics and medical informatics: collaboration on the road to genomic medicine? J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2003. 10:515–522.
Article4. He Q. Knowledge discovery through co-word analysis. Lib Trends. 1999. 48:133–159.5. Callon M, Courtial JP, Turner WA, Bauin S. From translations to problematic networks: an introduction to coword analysis. Soc Sci Inform. 1983. 22:191–235.
Article6. Morris TA. Structural relationships within medical informatics. Proc AMIA Symp. 2000. 590–594.7. Bansard JY, Rebholz-Schuhmann D, Cameron G, Clark D, van Mulligen E, Beltrame E, Barbolla E, Martin-Sanchez Fdel H, Milanesi L, Tollis I, van der Lei J, Coatrieux JL. Medical informatics and bioinformatics: a bibliometric study. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2007. 11:237–243.
Article8. Mane KK, Börner K. Mapping topics and topic bursts in PNAS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. 101:Suppl 1. 5287–5290.
Article9. Garfield E. Mapping the world of biomedical engineering: Alza lecture (1985). Ann Biomed Eng. 1986. 14:97–108.
Article10. Pickens J, MacFarlane A. Term context models for information retrieval. Proceedings of 15th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. 2006. Nov 5-11; Arlington, VA. 559–560.
Article11. Rebholz-Schuhman D, Cameron G, Clark D, van Mulligen E, Coatrieux JL, Del Hoyo Barbolla E, Martin-Sanchez F, Milanesi L, Porro I, Beltrame F, Tollis I, Van der Lei J. SYMBIOmatics: synergies in medical informatics and bioinformatics - exploring current scientific literature for emerging topics. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. 8:Suppl 1. S18.
Article12. Stegmann J, Grohmann G. Hypothesis generation guided by co-word clustering. Scientometrics. 2003. 56:111–135.13. Swanson DR. Undiscovered public knowledge. Libr Q. 1986. 56:103–118.
Article14. Swanson DR. Fish oil, Raynaud's syndrome, and undiscovered public knowledge. Perspect Biol Med. 1986. 30:7–18.
Article15. Stegmann J, Grohmann G. Transitive text mining for information extraction and hypothesis generation [Internet]. 2005. cited 2008 Jul 10. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/cs/0509020.16. Swanson DR. Migraine and magnesium: eleven neglected connections. Perspect Biol Med. 1988. 31:526–557.
Article17. Mann GS, Mimno D, McCallum A. Bibliometric impact measures leveraging topic analysis. Proceedings of the 6th ACM/IEEE-CS Joint Conference on Digital Libraries. 2006. June 11-15; Chapel Hill, NC. 65–74.
Article18. Noyons E. Bibliometric mapping of science in a policy context. Scientometrics. 2001. 50:83–98.19. Kleinberg JM. Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked environment. J ACM. 1999. 46:604–632.
Article20. Jeong S, Kim HG. Intellectual structure of biomedical informatics reflected in scholarly events. Scientometrics. Epub 2010 Feb 11. DOI: 10.1007/s11192-010-0166-z.
Article21. Bekhuis T. Conceptual biology, hypothesis discovery, and text mining: Swanson's legacy. Biomed Digit Libr. 2006. 3:2.
Article22. Jeong S, Lee SK, Kim HG. Knowledge structure of Korean medical informatics. Proceedings of CJKMI Fall Conference. 2009. Oct 30-31; Daejeon, KR. 49–51.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors based on Social Network Analysis
- Knowledge Structure of the Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing through Network Analysis
- Analysis of Scientific Publication Networks among Medical Schools in Korea
- A Social Network Analysis of Research Topics in Korean Nursing Science
- An Identification of the Knowledge Structure on the Resilience of Caregivers of People with Dementia using a Text Network Analysis