Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Aug;38(4):581-584. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.4.581.
Balloon Dilatation for an Esophageal Stricture by Long-Term Use of a Nasogastric Tube: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Presbyterian Medical Center, Jeonju, Korea. kijoyu@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Radiology, Presbyterian Medical Center, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2165744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.4.581
Abstract
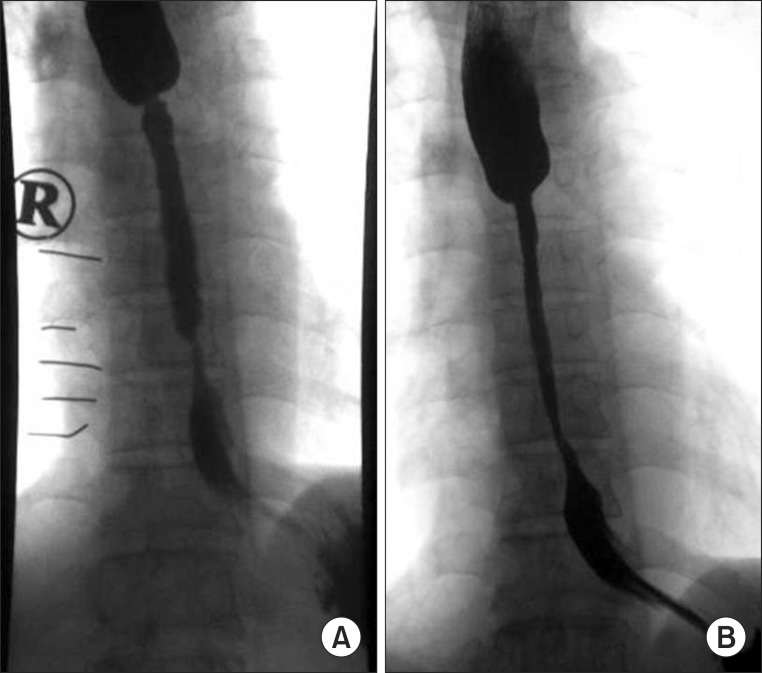
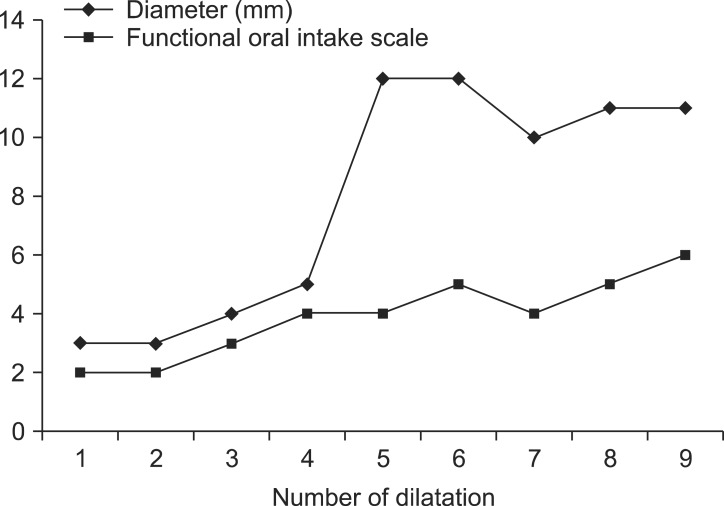
- In the present report, we describe a case of long-term follow-up esophageal stricture occurring in a patient with nasogastric tube use. A 63-year-old man who had experienced dislocation of the 6th and 7th cervical vertebrae as the result of an external injury received treatment at another hospital and was admitted to the rehabilitation department of our hospital. After he exhibited normal swallowing in a videofluoroscopic swallowing test, the nasogastric tube was removed and oral feeding with a dysphagia diet was initiated. However, during oral feeding, the patient complained of swallowing difficulties in his lower throat. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy was performed to examine the lesions below the pharynx and a 2-mm stricture was observed. A balloon dilatation was performed for a total of 9 times to extend the stricture. After the procedure, the patient was able to easily swallow a normal diet through the esophagus and the vomiting symptoms disappeared. An esophagography showed that the diameter of the esophageal stricture was 11 mm.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kirby DF, Delegge MH, Fleming CR. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on tube feeding for enteral nutrition. Gastroenterology. 1995; 108:1282–1301. PMID: 7698596.
Article2. Pancorbo-Hidalgo PL, Garcia-Fernandez FP, Ramirez-Perez C. Complications associated with enteral nutrition by nasogastric tube in an internal medicine unit. J Clin Nurs. 2001; 10:482–490. PMID: 11822496.
Article3. Groher ME, Crary MA. Dysphagia: clinical management in adults and children. 1st ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;2010. p. 308–322.4. Banfield WJ, Hurwitz AL. Esophageal stricture associated with nasogastric intubation. Arch Intern Med. 1974; 134:1083–1086. PMID: 4433188.
Article5. Zaninotto G, Bonavina L, Pianalto S, Fassina A, Ancona E. Esophageal strictures following nasogastric intubation. Int Surg. 1986; 71:100–103. PMID: 3733352.6. Nam BH, Kang YW. Endoscopic balloon dilatation for benign and malignant esophageal strictures. Korean J Med. 1995; 48:200–206.7. Yang US, Park SK, Kang DH, Song CS, Cho M, Song GA. The effect of bougie and balloon dilatation on benign esophageal stricture. Korean J Med. 1998; 54:660–665.8. Crary MA, Mann GD, Groher ME. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:1516–1520. PMID: 16084801.
Article9. Nagler R, Wolfsohn AW, Lowman RM, Spiro HM. Effects of gastric intubation on normal mechanisms preventing gastroesophageal reflux. N Engl J Med. 1960; 262:1325–1328. PMID: 14425796.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Endoscopic Balloon Dilation in the Treatment of Esophageal Strictures
- A Comparison Between Savary - Gilliard and Balloon Dilatation in Benign Esophageal Stricture
- Balloon catheter dilatation of esophageal strictures
- The Effect of Bougie and Balloon Dilatation on Benign Esophageal Stricture
- Balloon Dilatation and Bougienage of Post-operative Anastomotic Site Stricture of Upper G-I Tract