Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Dec;39(6):1028-1032. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.1028.
High Resolution Manometry Analysis of a Patient With Dysphagia After Occiput-C3/4 Posterior Fusion Operation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. jseok337@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2165631
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.1028
Abstract
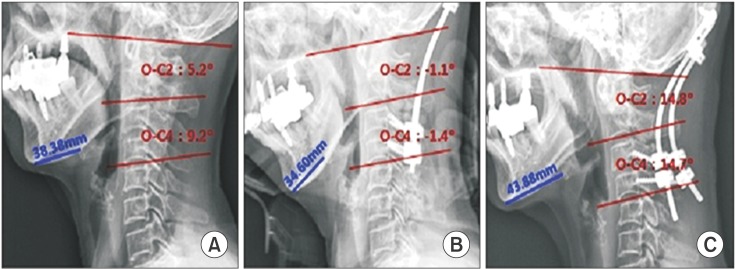
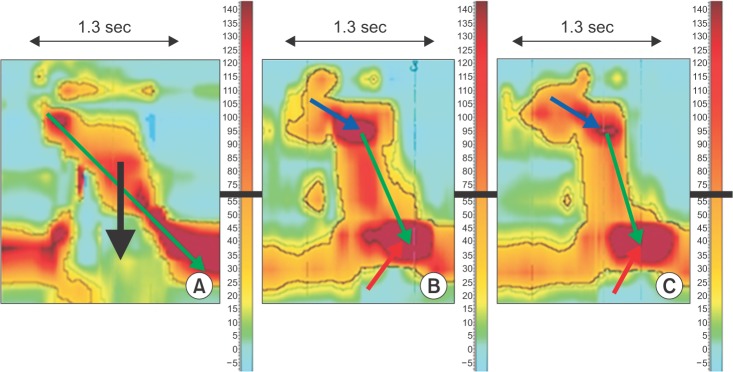
- Many reports of changes in cervical alignment after posterior occipitocervical (O-C) fusion causing dysphagia are available. The clinical course can range from mild discomfort to severe aspiration. However, the underlying pathogenesis is not well known. We report an 80-year-old female with videofluoroscopic swallowing study evidence of aspiration that developed after occiput-C3/4 posterior fusion. Pharyngeal pressure was analyzed using high resolution manometry (HRM). Impaired upper esophageal sphincter opening along with diminished peristalsis and pharyngeal pressure gradient were revealed by HRM to be the main characteristics in such patients. The patient fully recovered after a revision operation for cervical angle correction. Distinct pressure patterns behind reversible dysphagia caused by a change in cervical alignment were confirmed using HRM analysis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of Chin-Down Maneuver on Pharyngeal Pressure Generation According to Dysphagia and Viscosity
Sun Myoung Lee, Ban Hyung Lee, Jung Woo Kim, Joon Young Jang, Eun Gyeong Jang, Ju Seok Ryu
Ann Rehabil Med. 2020;44(6):493-501. doi: 10.5535/arm.20016.
Reference
-
1. Izeki M, Neo M, Takemoto M, Fujibayashi S, Ito H, Nagai K, et al. The O-C2 angle established at occipito-cervical fusion dictates the patient's destiny in terms of postoperative dyspnea and/or dysphagia. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23:328–336. PMID: 23982903.
Article2. Tian W, Yu J. The role of C2-C7 and O-C2 angle in the development of dysphagia after cervical spine surgery. Dysphagia. 2013; 28:131–138. PMID: 22918711.
Article3. Ota M, Neo M, Aoyama T, Ishizaki T, Fujibayashi S, Takemoto M, et al. Impact of the O-C2 angle on the oropharyngeal space in normal patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:E720–E726. PMID: 21270693.
Article4. Miyata M, Neo M, Fujibayashi S, Ito H, Takemoto M, Nakamura T. O-C2 angle as a predictor of dyspnea and/or dysphagia after occipitocervical fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:184–188. PMID: 19139669.
Article5. Fox MR, Bredenoord AJ. Oesophageal high-resolution manometry: moving from research into clinical practice. Gut. 2008; 57:405–423. PMID: 17895358.
Article6. Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Dantas RO, Massey B, Kern MK, Lang IM, et al. Opening mechanisms of the human upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol. 1989; 257(5 Pt 1):G748–G759. PMID: 2596608.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High-resolution esophageal manometry in children
- Emerging Issues in Dysphagia
- Dyspnea and Dysphagia after Posterior Atlantoaxial Instrumented Fusion
- Dysphagia after Occipitocervical Posterior Fusion and Significance of Occipitoaxial Angle: case report
- How to Perform and Interpret Upper Esophageal Sphincter Manometry