J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs.
2015 Dec;24(4):330-341. 10.12934/jkpmhn.2015.24.4.330.
The Effects of a Parental Education Program based on Satir Transformational Systemic Therapy Model for Preschoolers' Mothers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Kwangju Women's University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea. pinehillkim@naver.com
- 3Chonnam Research Institute of Nursing Science, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2151877
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12934/jkpmhn.2015.24.4.330
Abstract
- PURPOSE
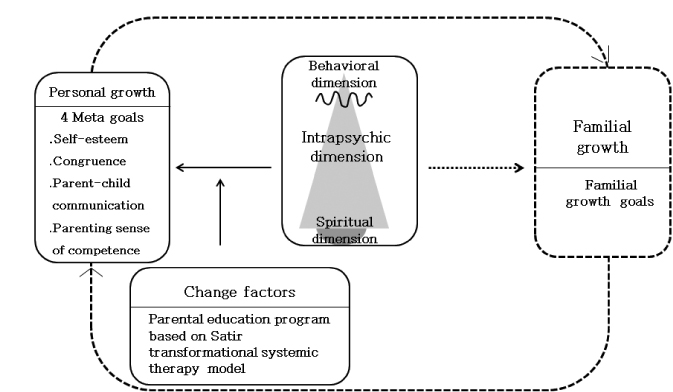
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a parental education program based on the Satir transformational systemic therapy model on self-esteem, congruence, parent-child communication, and parenting sense of competence of the preschoolers' mothers.
METHODS
Non-equivalent control group pretest and posttest design was used. The participants were 36 (experimental group 18, control group 18) preschoolers' mothers who volunteered from kindergartens and children's homes. The treatment for this study was based on Satir's systemic training program for parenting skills. Data were analyzed using percentage, chi2-test, t-test and t-test with SPSS 21.0 Version.
RESULTS
Statistically, there were significant increase in self-esteem, congruence, parent-child communication, and parenting sense of competence in the experimental group compared to the control group.
CONCLUSION
Findings suggested that parental education program based on the Satir transformational systemic therapy model can be used by preschoolers' mothers for effective psychiatric nursing interventions in parenting and preschoolers' mental health promotion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee SH, Min HY, Kwon HJ, Jung YJ, Han YJ, Choi YK, et al. Parent education. Seoul: Hakjisa;2012. p. 75.2. Kim JH, Jung JN, Jo YJ, Han JA. Parent education. Paju: Yangseowon;2013. p. 412.3. Lee JS, Kang MO, Ko KH, Ko MJ, Kong SJ, Kim SJ, et al. Psychiatric mental health nursing. Seoul: Hyunmoonsa;2008. p. 748.4. Kim YA. An integrative Satir transformational systemic therapy: theory and practice. Seoul: Institute of Kimyoungae Family Therapy;2011. p. 342.5. Yoo IY, Yoo HJ. Factors Associated with the Problem Behaviors Perceived by Mothers of Pre-school Age Children. Child Health Nurs Res. 2010; 16(2):112–119. DOI: 10.4094/jkachn.2010.16.2.112.
Article6. Cho ES, Seo JM. Factors influencing children's mental health state. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2010; 19(1):57–66. DOI: 10.12934/jkpmhn.2010.19.1.57.
Article7. Kim JI, Chung MJ. The effectiveness of the counseling-utilized parent education for mothers. J Korean Home Econ Assoc. 2006; 44(7):53–62.8. Huh BY, Han KJ. Father involvement in child-rearing and maternal depression during early childhood. Korean Parent Child Health J. 2009; 12(2):131–146.9. Ministry of Health & Welfare. The survey on status of child abuse. 2011. Available from: http://www.mohw.go.kr/front_new/jb/sjb030301vw.jsp.10. Kang EJ. Korea Children's mental health status and policy implications. Health-Welfare Policy Forum;2007. p. 61–72.11. Jo KR, Ham KA, Cheon SM. A meta-analysis on the effects of parent education programs. J Rehabil Psychol. 2013; 20(2):371–376.12. Kim YA. Making a beautiful people; satir's systemic training program for parenting skills. Seoul: Institute of Kimyoungae Family Therapy;2005. p. 206.13. Banmen J. The Satir model: yesterday and today. Contemp Fam Ther. 2002; 24(1):7–22.14. Kim MK. The effect of Satir model based growth and parent education program on the self-esteem and congruency of parents and adolescent children's self-esteem. J Creative Personal MeFOT. 2014; 3(1):161–183.15. Lee KM, Lee IS. Anger management group therapy for parents: a Satir-based approach. Korean J Fam Ther. 2013; 21(2):231–255.
Article16. Lee DS. Effects of a Marital Growth Program on Middle-aged Couples. Korean J Fam Ther. 2008; 16(1):81–111.
Article17. Kang YJ, Ku JG. The effectiveness of the bibliotherapy program for children's mothers influences on communication with their children and congruence. J Bibliother. 2011; 4(1):25–44.18. Lee DJ, Cho GP. The effect of group art therapy using Satir model on mother's communication, emotional expressiveness and self-efficacy. Korean J Art Ther. 2013; 20(2):379–407.19. Rosenberg M. Society and adolescent self-image. Soci For. 1965; 44(2):255. DOI: 10.2307/2575639.20. Jon BJ. Self-esteem: A test of its measurability. Yonsei Nonchong. 1974; 11:107–130.21. Ko MJ, Kim BH. Development and validity of the congruence scale based on Satir's growth model. J Korean Assoc Psychother. 2009; 21(3):643–660.22. Lee JS. A study the relationship of the family system and mother-child communications and the child's depression [master's thesis]. Iksan: Wonkwang University;1993. 19–20.23. Sim SK. Relationship between mother-child communication and the self-concept of young children. Korean J Child Stud. 1996; 17(2):47–59.24. Park JE. Effects of parent education using emotion coaching on the self-efficacy of raising children and communication between parents-children [master's thesis]. Suwon: Gyonggi University;2012. 39.25. Gibaud-Wallston J, Wandersman LP. Development and utility of the parenting sense of competence scale. Toronro, Canada: Paper presemed at the meeting of the American Psychological Association;1978.26. Johnston C, Mash EJ. A measure of parenting satisfaction and efficacy. J Clin Child Psychol. 1989; 18:167–175.
Article27. Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 2nd ed. HS Lee SJ Kim SH Jon . Seoul: Hakjisa;2010. p. 81.28. Song HS. An analysis on the process and effects of the Satir's family group counseling of high school girls. [dissertation]. Iksan: Wonkwang University;2008. 93.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and Application of Dietary Education to Improve the Vegetable Intake of Preschoolers
- Effects of a Maternal Sexuality Education Program for Mothers of Preschoolers
- Study on the Correlation Between the Dietary Habits of Mothers and Their Preschoolers and the Mother's Need for Nutritional Education for Preschoolers
- Parental Role Stress and Perception of the Newborn in Mothers of Preterm Babies
- Parenting Stress, Parental Behaviors and Need for Parental Education Relative to Children Characteristics of Young Women with Breast Cancer