Hip Pelvis.
2015 Dec;27(4):250-257. 10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.250.
Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head Treated with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy: Analysis of Short-term Clinical Outcomes of Treatment with Radiologic Staging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. oselite@naver.com
- KMID: 2150513
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.250
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate clinical results of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) with radiographic staging on patients with avascular necrosis of femoral head (AVNFH).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We evaluated 24 patients diagnosed with AVNFH (32 hip joints) who were treated with ESWT from 1993 to 2012. Average follow-up period was 27 months, and the average age of patients was 47.8 years. The Association Research Circulation Osseous (ARCO) system was used to grade radiographic stage prior to treatment. For this study patients were divided into two groups based on their ARCO stage, group 1 (ARCO stages I and II) and group 2 (ARCO stage III). Comparative analyses were done between the two groups using the visual analogue scale (VAS) score and the Harris hip score (HHS) at pre-treatment and 3, 6, 12, and 24 months after treatment. Failure was defined when radiographic stage progressed or arthroplasty surgery was needed due to clinical exacerbation.
RESULTS
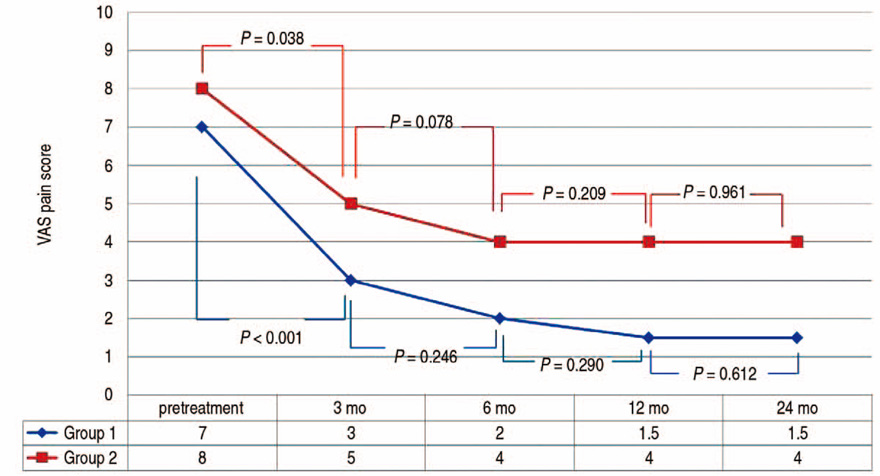
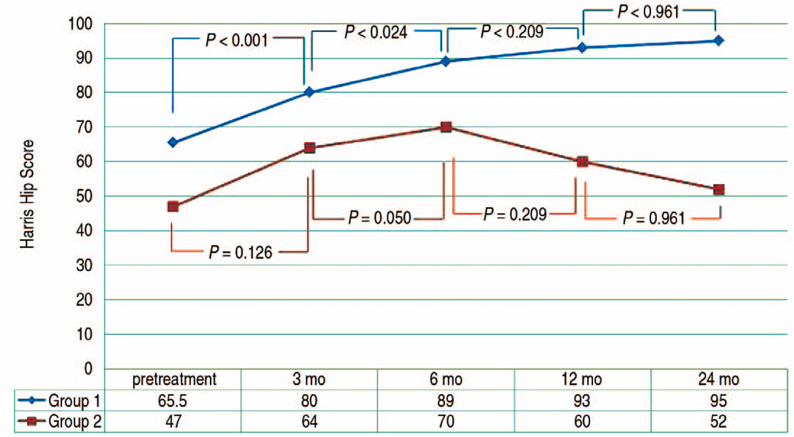
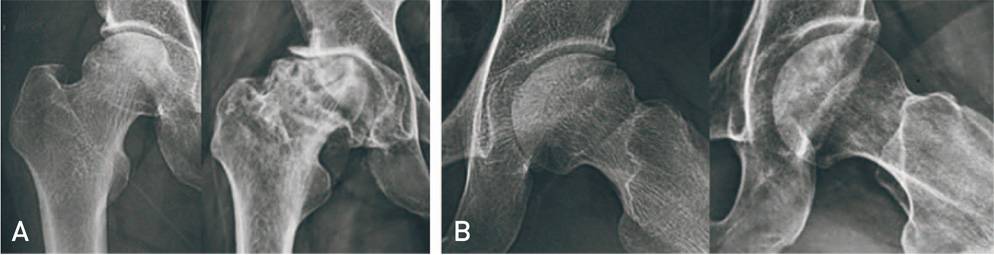
Both groups showed clinical improvements with VAS scoring at final follow-up (group 1: median 7 to 1.5, P<0.001; group 2: mean 7 to 4, P=0.056). Using HHS, group 1 showed a significant improvement (from 65.5 to 95 [P<0.001]), while no significance was observed for group 2 (P=0.280). At final follow-up, 3 hips from group 1 and one hip from group 2 showed radiographic improvement; however, two patients underwent total hip arthroplasty due to persistent pain and dysfunction.
CONCLUSION
ESWT can be considered as an interventional option before surgical treatment in patients with not only early stage AVNFH but also with mid stage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aldridge JM 3rd, Urbaniak JR. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head: etiology, pathophysiology, classification, and current treatment guidelines. Am J Orthop (BelleMead NJ). 2004; 33:327–332.2. Koo KH, Kim R, Kim YS, et al. Risk period for developing osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients on steroid treatment. Clin Rheumatol. 2002; 21:299–303.
Article3. Wang GJ, Cui Q, Balian G. The Nicolas Andry award. The pathogenesis and prevention of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Clin OrthopRelat Res. 2000; (370):295–310.4. Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, et al. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the hip: comparison of extracorporeal shockwave with shockwave and alendronate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008; 128:901–908.
Article5. Wang CJ, Wang FS, Huang CC, Yang KD, Weng LH, Huang HY. Treatment for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: comparison of extracorporeal shock waves with core decompression and bone-grafting. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:2380–2387.
Article6. Wang CJ, Wang FS, Ko JY, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows regeneration in hip necrosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47:542–546.
Article7. Steinberg ME, Hayken GD, Steinberg DR. A quantitative system for staging avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77:34–41.
Article8. Hungerford DS. [Role of core decompression as treatment method for ischemic femur head necrosis]. Orthopade. 1990; 19:219–223. In German.9. Mont MA, Jones LC, Hungerford DS. Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: ten years later. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:1117–1132.10. Iorio R, Healy WL, Abramowitz AJ, Pfeifer BA. Clinical outcome and survivorship analysis of core decompression for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13:34–41.
Article11. Kim SY, Kim YG, Kim PT, Ihn JC, Cho BC, Koo KH. Vascularized compared with nonvascularized fibular grafts for large osteonecrotic lesions of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:2012–2018.
Article12. Scully SP, Aaron RK, Urbaniak JR. Survival analysis of hips treated with core decompression or vascularized fibular grafting because of avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80:1270–1275.
Article13. Ludwig J, Lauber S, Lauber HJ, Dreisilker U, Raedel R, Hotzinger H. High-energy shock wave treatment of femoral head necrosis in adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (387):119–126.
Article14. Chen JM, Hsu SL, Wong T, Chou WY, Wang CJ, Wang FS. Functional outcomes of bilateral hip necrosis: total hip arthroplasty versus extracorporeal shockwave. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129:837–841.
Article15. Buchbinder R, Green SE, Youd JM, Assendelft WJ, Barnsley L, Smidt N. Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of shock wave therapy for lateral elbow pain. J Rheumatol. 2006; 33:1351–1363.16. Disch AC, Matziolis G, Perka C. The management of necrosis-associated and idiopathic bone-marrow oedema of the proximal femur by intravenous iloprost. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:560–564.
Article17. Lai KA, Shen WJ, Yang CY, Shao CJ, Hsu JT, Lin RM. The use of alendronate to prevent early collapse of the femoral head in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis. A randomized clinical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:2155–2159.
Article18. Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969; 51:737–755.
Article19. Ficat RP. Idiopathic bone necrosis of the femoral head. Early diagnosis and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985; 67:3–9.
Article20. Ohzono K, Takaoka K, Saito S, Saito M, Matsui M, Ono K. Intraosseous arterial architecture in nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Microangiographic and histologic study. Clin Orthop Relat Resx. 1992; (277):79–88.21. Zhou Q, Li Q, Yang L, Liu F. [Changes of blood vessels in glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head in rabbits]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2000; 38:212–215,13. In Chinese.22. Desai MM, Sonone S, Bhasme V. Efficacy of alendronate in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the hip. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:1331–1332. author reply 1332
Article23. Ma HZ, Zeng BF, Li XL, Chai YM. Temporal and spatial expression of BMP-2 in sub-chondral bone of necrotic femoral heads in rabbits by use of extracorporeal shock waves. Acta Orthop. 2008; 79:98–105.
Article24. McCormack D, Lane H, McElwain J. The osteogenic potential of extracorporeal shock wave therapy. an in-vivo study. Ir J Med Sci. 1996; 165:20–22.
Article25. Wang FS, Wang CJ, Sheen-Chen SM, Kuo YR, Chen RF, Yang KD. Superoxide mediates shock wave induction of ERK-dependent osteogenic transcription factor (CBFA1) and mesenchymal cell differentiation toward osteoprogenitors. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:10931–10937.
Article26. Wang FS, Wang CJ, Huang HJ, Chung H, Chen RF, Yang KD. Physical shock wave mediates membrane hyperpolarization and Ras activation for osteogenesis in human bone marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001; 287:648–655.
Article27. Levin D, Norman D, Zinman C, et al. Treatment of experimental avascular necrosis of the femoral head with hyperbaric oxygen in rats: histological evaluation of the femoral heads during the early phase of the reparative process. Exp Mol Pathol. 1999; 67:99–108.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Concepts in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
- Treatment of Nonunion of Tibia with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy: A Case Report
- The Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Refractory Plantar Fasciitis
- Effect of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Patients With Fabella Syndrome