J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2013 Dec;17(4):326-333. 10.13104/jksmrm.2013.17.4.326.
H1 Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Cystic Ovarian Lesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inha University School of Medicine, Korea. mykim@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Inha University School of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Department of Gynecology, Inha University School of Medicine, Korea.
- 4College of pharmacology, Seoul National University, Korea.
- 5Biology, New York University, USA.
- KMID: 2144336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2013.17.4.326
Abstract
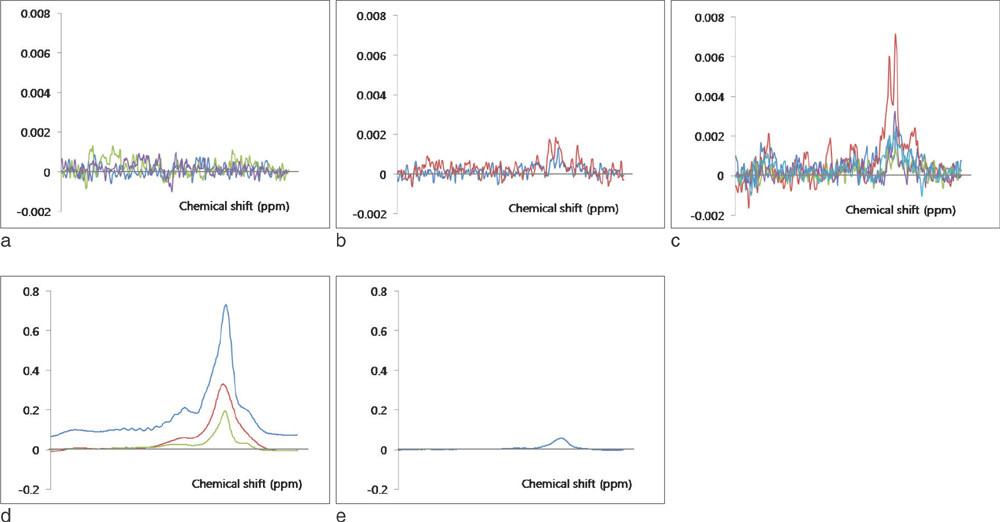
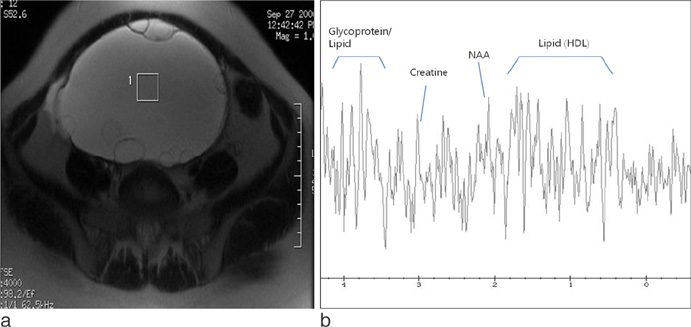
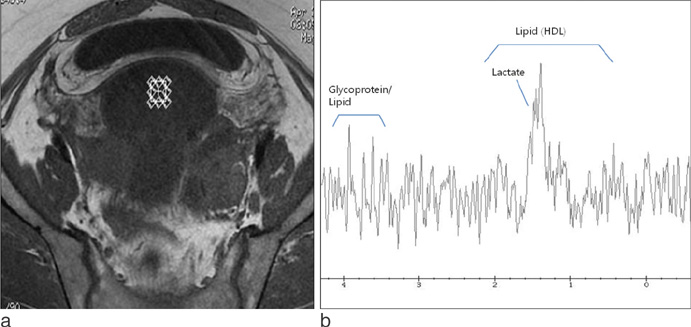
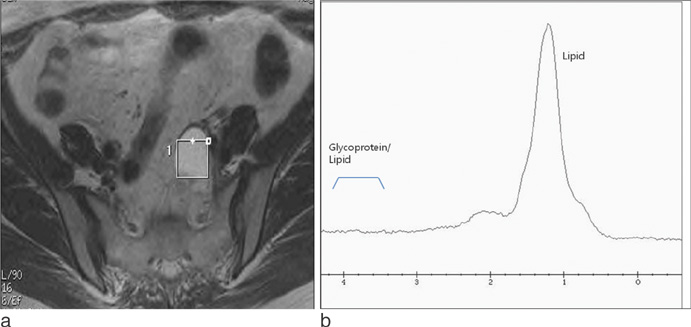
- On H1 MRS (magnetic resonance spectroscopy), malignant tumors show higher concentration of metabolite than benign lesions. Lactate double peak was detected in malignant tumor and endometriosis, and more prominent high concentration was demonstrated in endometriosis. Tuboovarian abscesses and salpingitis do not show prominent peak. Dermoid cysts show high levels of lipid peak. Paratubal cyst and follicular cyst can be showed the lipid peak, however, the concentration of lipid is lower than that of dermoid cyst. H1 MRS of ovarian cystic lesions can give valuable information about the presence of metabolites of ovarian cystic lesions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Imaoka I, Wada A, Kaji Y, et al. Developing an MR imaging strategy for diagnosis of ovarian masses. Radiographics. 2006; 26:1431–1448.2. Jung SE, Lee JM, Rha SE, et al. CT and MR imaging of ovarian tumors with emphasis on differential diagnosis. Radiographics. 2002; 22:1305–1325.3. Kawamoto S, Urban BA, Fishman EK. CT of epithelial ovarian tumors. Radiographics. 1999; 19 Spec No:S85–S102. quiz S263-264.4. Sutton CL, McKinney CD, Jones JE, Gay SB. Ovarian masses revisited: radiologic and pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1992; 12:853–877.5. Kolwijck E, Engelke UF, van der Graaf M, et al. N-acetyl resonances in in vivo and in vitro NMR spectroscopy of cystic ovarian tumors. NMR Biomed. 2009; 22:1093–1099.6. Mahon MM, Williams AD, Soutter WP, et al. 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy of invasive cervical cancer: an in vivo study with ex vivo corroboration. NMR Biomed. 2004; 17:1–9.7. Burtscher IM, Holtås S. Proton MR spectroscopy in clinical routine. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001; 13:560–567.8. Ross B, Michaelis T. Clinical applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Q. 1994; 10:191–247.9. Yoon SH, Park CM, Lee CH, Song IC, Lee HJ, Goo JM. Feasibility of in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy for lung cancer. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2012; 16:40–46.10. Okada T, Harada M, Matsuzaki K, Nishitani H, Aono T. Evaluation of female intrapelvic tumors by clinical proton MR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001; 13:912–917.11. Massuger LF, van Vierzen PB, Engelke U, Heerschap A, Wevers R. 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a new technique to discriminate benign from malignant ovarian tumors. Cancer. 1998; 82:1726–1730.12. Park SH, Kim MY, Suh CH, Lee KY, Choi SJ, Cho JY. MR Images and 1H MR spectroscopy of enteric duplication cyst of the pancreas in an adult. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2010; 14:139–144.13. Kim SH, Chang KH, Song IC, et al. Brain abscess and brain tumor: discrimination with in vivo H-1 MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1997; 204:239–245.14. Mun CW, Cho JY, Shin WJ, et al. Ex vivo proton MR spectroscopy (1H-MRS) for evaluation of human gastric carcinoma. Magn Reson Imaging. 2004; 22:861–870.15. Hagberg H, Siegbahn A. Prognostic value of serum lactic dehydrogenase in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Scand J Haematol. 1983; 31:49–56.16. Boss EA, Moolenaar SH, Massuger LF, et al. High-resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of ovarian cyst fluid. NMR Biomed. 2000; 13:297–305.17. Comerci JT Jr, Licciardi F, Bergh PA, Gregori C, Breen JL. Mature cystic teratoma: a clinicopathologic evaluation of 517 cases and review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol. 1994; 84:22–28.18. Outwater EK, Siegelman ES, Hunt JL. Ovarian teratomas: tumor types and imaging characteristics. Radiographics. 2001; 21:475–490.19. Cho SW, Cho SG, Lee JH, et al. In-vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in adnexal lesions. Korean J Radiol. 2002; 3:105–112.20. Hascalik S, Celik O, Sarac K, et al. Metabolic changes in pelvic lesions: findings at proton MR spectroscopic imaging. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2005; 60:121–127.21. Hascalik S, Celik O, Erdem G. Magnetic resonance spectral analysis of ovarian teratomas. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2005; 90:152–154.22. Woodward PJ, Sohaey R, Mezzetti TP Jr. Endometriosis: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2001; 21:193–216. questionnaire 288-294.23. Bis KG, Vrachliotis TG, Agrawal R, et al. Pelvic endometriosis: MR imaging spectrum with laparoscopic correlation and diagnostic pitfalls. Radiographics. 1997; 17:639–655.24. Ha HK, Lim GY, Cha ES, et al. MR imaging of tubo-ovarian abscess. Acta Radiol. 1995; 36:510–514.25. Gotsis ED, Fountas K, Kapsalaki E, et al. In vivo proton MR spectroscopy: the diagnostic possibilities of lipid resonances in brain tumors. Anticancer Res. 1996; 16:1565–1567.26. Lai PH, Li KT, Hsu SS, et al. Pyogenic brain abscess: findings from in vivo 1.5-T and 11.7-T in vitro proton MR spectroscopy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:279–288.27. Piñero-Sagredo E, Nunes S, de Los Santos MJ, Celda B, Esteve V. NMR metabolic profile of human follicular fluid. NMR Biomed. 2010; 23:485–495.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
- Perirectal Cystic Lesions - Comprehensive CT and MRI Findings
- Comparison of in Vivo, in Vitro 3T MR Spectroscopy and Proton NMR Spectroscopy for the Fluid from Cystic Tumor: Preliminary Study
- Usefulness of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Ovarian Cystic Tumors Using Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Usefulness of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Ovarian Cystic Tumors Using Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging