J Korean Bone Joint Tumor Soc.
2011 Jun;17(1):44-50. 10.5292/jkbjts.2011.17.1.44.
Surgical Treatment for Pathologic Fracture of Skeletal Metastatic Lesion of the Proximal Femur: Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Prosthetic Joint Replacement and Osteosynthetic Fixation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. shinds@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2137043
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5292/jkbjts.2011.17.1.44
Abstract
- PURPOSE
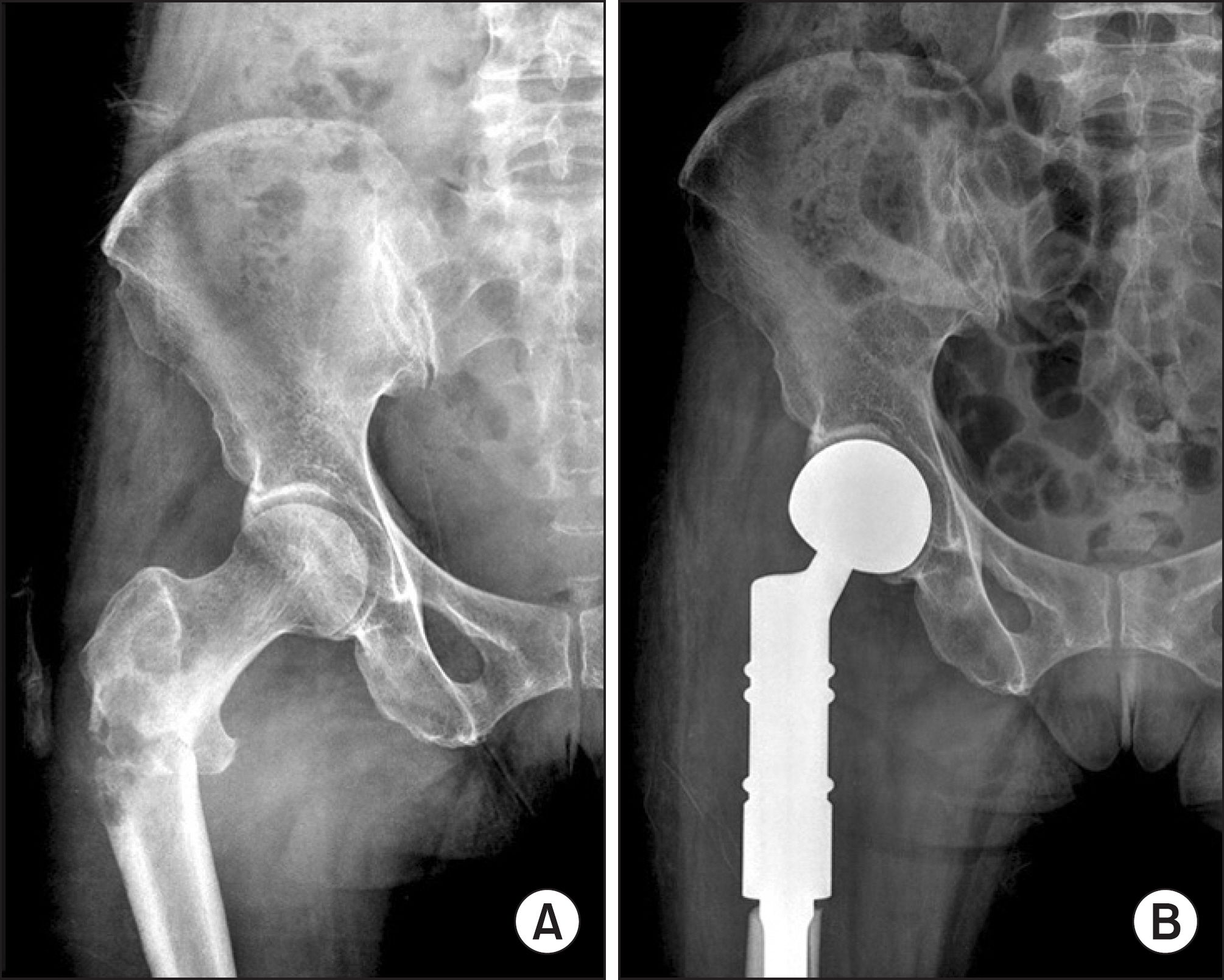
To compare clinical outcomes of the tumor prosthetic replacement and osteosynthetic fixation for pathologic fracture of skeletal metastatic lesion of the proximal femur.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
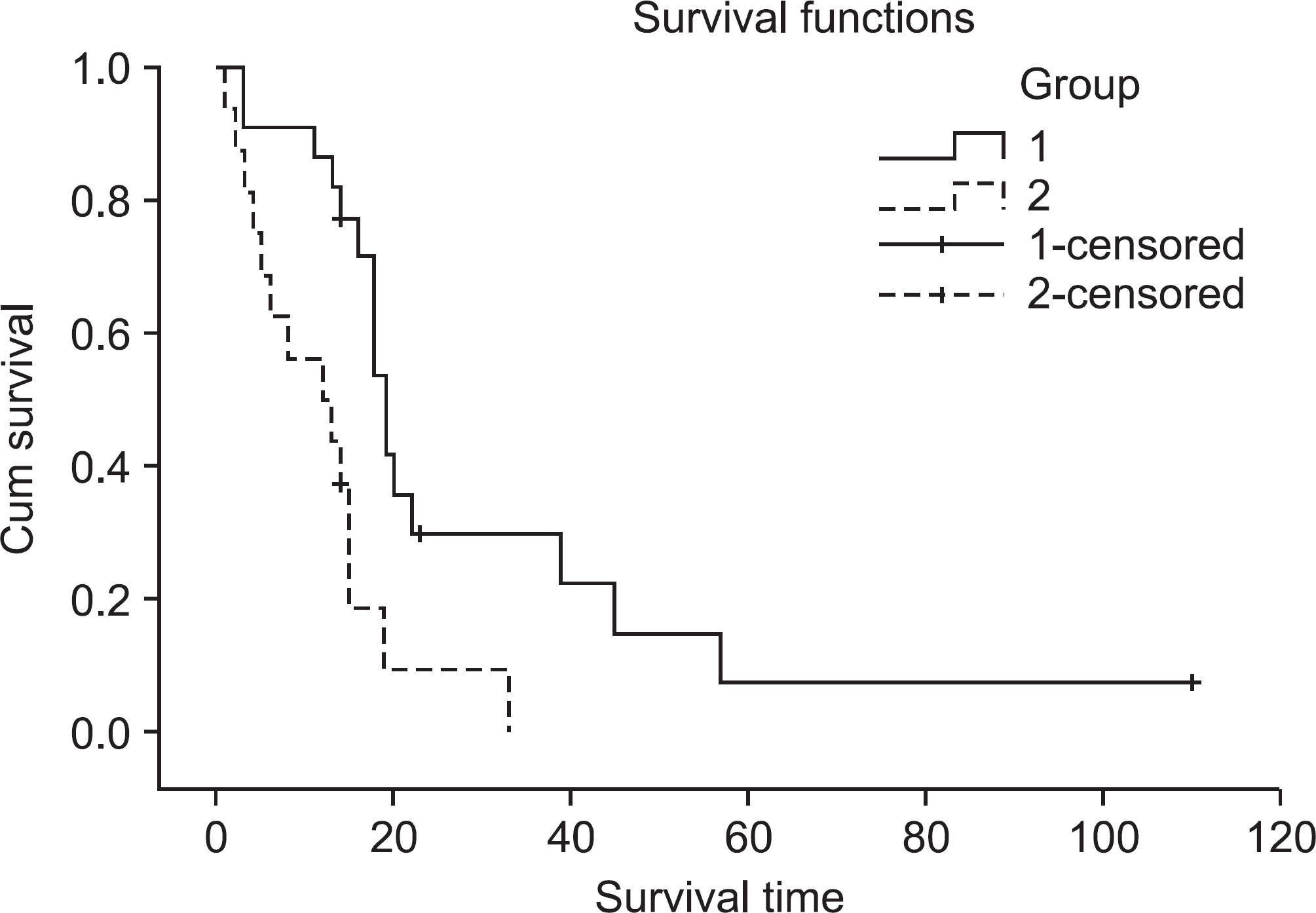
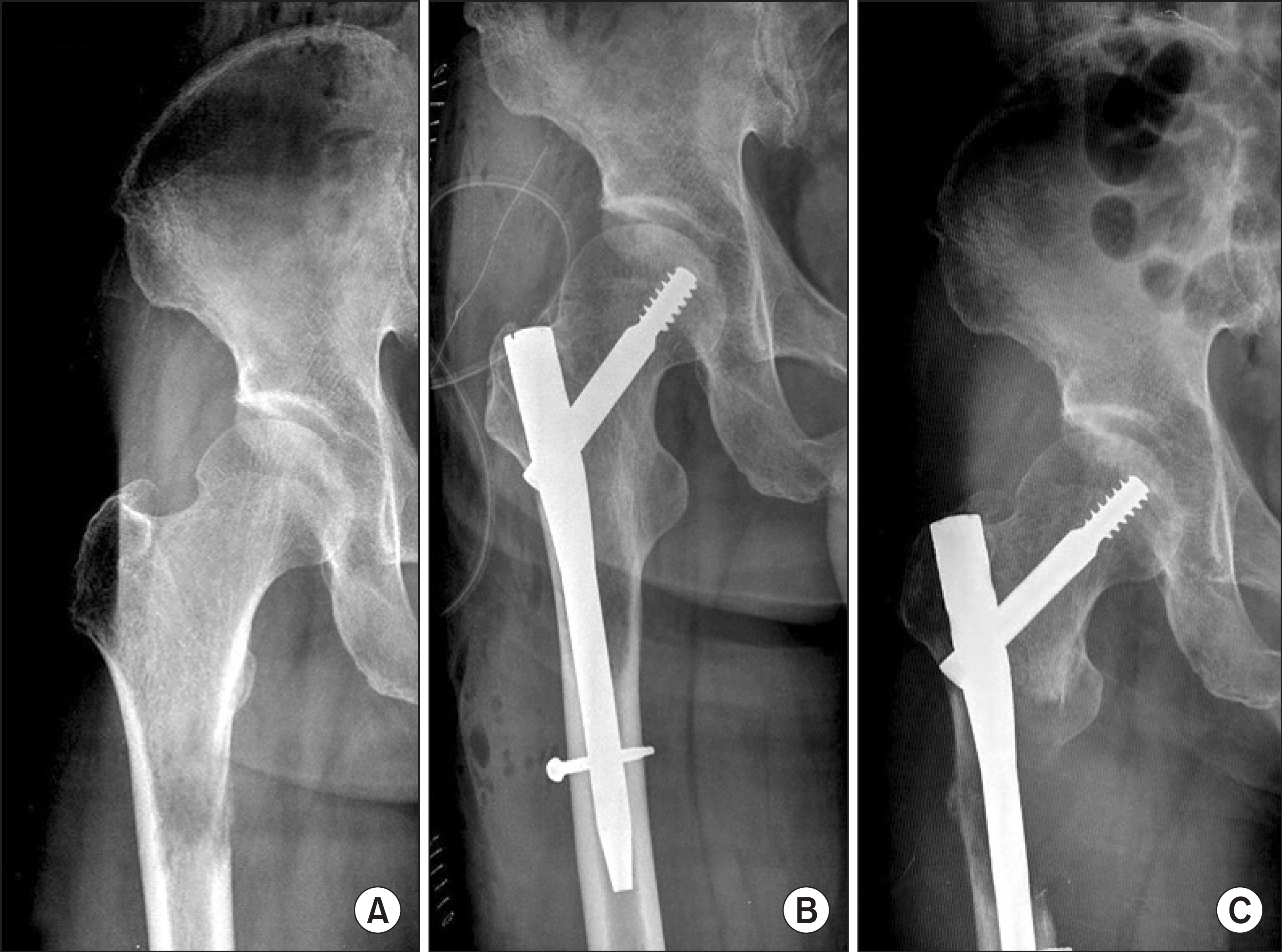
From 1994 May to 2009 May, medical records of 22 patients who underwent tumor prosthetic replacement with tumor resection (group 1) and 15 others (16 hips) who underwent osteosynthetic fixation without tumor resection (group 2) were reviewed. The mean age of overall patients were 59 (group 1) and 60 (group 2). Mean follow up periods were 23 and 11 months. The oncological and functional results were evaluated with Kaplan-Meier methods and Musculoskeletal Tumor Society (MSTS) scoring system, 1993. The statistical evaluation was assessed with Log rank test and t-test.
RESULTS
The mean survival periods were 24 months in group 1 and 11months in group 2. The 1 year survival rates were 86% in group 1 and 50 % in group 2, and 2 year survival rates were 29.7% in group 1 and 9.4% in group 2. The mean MSTS functional score were 26.4 (19-30), 87.9% in group 1 and 15.3 (10-23), 51.0% in group 2.
CONCLUSION
The results of tumor resection and prosthetic replacement in selected cases was better than osteosynthetic fixation without tumor resection for metastatic bone tumors around proximal femur in oncological and functional aspects.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Damron TA, Sim FH. Surgical treatment for metastatic disease of the pelvis and the proximal end of the femur. Instr Course Lect. 2000; 49:461–70.2. Swanson KC, Pritchard DJ, Sim FH. Surgical treatment of metastatic disease of the femur. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000; 8:56–65.
Article3. Lee SH, Kim HS, Kim SR, Park YB, Yoo KH, Lee HK. Functional outcome following surgical treatment of metastatic tumors involving the femur. Orthopedics. 2000; 23:1075–9.
Article4. Capanna R, Campanacci DA. Indications for the surgical treatment of long bone metastases. Jasmin C, Capanna R, Coia L, Coleman R, Saillant G, editors. Textbook of bone metastases. Chantilly: Wiley;2005. p. 135–46.
Article5. Jacofsky DJ, Haidukewych GJ. Management of pathologic fractures of the proximal femur: state of the art. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:459–69.6. Eckardt JJ, Kabo JM, Kelly CM, Ward WG Sr, Cannon CP. Endoprosthetic reconstructions for bone metastases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; 415(Suppl):S254–62.
Article7. Swanson KC, Pritchard DJ, Sim FH. Surgical treatment of metastatic disease of the femur. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000; 8:56–65.
Article8. Enneking WF, Dunham W, Gebhardt MC, Malawar M, Pritchard DJ. A system for the functional evaluation of reconstructive procedures after surgical treatment of tumors of the musculoskeletal system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 286:241–6.
Article9. Talbot M, Turcotte RE, Isler M, Normandin D, Iannuzzi D, Downer P. Function and health status in surgically treated bone metastases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 438:215–20.
Article10. Harrington K. Management of lower extremity metastases. Harrington K, editor. Orthopaedic management of metastatic bone disease. St. louis: CV Mosby;1998. p. 141–214.11. Harrington K. Prophylactic management of impending fractures. Harrington K, editor. Orthopaedic management of metastatic bone disease. St. louis: CV Mosby;1988. p. 283–307.12. Vincent T, Devita Jr. Principles & practice of oncology. 4th ed.Rosenberg: Steven A;1993. 160-1.13. Harrington KD. New trends in the management of lower extremity metastases. Clin Orthop. 1982; 169:53–61.
Article14. Kim JD, Park PJ, Kwon YH, Jang JH, Lee YG. Surgical treatment of metastatic tumor in proximal femur with recycling autograft prosthetic composite after wide excision. J of Korean Bone & Joint Tumor Soc. 2005; 11:71–80.15. Sim FH. Metastatic bone disease of the pelvis and femur. Instr Course Lect. 1992; 41:317–27.16. Harrington KD, Sim FH, Enis JE, et al. Methylmethacrylate as an adjunct in internal fixation of pathologic fractures: experience with 375 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58A:1047–55.17. Karachalios T, Atkins RM, Sarangi PP, Crichlow TP, Solomon L. Reconstruction nailing for pathological subtrochanteric fractures with coexisting femoral shaft metastases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993; 75:119–22.
Article18. Van der Hulst RR, van den Wildenberg FA, Vroemen JP, Greve JW. Intramedullary nailing of (impending) pathologic fractures. J Trauma. 1994; 36:211–5.
Article19. Weikert DR, Schwartz HS. Intramedullary nailing for impending pathological subtrochanteric fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:668–70.
Article20. Algan SM, Horowitz SM. Surgical treatment of pathologic hip lesions in patients with metastatic disease. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1996; 332:223–31.
Article21. Sim FH, Frassica FJ, Chao EY. Orthopaedic management using new devices and prostheses. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; 312:160–72.22. Habermann ET, Sachs R, Stern RE, Hirsh DM, Anderson WJ Jr. The pathology and treatment of metastatic disease of the femur. Clin Orthop. 1982; 169:70–82.
Article23. Keating JF, Burke T, Macauley P. Proximal femoral replacement for pathological fracture. Injury. 1990; 21:231–3.
Article24. Hattori H, J Mibe, Matsuoka H, Nagai S, Yamamoto K. Surgical management of metastatic disease of the proximal femur. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery. 2007; 15:295–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Functional Review of the Hemiarthroplasty Vs, Total Joint Replacement in the Femur Neck Fracture
- Non-neoplastic indications and outcomes of the proximal and distal femur megaprosthesis: a critical review
- A Operative treatment of the three-part, four-part Fracture and Fracture dislocation in proximal humerus
- Total Hip Replacement of Pathologic Fracture in Fibrous Dysplasia involving Proximal Part of the Femur
- Surgical Treatment of Ipsilateral Fracture of the Femur and Tibia("Floating Knee")