Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Sep;5(3):170-172. 10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.170.
Pulsatile Tinnitus as the Sole Manifestation of an Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm Successfully Treated by Coil Embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. snparkmd@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2134601
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.170
Abstract
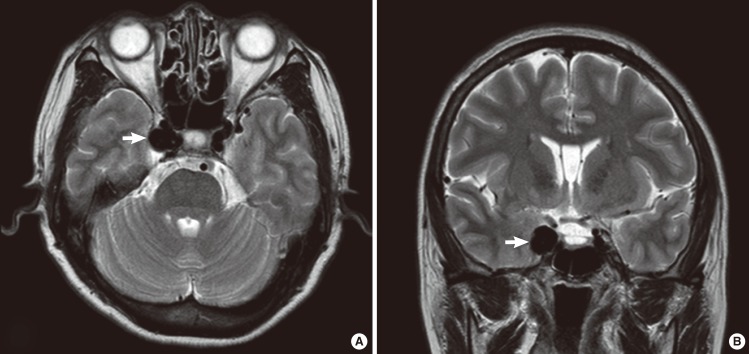
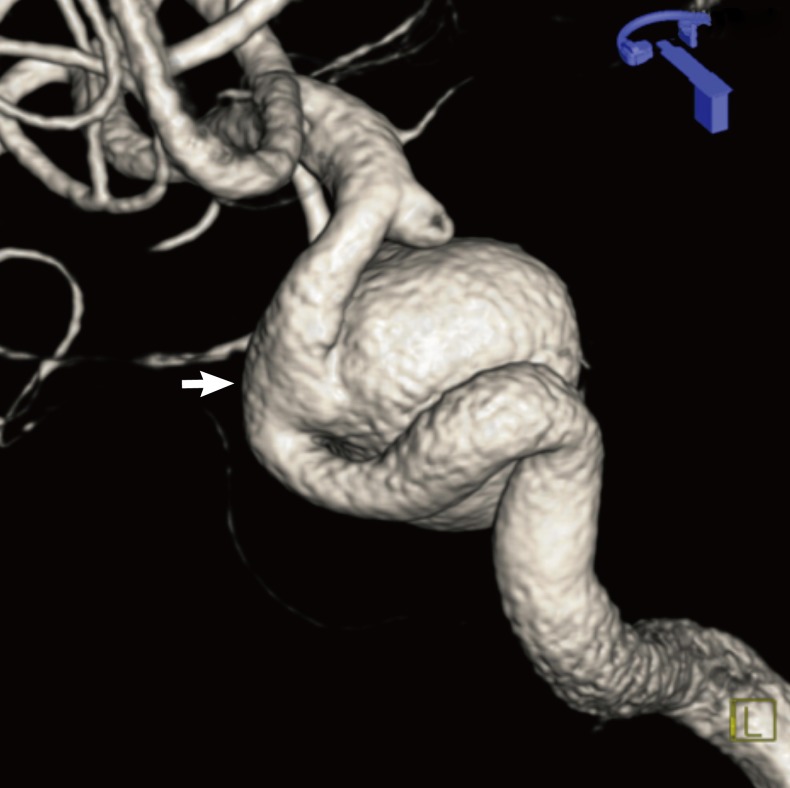
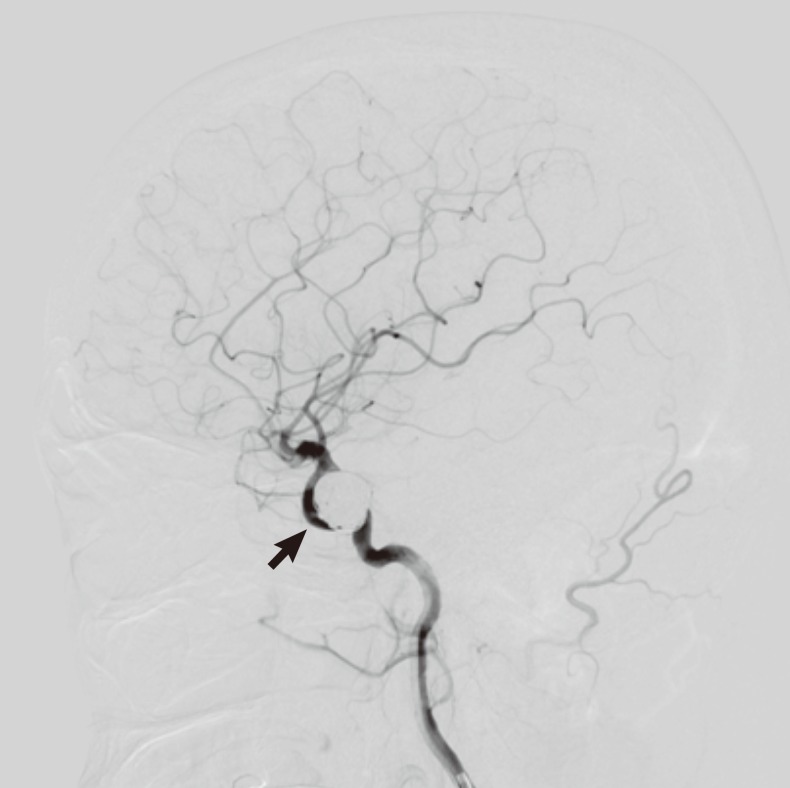
- Pulsatile tinnitus is tinnitus that coincides with the patient's heartbeat. It constitutes a small portion of all tinnitus, but it is often the first or sole manifestation of a serious disease in the nervous system. Aneurysm of the internal carotid artery is known as a rare cause of pulsatile tinnitus and, in the main, aneurysms of the petrous portion have been reported as a cause of pulsatile tinnitus. We present an interesting case of pulsatile tinnitus that was caused by a paraclinoid aneurysm in this report and discuss clinical features and treatment of paraclinoid aneurysm.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Objective Tinnitus
Shi Nae Park
Hanyang Med Rev. 2016;36(2):99-108. doi: 10.7599/hmr.2016.36.2.99.Petrous Carotid Aneurysm Causing Pulsatile Tinnitus: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Seong-Mook Kim, Chang-Hyun Kim, Chang-Young Lee
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2018;20(1):35-39. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2018.20.1.35.Single-Center 10-Year Experience in Treating Patients With Vascular Tinnitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Treatment Outcomes
Seong Cheon Bae, Dong Kee Kim, Sang Won Yeo, So Young Park, Shi Nae Park
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;8(1):7-12. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.1.7.
Reference
-
1. Waldvogel D, Mattle HP, Sturzenegger M, Schroth G. Pulsatile tinnitus: a review of 84 patients. J Neurol. 1998; 3. 245(3):137–142. PMID: 9553842.
Article2. Sonmez G, Basekim CC, Ozturk E, Gungor A, Kizilkaya E. Imaging of pulsatile tinnitus: a review of 74 patients. Clin Imaging. 2007; Mar-Apr. 31(2):102–108. PMID: 17320776.
Article3. Moonis G, Hwang CJ, Ahmed T, Weigele JB, Hurst RW. Otologic manifestations of petrous carotid aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; Jun-Jul. 26(6):1324–1327. PMID: 15956490.4. Liu JK, Gottfried ON, Amini A, Couldwell WT. Aneurysms of the petrous internal carotid artery: anatomy, origins, and treatment. Neurosurg Focus. 2004; 11. 17(5):E13. PMID: 15633978.
Article5. Palacios E, Gomez J, Alvernia JE, Jacob C. Aneurysm of the petrous portion of the internal carotid artery at the foramen lacerum: anatomic, imaging, and otologic findings. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010; 7. 89(7):303–305. PMID: 20628987.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Petrous Carotid Aneurysm Causing Pulsatile Tinnitus: Case Report and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Therapeutic Percutaneous Embolization of Spontaneous Arteriovenous Fistulas with Pulsatile Tinnitus Involving the Branches of the Left External Carotid Artery
- Pulsatile Tinnitus Caused by Arteriovenous Fistula of External Carotid Artery
- Stent-assisted Coil Embolization of Petrous ICA in a Teenager with Neurofibromatosis
- Pulsatile Tinnitus Arising from Aberrant Internal Carotid Artery at Nasopharynx