J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2015 Dec;41(6):352-356. 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.6.352.
Basal cell adenoma in the deep portion of the parotid gland: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Dankook University Dental Hospital, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea. kimchoms@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2133185
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.6.352
Abstract
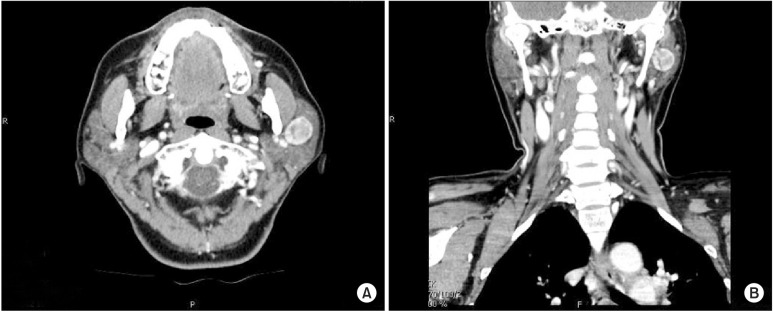
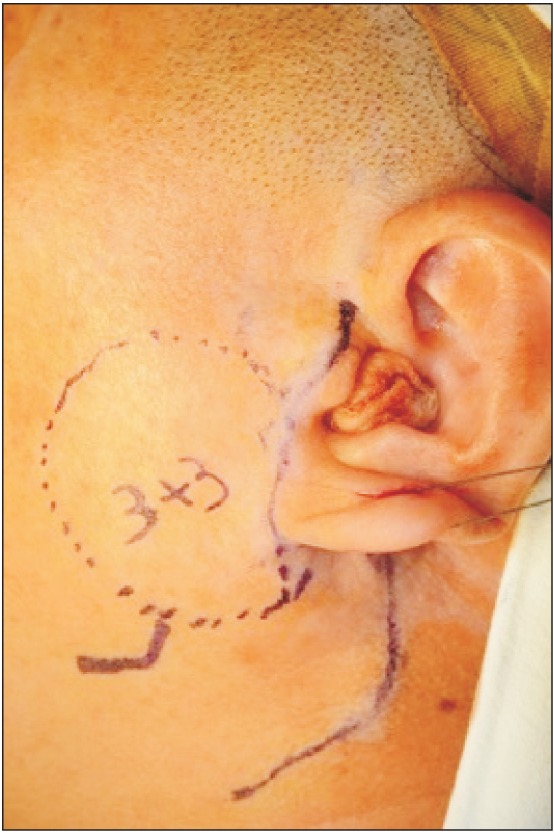
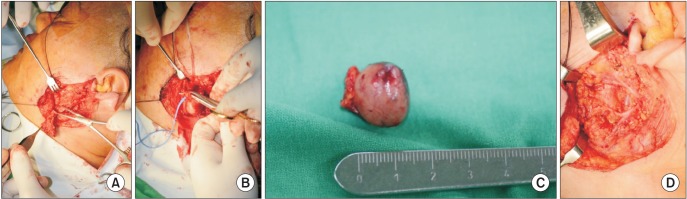
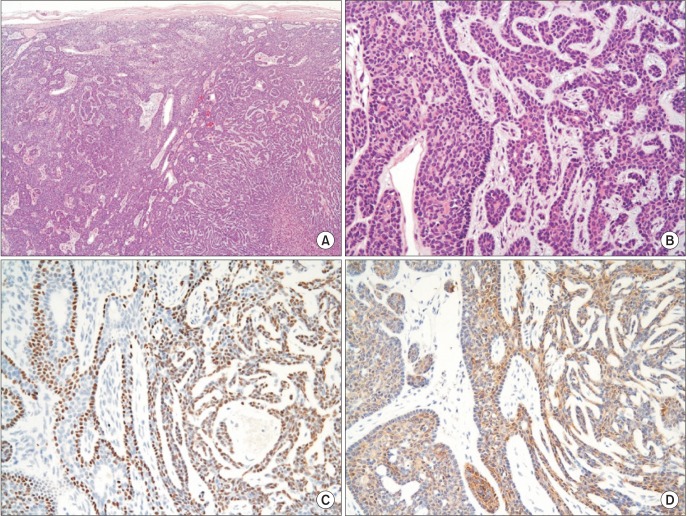
- Basal cell adenoma (BCA) is a rare, benign neoplasm that most frequently arises in the parotid gland. We treated a 54-year-old female patient with BCA that had developed in the deep portion of the left parotid gland. The patient presented with gradual facial swelling with no other symptoms. We performed a total parotidectomy to excise the mass, but we preserved the facial nerve. Histopathology revealed a well-encapsulated mass. The tumor was composed of islands of comparatively uniform, small, dark, basaloid epithelial cells in the stroma. Histologic and immunohistochemical studies concluded that the BCA tumors were mostly trabecular. Postoperatively, there was no facial nerve weakness, and the tumor did not recur during the 24-month follow-up period.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vicandi B, Jiménez-Heffernan JA, López-Ferrer P, González-Peramato P, Patrón M, Viguer JM. Fine needle aspiration cytology of basal cell adenoma of the salivary gland: a cytohistological correlation study of 35 cases. Cytopathology. 2012; 23:315–319. PMID: 21838722.
Article2. Nakabayashi M, Shomori K, Kiya S, Shiomi T, Nosaka K, Ito H. Tubular-trabecular type basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland: a patient report. Yonago Acta Med. 2010; 53:65–69. PMID: 24031120.3. González-García R, Nam-Cha SH, Muñoz-Guerra MF, Gamallo-Amat C. Basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland: case report and review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006; 11:E206–E209. PMID: 16505803.4. Wasson J, Karim H, Yeo J, Panesar J. Cervicomastoidfacial versus modified facelift incision for parotid surgery: a patient feedback comparison. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92:40–43. PMID: 20056059.
Article5. Saha S, Pal S, Sengupta M, Chowdhury K, Saha VP, Mondal L. Identification of facial nerve during parotidectomy: a combined anatomical & surgical study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014; 66:63–68. PMID: 24605304.6. Kudoh M, Harada H, Sato Y, Omura K, Ishii Y. A case of basal cell adenoma of the upper lip. Case Rep Med. 2014; DOI: 10.1155/2014/795356.
Article7. Chaudhry AP, Cutler LS, Satchidanand S, Labay G, SunderRaj M. Ultrastructure of monomorphic adenoma (ductal type) of the minor salivary glands. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983; 109:118–122. PMID: 6849665.
Article8. Fantasia JE, Neville BW. Basal cell adenomas of the minor salivary glands: a clinicopathologic study of seventeen new cases and a review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1980; 50:433–440. PMID: 6935599.9. Kim CW, Kim SG. Basal cell adenoma misdiagnosed as an adenoid cystic carcinoma in the parotid gland. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 38:314–317.
Article10. Nagao K, Matsuzaki O, Saiga H, Sugano I, Shigematsu H, Kaneko T, et al. Histopathologic studies of basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland. Cancer. 1982; 50:736–745. PMID: 6284339.
Article11. Ogawa I, Nikai H, Takata T, Miyauchi M, Ito H, Ijuhin N. The cellular composition of basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland: an immunohistochemical analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1990; 70:619–626. PMID: 2234882.
Article12. Yu GY, Ubmüller J, Donath K. Membranous basal cell adenoma of the salivary gland: a clinicopathologic study of 12 cases. Acta Otolaryngol. 1998; 118:588–593. PMID: 9726688.13. Junquera L, Gallego L, de Vicente JC, Fresno MF. Bilateral parotid basal cell adenoma: an unusual case report and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:179–182. PMID: 20006174.
Article14. Olsen KD, Moore EJ. Deep lobe parotidectomy: clinical rationale in the management of primary and metastatic cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 271:1181–1185. PMID: 23832259.
Article15. Kidd HA. Diseases of the parotid gland and the Frey syndrome. Br J Hosp Med. 1969; 2:1513–1522.16. Laccourreye H, Laccourreye O, Cauchois R, Jouffre V, Ménard M, Brasnu D. Total conservative parotidectomy for primary benign pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: a 25-year experience with 229 patients. Laryngoscope. 1994; 104:1487–1494. PMID: 7990639.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Basal Cell Adenocarcinoma Arising from the Bilateral Parotid Gland
- Basal cell adenoma misdiagnosed as an adenoid cystic carcinoma in the parotid gland
- Basal Cell Adenoma Presenting as a Parapharyngeal Space Mass: A Case Report
- A Case of Basal Cell Adenocarcinoma in the Parotid Gland
- Basal cell adenoma of parotid gland: two case reports and literature review