Yonsei Med J.
2014 Jul;55(4):999-1004. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.4.999.
Production of Egg Yolk Antibodies Specific to House Dust Mite Proteins
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics and Institute of Allergy, Brain Korea 21 Plus Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kekim@yuhs.ac
- 2Optipharm Inc., Osong, Korea.
- 3Department of Agricultural Biotechnology, WCU Biomodulation Major, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2130826
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.4.999
Abstract
- PURPOSE
House dust mites (HDMs) are an important source of indoor allergens associated with asthma, rhinitis and atopic dermatitis. Chicken immunoglobulin (Ig) Y is known to be a good alternative to mice and rabbit antibody production. In this study, we produced IgYs specific to HDMs and investigated their IgE immunoreactivities.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Total IgYs were isolated from the yolks of White Leghorn hens immunized with either Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus or D. farinae protein extract. Control antibodies were separated from the yolks of immunized hens with phosphate buffered saline. IgYs specific to HDMs were analyzed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blotting analysis.
RESULTS
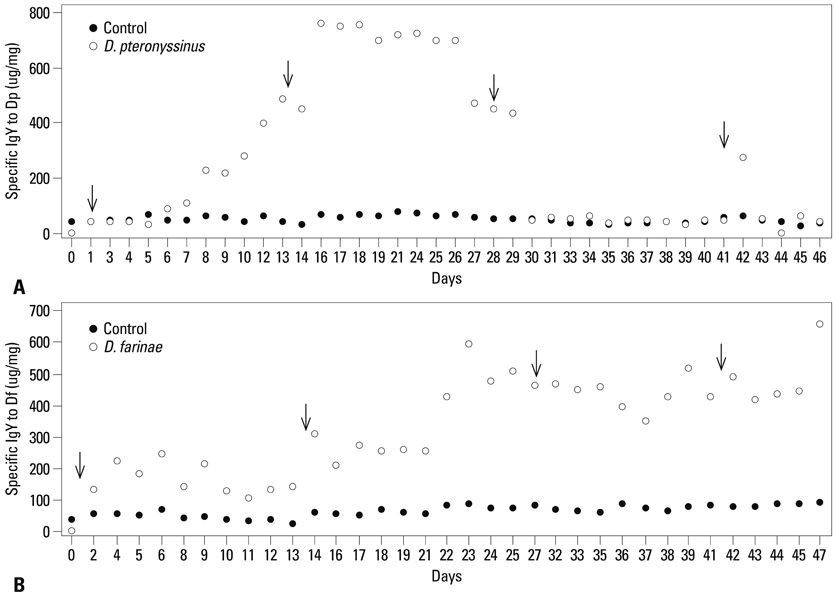
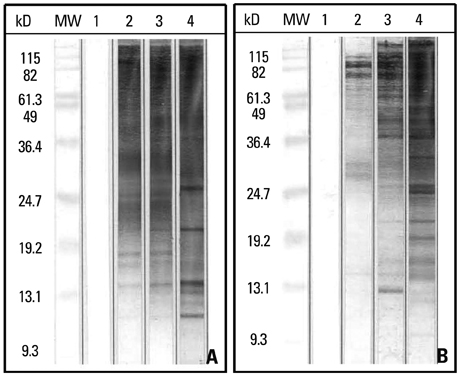
The concentration of egg IgY specific to D. farinae in an immunized hen increased and the highest achieved was 661.3 ug/mg (per an egg) on day 47, compared with 760 ug/mg IgY specific to D. pteronyssinus on day 16. The D. pteronyssinus or D. farinae-specific IgY was detected by binding of each mite proteins, and their immunoreactivities were elevated dependent of the specific IgY concentration.
CONCLUSION
IgY specific to HDMs may be a promising antibody for immunological diagnosis as well as identification of possible resistance relating to HDM allergy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gregory LG, Lloyd CM. Orchestrating house dust mite-associated allergy in the lung. Trends Immunol. 2011; 32:402–411.
Article2. Nahm DH, Kim ME. Treatment of severe atopic dermatitis with a combination of subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy and cyclosporin. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:158–163.
Article3. Trompette A, Divanovic S, Visintin A, Blanchard C, Hegde RS, Madan R, et al. Allergenicity resulting from functional mimicry of a Toll-like receptor complex protein. Nature. 2009; 457:585–588.
Article4. Nathan AT, Peterson EA, Chakir J, Wills-Karp M. Innate immune responses of airway epithelium to house dust mite are mediated through beta-glucan-dependent pathways. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:612–618.
Article5. Diette GB, McCormack MC, Hansel NN, Breysse PN, Matsui EC. Environmental issues in managing asthma. Respir Care. 2008; 53:602–615.6. Yuuki T, Okumura Y, Ando T, Yamakawa H, Suko M, Haida M, et al. Cloning and expression of cDNA coding for the major house dust mite allergen Der f II in Escherichia coli. Agric Biol Chem. 1991; 55:1233–1238.
Article7. Chua KY, Doyle CR, Simpson RJ, Turner KJ, Stewart GA, Thomas WR. Isolation of cDNA coding for the major mite allergen Der p II by IgE plaque immunoassay. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990; 91:118–123.
Article8. Zhang J, Saint-Remy JM, Garrod DR, Robinson C. Comparative enzymology of native and recombinant house dust mite allergen Der p 1. Allergy. 2009; 64:469–477.
Article9. Taylor AI, Gould HJ, Sutton BJ, Calvert RA. Avian IgY binds to a monocyte receptor with IgG-like kinetics despite an IgE-like structure. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:16384–16390.
Article10. Chalghoumi R, Théwis A, Portetelle D, Beckers Y. Production of hen egg yolk immunoglobulins simultaneously directed against Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium in the same egg yolk. Poult Sci. 2008; 87:32–40.
Article11. Warr GW, Magor KE, Higgins DA. IgY: clues to the origins of modern antibodies. Immunol Today. 1995; 16:392–398.
Article12. Dias da Silva W, Tambourgi DV. IgY: a promising antibody for use in immunodiagnostic and in immunotherapy. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010; 135:173–180.
Article13. Hädge D, Ambrosius H. Evolution of low molecular weight immunoglobulins-IV. IgY-like immunoglobulins of birds, reptiles and amphibians, precursors of mammalian IgA. Mol Immunol. 1984; 21:699–707.
Article14. Matthews R, Burnie J. The role of hsp90 in fungal infection. Immunol Today. 1992; 13:345–348.
Article15. Casadevall A. Antibody immunity and invasive fungal infections. Infect Immun. 1995; 63:4211–4218.
Article16. Ibrahim el-SM, Rahman AK, Isoda R, Umeda K, Van Sa N, Kodama Y. In vitro and in vivo effectiveness of egg yolk antibody against Candida albicans (anti-CA IgY). Vaccine. 2008; 26:2073–2080.
Article17. Spillner E, Braren I, Greunke K, Seismann H, Blank S, du Plessis D. Avian IgY antibodies and their recombinant equivalents in research, diagnostics and therapy. Biologicals. 2012; 40:313–322.
Article18. Polson A, von Wechmar MB, van Regenmortel MH. Isolation of viral IgY antibodies from yolks of immunized hens. Immunol Commun. 1980; 9:475–493.
Article19. Griffin P, Ford AW, Alterman L, Thompson J, Parkinson C, Blainey AD, et al. Allergenic and antigenic relationship between three species of storage mite and the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989; 84:108–117.
Article20. Thomas WR, Heinrich TK, Smith WA, Hales BJ. Pyroglyphid house dust mite allergens. Protein Pept Lett. 2007; 14:943–953.
Article21. Asturias JA, Ibarrola I, Arilla MC, Vidal C, Ferrer A, Gamboa PM, et al. Engineering of major house dust mite allergens Der p 1 and Der p 2 for allergen-specific immunotherapy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:1088–1098.
Article22. Xie QM, Wu X, Wu HM, Deng YM, Zhang SJ, Zhu JP, et al. Oral administration of allergen extracts from Dermatophagoides farinae desensitizes specific allergen-induced inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008; 8:1639–1645.
Article23. Luczynska CM, Arruda LK, Platts-Mills TA, Miller JD, Lopez M, Chapman MD. A two-site monoclonal antibody ELISA for the quantification of the major Dermatophagoides spp. allergens, Der p I and Der f I. J Immunol Methods. 1989; 118:227–235.
Article24. Earle CD, King EM, Tsay A, Pittman K, Saric B, Vailes L, et al. High-throughput fluorescent multiplex array for indoor allergen exposure assessment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:428–433.
Article25. Schade R, Calzado EG, Sarmiento R, Chacana PA, Porankiewicz-Asplund J, Terzolo HR. Chicken egg yolk antibodies (IgY-technology): a review of progress in production and use in research and human and veterinary medicine. Altern Lab Anim. 2005; 33:129–154.
Article26. Meenatchisundaram S, Parameswari G, Michael A, Ramalingam S. Neutralization of the pharmacological effects of Cobra and Krait venoms by chicken egg yolk antibodies. Toxicon. 2008; 52:221–227.
Article27. Hamal KR, Burgess SC, Pevzner IY, Erf GF. Maternal antibody transfer from dams to their egg yolks, egg whites, and chicks in meat lines of chickens. Poult Sci. 2006; 85:1364–1372.
Article28. Yokoyama H, Hashi T, Umeda K, Icatlo FC Jr, Kuroki M, Ikemori Y, et al. Effect of oral egg antibody in experimental F18+ Escherichia coli infection in weaned pigs. J Vet Med Sci. 1997; 59:917–921.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Food and house dust mite allergens in children with atopic dermatitis
- Local production of specific IgE antibody to house dust mite in nasal polyp tissues
- The Effects of Nonspecific IgE and IgG Antibodies on Basophil Histamine Release mediated by Specific IgE Antibodies
- Validation of measurement of house dust mite-specific IgE antibodies in serum using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- Production and Characterization of Egg Yolk Antibodies to Human Rotavirus