Healthc Inform Res.
2015 Jul;21(3):196-200. 10.4258/hir.2015.21.3.196.
Application of Telemedicine System to Prehospital Medical Control
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. advanced@lifesupport.pe.kr
- KMID: 2125189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2015.21.3.196
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Although ambulance-based telemedicine has been reported to be safe and feasible, its clinical usefulness has not been well documented, and different prehospital management systems would yield different results. The authors evaluated the feasibility and usefulness of telemedicine-assisted direct medical control in the Korean emergency medical service system.
METHODS
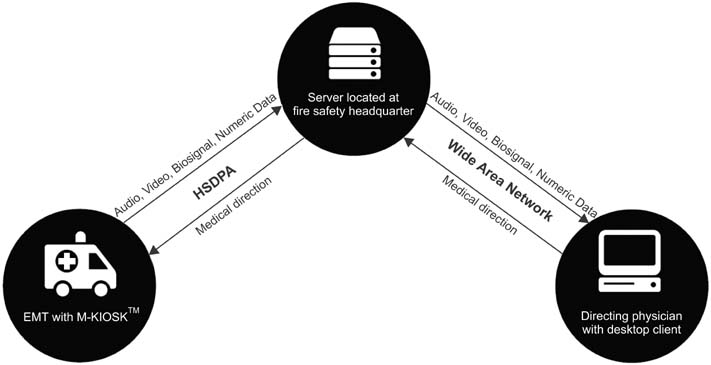
Twenty ambulances in the Busan area were equipped with a telemedicine system. Three-lead electrocardiogram, blood pressure, and pulse oximetry data from the patient and audiovisual input from the scene were transferred to a server. Consulting physicians used desktop computers and the internet to connect to the server. Both requesting emergency medical service (EMS) providers and consulting physicians were asked to fill out report forms and submit them for analysis.
RESULTS
In the 41 cases in which telemedicine equipment was used, cellular phones were concomitantly used in 28 cases (68.35%) to compensate for the poor audio quality provided by the equipment. The EMS providers rated the video transmission quality with a 4-point average score (interquartile range [IQR] 2-5) on a 5-point scale, and they rated the biosignal transmission quality as 4 (IQR 3-5). The consulting physicians rated the video quality as 4 (IQR 2.5-4) and the biosignal quality as 4 (IQR 3-4). The physicians' ratings for usefulness for making diagnosis or treatment decisions did not differ significantly in relation to the method of communication used.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study did not find any significant advantage of implementing telemedicine over the use of voice calls in delivering on-line medical control. More user-friendly, smaller devices with clear advantages over voice communication would be required before telemedicine can be successfully implemented in prehospital patient care.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
High Time to Discuss Future-Oriented Telemedicine
In Ho Kwon
Healthc Inform Res. 2015;21(4):211-212. doi: 10.4258/hir.2015.21.4.211.
Reference
-
1. Roine R, Ohinmaa A, Hailey D. Assessing telemedicine: a systematic review of the literature. CMAJ. 2001; 165(6):765–771.2. Park IC, Cho JH, Kim SH, Kim DK, Yoo SK, Oh JH. Design of a multimedia telemedicine system for interhospital emergency consultation. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2003; 14(5):467–474.3. Yoon DH, Kim SP, Kim SJ, Cho SH, Cho NS. Influence on a doctorless island residents' health care utilization by video telemedicine. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2008; 19(4):359–365.4. Yperzeele L, Van Hooff RJ, De Smedt A, Valenzuela Espinoza A, Van Dyck R, Van de Casseye R, et al. Feasibility of AmbulanCe-Based Telemedicine (FACT) study: safety, feasibility and reliability of third generation inambulance telemedicine. PLoS One. 2014; 9(10):e110043.
Article5. Latifi R, Weinstein RS, Porter JM, Ziemba M, Judkins D, Ridings D, et al. Telemedicine and telepresence for trauma and emergency care management. Scand J Surg. 2007; 96(4):281–289.
Article6. Hwang SO, Lee CC, Singer AJ, Kim TM. The current status of the emergency medical system in Korea. Am J Emerg Med. 2007; 25(7):846–848.
Article7. Galli R. Innovation possibilities for prehospital providers. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2006; 10(3):317–319.
Article8. Beuran M, Paun S, Gaspar B, Vartic N, Hostiuc S, Chiotoroiu A, et al. Prehospital trauma care: a clinical review. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2012; 107(5):564–570.9. Kim DK, Yoo SK, Jung SM, Kim NH. Evaluation of webbased real-time telemedicine application using ActiveX controls for medical moving picture analysis. J Korean Soc Med Inform. 2003; 9(3):261–267.
Article10. Banitsas K, Tachakra S, Stefanidis E, Boletis K. Using HSPA to improve the telemedical links on a moving ambulance. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2008; 2008:739–742.
Article11. Hollander JE, Delagi R, Sciammarella J, Viccellio P, Ortiz J, Henry MC. On-line telemetry: prospective assessment of accuracy in an all-volunteer emergency medical service system. Acad Emerg Med. 1995; 2(4):280–286.
Article12. Dhruva VN, Abdelhadi SI, Anis A, Gluckman W, Hom D, Dougan W, et al. ST-Segment Analysis Using Wireless Technology in Acute Myocardial Infarction (STATMI) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 50(6):509–513.
Article13. Campbell PT, Patterson J, Cromer D, Wall K, Adams GL, Albano A, et al. Prehospital triage of acute myocardial infarction: wireless transmission of electrocardiograms to the on-call cardiologist via a handheld computer. J Electrocardiol. 2005; 38(4):300–309.
Article14. Zanaboni P, Wootton R. Adoption of telemedicine: from pilot stage to routine delivery. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012; 12:1.
Article15. Cicero MX, Walsh B, Solad Y, Whitfill T, Paesano G, Kim K, et al. Do you see what I see? Insights from using google glass for disaster telemedicine triage. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2015; 30(1):4–8.
Article16. Jeroudi OM, Christakopoulos G, Christopoulos G, Kotsia A, Kypreos MA, Rangan BV, et al. Accuracy of remote electrocardiogram interpretation with the use of Google Glass technology. Am J Cardiol. 2015; 115(3):374–377.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Design of Collaborative Telemedicine Application System on Integrated Multimedia DooRae Framework
- Survey study of telemedicine-experienced physicians on the acceptability of telemedicine: using propensity score matching method
- Telemedicine in the U.S.A. with Focus on Clinical Applications and Issues
- The Law and Telemedicine
- Telemedicine System Using a High-Speed Network: Past, Present, and Future