J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2015 Apr;50(2):154-159. 10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.2.154.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection in the Shoulder after Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kimjunghan74@gmail.com
- KMID: 2106752
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.2.154
Abstract
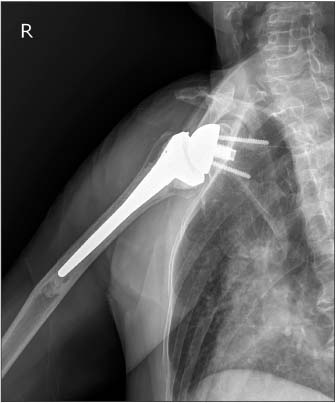
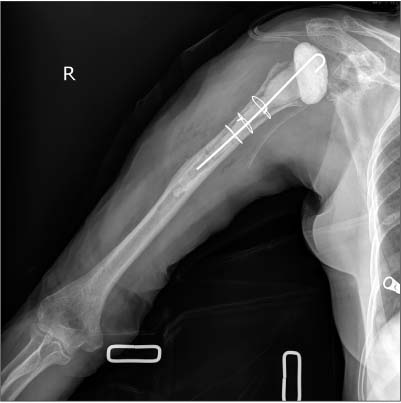
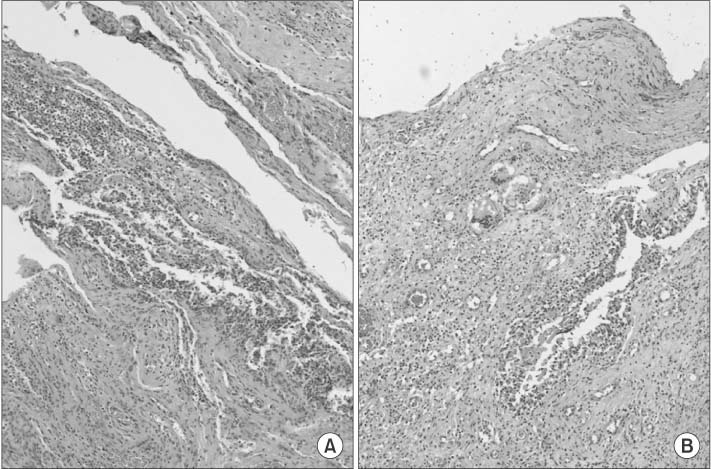
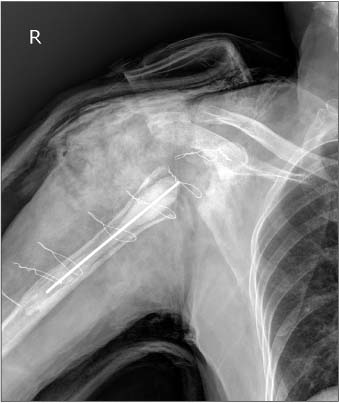
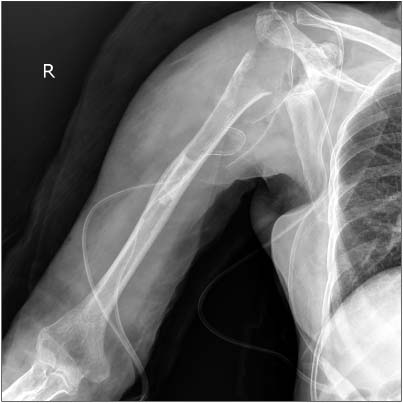
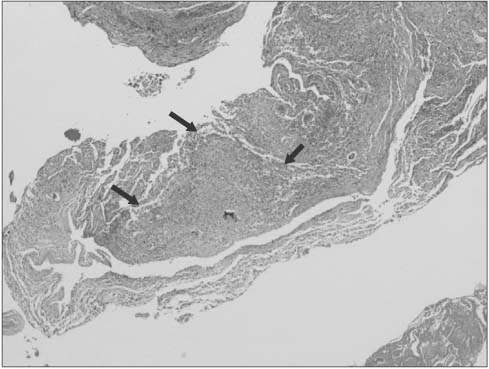
- Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty has recently received attention for treatment of rotator cuff tear arthropathy. However, many complications of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty have also been reported, and infection is a major complication. We are reporting on a case of an approximately 77-year-old female patient who underwent reverse total shoulder arthroplasty with surgical site infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The patient had undergone irrigation and debridement two times due to infectious signs at 8 months after a reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. At the last debridement operation, we performed AFB staining, culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and biopsy. Mycobacterium tuberculosis was cultured and we did not hesitate to administer 4 regimen therapy for tuberculosis. The outpatient follow-up result was satisfactory without recurrence. At the time of the latest follow-up, the degree of pain and function were good.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sirveaux F, Favard L, Oudet D, Huquet D, Walch G, Molé D. Grammont inverted total shoulder arthroplasty in the treatment of glenohumeral osteoarthritis with massive rupture of the cuff. Results of a multicentre study of 80 shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:388–395.2. Walch G, Wall B, Mottier F. Complications and revision of the reverse prosthesis, a multicenter study of 457 cases. In : Walch G, Boileau P, Mole D, Favard L, Levigne C, Sirveaux F, editors. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty: clinical results, complications, revision. Montpellier, France: Sauramps Medical;2006. p. 335–352.3. Wierks C, Skolasky RL, Ji JH, McFarland EG. Reverse total shoulder replacement: intraoperative and early postoperative complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:225–234.
Article4. Cheung EV, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Infection associated with hematoma formation after shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:1363–1367.
Article5. Cuff D, Pupello D, Virani N, Levy J, Frankle M. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of rotator cuff deficiency. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:1244–1251.
Article6. Hattrup SJ. Early complications with the delta reverse shoulder arthroplasty: Influence of the learning curve. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007; 16:e55.7. Wall B, Nové-Josserand L, O'Connor DP, Edwards TB, Walch G. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a review of results according to etiology. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:1476–1485.8. Werner CM, Steinmann PA, Gilbart M, Gerber C. Treatment of painful pseudoparesis due to irreparable rotator cuff dysfunction with the Delta III reverse-ball-and-socket total shoulder prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:1476–1486.
Article9. Hattrup SJ, Bhagia UT. Shoulder arthroplasty complicated by mycobacterium tuberculosis infection: a case report. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008; 17:e5–e7.
Article10. Lederman E, Kweon C, Chhabra A. Late Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in the shoulder of an immunocompromised host after hemiarthroplasty: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:e67(1-4).
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Isolated Musculocutaneous Nerve Palsy after the Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
- Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Techniques and Pitfalls
- Acromion Fracture after Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
- Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Clinical Results and Prevention of Complications
- The Primary Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty for Post-septic Destroyed Shoulder: A Case Report