J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2013 Jun;48(3):246-250. 10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.3.246.
Intervertebral Foraminal Widening Caused by the Tortuous Cervical Vertebral Artery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Othopedic Surgery, Dankook University Medical College, Cheonan, Korea. osmin71@naver.com
- KMID: 2106680
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.3.246
Abstract
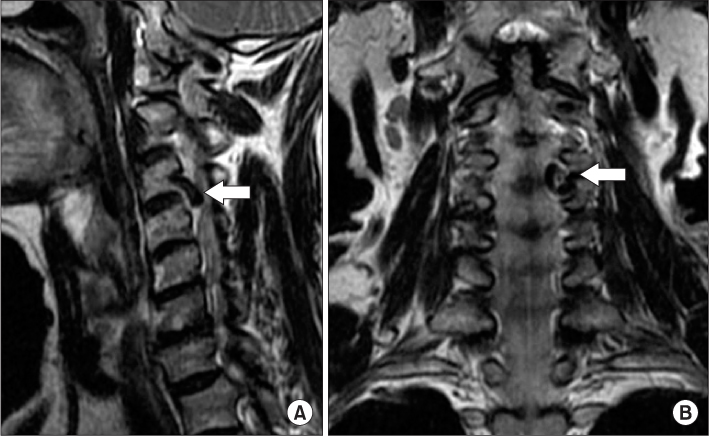
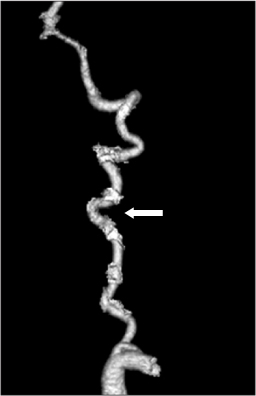
- Tortuousity of the vertebral artery is clinically uncommon because it rarely causes symptoms. We described a patient with pain in the neck and both upper extremities in whom diagnosis of intervertebral foraminal widening and deformity of the vertebral artery were suggested by results of radiography and magnetic resonance. We confirmed the tortuous vertebral artery by results of computed tomography angiography. Correlation of the patient's symptoms and abnormalities was not clear; conservative treatment was administered.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hadley LA. Tortuosity and deflection of the vertebral artery. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1958; 80:306–312.2. Glover JR, Kennedy C, Coral A. Tortuous vertebral artery--onset of symptoms during pregnancy. Clin Radiol. 1990; 41:66–68.3. Anderson RE, Shealy CN. Cervical pedicle erosion and rootlet compression caused by a tortuous vertebral artery. Radiology. 1970; 96:537–538.
Article4. Sganzerla EP, Grimoldi N, Vaccari U, Rampini PM, Gaini SM. Cervical vertebral erosion due to tortuous vertebral artery. Surg Neurol. 1987; 28:385–389.
Article5. Freilich M, Virapongse C, Kier EL, Sarwar M, Bhimani S. Foramen transversarium enlargement due to tortuosity of the vertebral artery Computed tomographic appearance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1986; 11:95–98.6. Schimmel DH, Newton TH, Mani J. Widening of the cervical intervertebral foramen. Neuroradiology. 1976; 12:3–10.
Article7. Danziger J, Bloch S. The widened cervical intervertebral foramen. Radiology. 1975; 116:671–674.
Article8. Babin E, Haller M. Correlation between bony radiological signs and dolichoarterial loops of the cervical vertebral artery. Neuroradiology. 1974; 7:15–17.
Article9. Smith MD, Emery SE, Dudley A, Murray KJ, Leventhal M. Vertebral artery injury during anterior decompression of the cervical spine. A retrospective review of ten patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993; 75:410–415.
Article10. Maiuri F, Iaconetta G, Gallicchio B, Briganti F. Coiling of the vertebral artery presenting with neuralgic pain. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1997; 99:56–59.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cervical Radiculopathy Caused by Vertebral Artery Loop Formation : A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Computed tomography-guided cervical selective transforaminal epidural block for a patient with bilateral anatomical variations of vertebral artery: a case report
- The Relationship between Disc Degeneration and Morphologic Changes in the Intervertebral Foramen of the Cervical Spine: A Cadaveric MRI and CT Study
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by a Tortuous and Dilated Vertebral Artery
- Vertebral Artery Dissection as a Cause of Cervical Radiculopathy