J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Feb;42(1):8-15. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.1.8.
A New Innominate Osteotomy in Legg-Calve-Perthes' Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Chonnam National University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Center for Joint Disease, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Jeonnam, Korea. drjo2023@naver.com
- KMID: 2106369
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.1.8
Abstract
-
Purpose: To evaluate the clinical and radiological results of a new innominate osteotomy in Legg-Calve-Perthes' disease (LCPD).
Materials and Methods
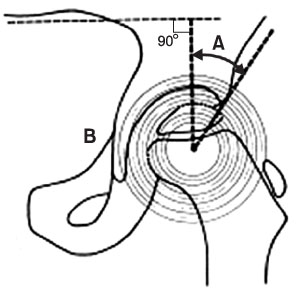
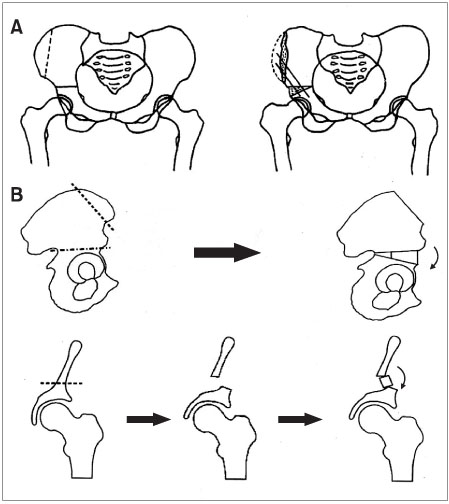
This study examined 25 hips that were treated with a new innominate osteotomy for LCPD. The treatment involved the anterior half of the ilium being osteomized in a direction of 45degrees to the coronal plane and 30degrees to 45degrees to the sagittal plane, and the posterior half of the ilium being cut using a Gigli saw according to the conventional method. The mean follow-up duration was 5.5 years. Stable interposition of the bone block was achieved using a single biodegradable screw in 8 hips, and without any fixation device in 17 hips.
Results
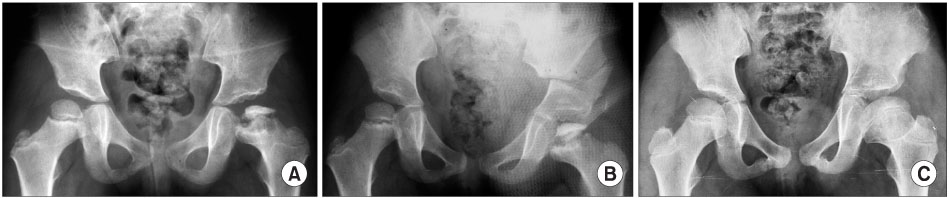
The clinical results according to the criteria of Robinson were good in 20 hips. Twelve hips was graded as good by the Mose method, according to the criteria of Stulberg, 8 hips were included in class I, 6 hips in class II, 8 hips in class III, and 3 hips in class IV. The mean center-edge angle improved from 19.4degrees to 30.2degrees.
Conclusion
The new innominate osteotomy is simpler and easier to perform than a routine Salter osteotomy, and satisfactory clinical results can be obtained without fixing the Kirschner wire.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Five Treatment Models of Dysplastic OA by the RAO
Chang Soo Kang
Hip Pelvis. 2012;24(3):165-185. doi: 10.5371/hp.2012.24.3.165.
Reference
-
1. Canale ST, D'Anca AF, Cotler JM, Snedden HE. Innominate osteotomy in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972. 54:25–40.2. Catterall A. The natural history of Perthes' disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1971. 53:37–53.
Article3. Herring JA, Neustadt JB, Williams JJ, Early JS, Browne RH. The lateral pillar classification of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992. 12:143–150.
Article4. Ingman AM, Paterson DC, Sutherland AD. A comparison between innominate osteotomy and hip spica in the treatment of Legg-Perthes' disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982. 163:141–147.
Article5. Ishida A, Kuwajima SS, Laredo Filho J, Milani C. Salter innominate osteotomy in the treatment of severe Legg-Calve-Perthes disease: clinical and radiographic results in 32 patients (37 hips) at skeletal maturity. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004. 24:257–264.6. Kitakoji T, Hattori T, Kitoh H, Katoh M, Ishiguro N. Which is a better method for Perthes' disease: femoral varus or Salter osteotomy? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 430:163–170.7. Millis MB, Hall JE. Transiliac lengthening of the lower extremity. A modified innominate osteotomy for the treatment of postural imbalance. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979. 61:1182–1194.
Article8. Moberg A, Hansson G, Kaniklides C. Results after femoral and innominate osteotomy in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. 334:257–264.9. Mose K. Methods of measuring in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease with special regard to the prognosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980. 150:103–109.10. Olney BW, Asker MA. Combined innominate and femoral osteotomy for the treatment of severe Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Pediar Orthop. 1985. 5:645–651.11. Robinson HJ Jr, Putter H, Sigmond MB, O'Connor S, Murray KR. Innominate osteotomy in Perthes disease. J Pediatr Orthop. 1988. 8:426–435.
Article12. Salter RB. Experimental and clinical aspects of Perthes' disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1966. 48:393.13. Salter RB. The present status of surgical treatment for Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:961–966.14. Salter RB. Treatment by innominate osteotomy. AAOS Instruct Course Lect. 1973. 22:309–316.15. Sponseller PD, Desai SS, Millis MB. Comparison of femoral and innominate osteotomies for the treatment of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988. 70:1131–1139.16. Stulberg SD, Cooperman DR, Wallensten R. The natural history of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981. 63:1095–1108.17. Vukasinovic Z, Slavkovic S, Milickovic S, Siqeca A. Combined salter innominate osteotomy with femoral shortening versus other methods of treatment for Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Pediar Orthop B. 2000. 9:28–33.18. Yoon TR, Rowe SM, Chung JY, Song EK, Mulyadi D, Anwar IB. A new innominate osteotomy in Perthes' disease. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003. 23:363–367.
Article19. Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint with special refernce to the complication of osteoarthritis. Acta Chir Scand. 1993. 83:Suppl 58. S1–S135.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Innominate Osteotomy in Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
- Innominate osteotomy for the treatment of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
- Femoral Varus Osteotomy Versus Salter Innominate Osteotomy in the Treatment of Legg - Calve - Perthes Disease
- Clinical Observation of the Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease: Preliminary Report
- Subtrochanteric Varization Osteotomy with Open Wedge Technic in a Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease