J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2013 Jun;17(2):154-157. 10.13104/jksmrm.2013.17.2.154.
Perilesional Steatosis in Ectopic Pancreas Mimicking Exogastric Mass : A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea. mykim@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Biology, New York University, USA.
- KMID: 2099875
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2013.17.2.154
Abstract
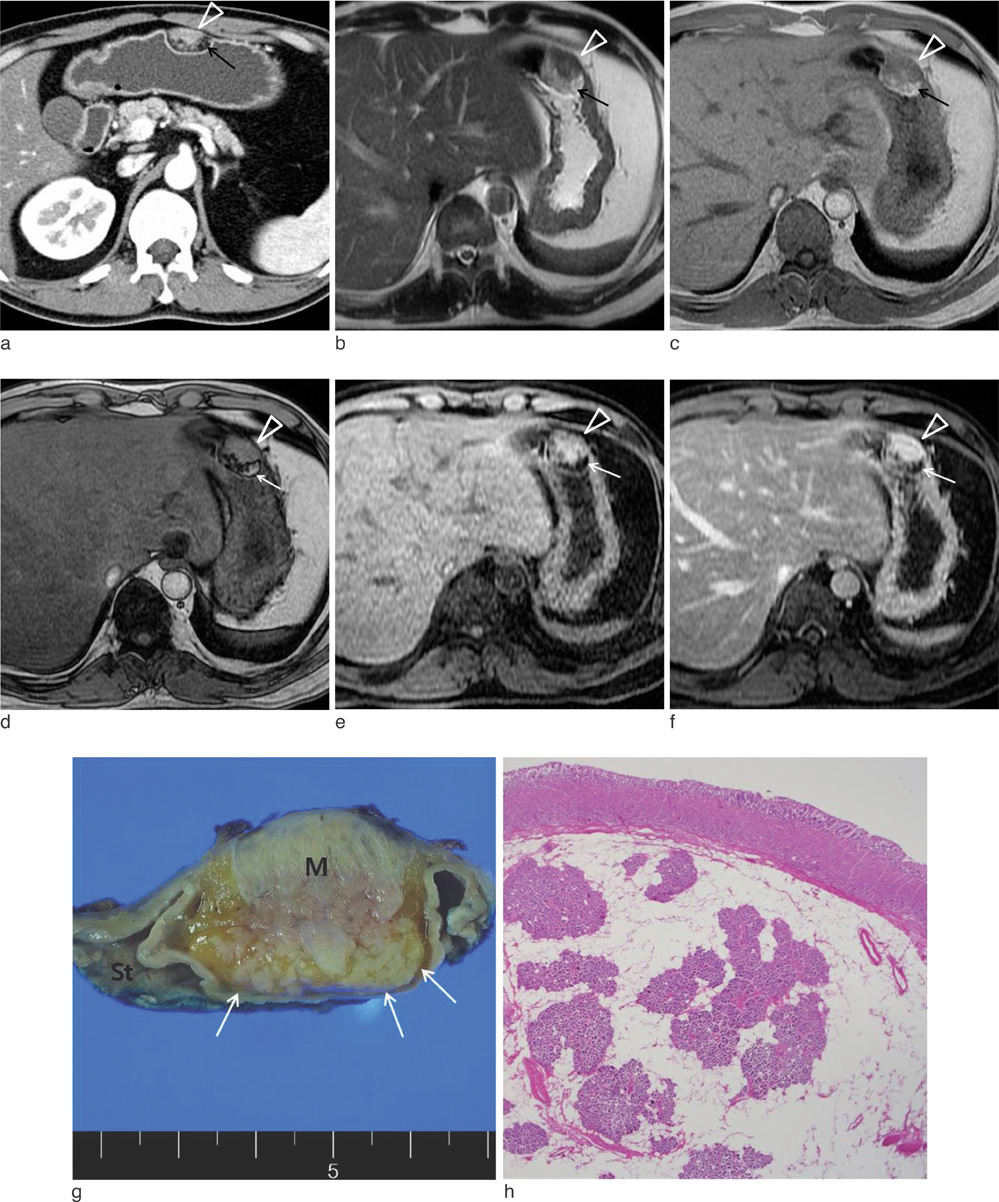
- We report an unusual case of ectopic pancreas that appeared on radiologic images as a lobulated, submucosal mass enclosed by fat component in the gastric lower body. Although, ectopic pancreas including fat component is extremely rare, in the setting of gastric submucosal mass with containing perilesional fat, these findings should be considered in ectopic pancreas as part of the differential diagnosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JY, Lee JM, Kim KW, et al. Ectopic pancreas: CT findings with emphasis on differentiation from small gastrointestinal stromal tumor and leiomyoma. Radiology. 2009; 252:92–100.2. Cho JS, Shin KS, Kwon ST, et al. Heterotopic pancreas in the stomach: CT findings. Radiology. 2000; 217:139–144.3. Katz DS, Hines J, Math KR, Nardi PM, Mindelzun RE, Lane MJ. Using CT to reveal fat-containing abnormalities of the pancreas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999; 172:393–396.4. Low G, Panu A, Millo N, Leen E. Multimodality imaging of neoplastic and nonneoplastic solid lesions of the pancreas. Radiographics. 2011; 31:993–1015.5. Soyer P, Spelle L, Pelage JP, et al. Cystic fibrosis in adolescents and adults: fatty replacement of the pancreas--CT evaluation and functional correlation. Radiology. 1999; 210:611–615.6. Matsumoto S, Mori H, Miyake H, et al. Uneven fatty replacement of the pancreas: evaluation with CT. Radiology. 1995; 194:453–458.7. Kawamoto K, Yamada Y, Utsunomiya T, et al. Gastrointestinal submucosal tumors: evaluation with endoscopic US. Radiology. 1997; 205:733.8. Kilman WJ, Berk RN. The spectrum of radiographic features of aberrant pancreatic rests involving the stomach. Radiology. 1977; 123:291–296.9. Ferrozzi F, Tognini G, Marchesi G, Spaggiari E, Pavone P. Gastric tumors with fat components. CT findings and differential diagnosis. Radiol Med. 2000; 100:343–347.10. Park SH, Han JK, Kim TK, et al. Unusual gastric tumors: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1999; 19:1435–1446.11. Patel S, Bellon EM, Haaga J, Park CH. Fat replacement of the exocrine pancreas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980; 135:843–845.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Case of an Ectopic Pancreas in the Stomach and Presenting as a Cystic Abscess
- Intussusception and Jejunal Atresia Caused by an Ectopic Pancreas in a Newborn
- A case of asymptomatic gastric ectopic pancreas associated with elevated serum CA 19-9
- Exogastric Mature Teratoma in an Infant: A Case Report
- Ectopic Pancreas Presenting as a Duodenal Obstructing Mass