Korean J Pain.
2014 Apr;27(2):112-117. 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.2.112.
Median Nerve Injuries Caused by Carpal Tunnel Injections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. painman70@gmail.com
- KMID: 2074056
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.2.112
Abstract
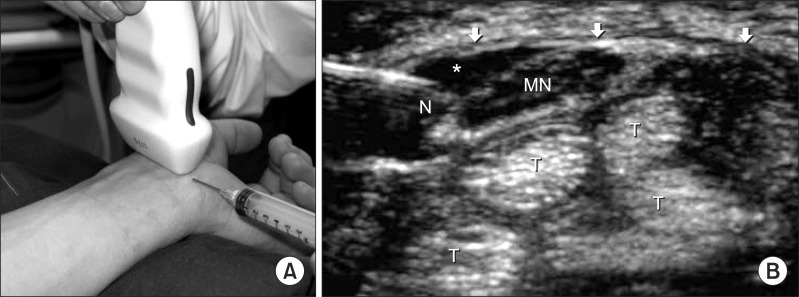
- Local steroid injections are widely used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in the management of carpal tunnel syndrome. The median nerve injury is the most serious complication in association with carpal tunnel injections although the incidence is low. A median nerve injury will be presented with shooting pain at the injection time along with other sensory distortion, motor weakness and muscle atrophy. The management includes a conservative treatment and a surgical exploration. Carpal tunnel injections should be used at a minimum only. If such steroid injection is required, an appropriate needle positioning is vital for the nerve injury prevention. The patient should not be heavily sedated and should be encouraged to inform experiences of numbness/paresthesia during the procedure immediately.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A survey of patients’ perspectives of steroid injection (ppyeojusa) in Korea
Bo-Mi Shin, Sung Jun Hong, Yun Hee Lim, Jae Hun Jeong, Ho Sik Moon, Hey Ran Choi, Sun Kyung Park, Richard Jin Woo Han, Jae Hun Kim
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(3):187-195. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.3.187.
Reference
-
1. McConnell JR, Bush DC. Intraneural steroid injection as a complication in the management of carpal tunnel syndrome. A report of three cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (250):181–184. PMID: 2293928.
Article2. Phalen GS. The carpal-tunnel syndrome. Seventeen years' experience in diagnosis and treatment of six hundred fifty-four hands. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1966; 48:211–228. PMID: 5934271.3. Green DP. Diagnostic and therapeutic value of carpal tunnel injection. J Hand Surg Am. 1984; 9:850–854. PMID: 6512200.
Article4. Gelberman RH, Aronson D, Weisman MH. Carpal-tunnel syndrome. Results of a prospective trial of steroid injection and splinting. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980; 62:1181–1184. PMID: 7000789.
Article5. Goodman HV, Foster JB. Effect of local corticosteroid injection on median nerve conduction in carpal tunnel syndrome. Ann Phys Med. 1962; 6:287–294. PMID: 13900311.
Article6. Ozdoğan H, Yazici H. The efficacy of local steroid injections in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: a double-blind study. Br J Rheumatol. 1984; 23:272–275. PMID: 6487932.
Article7. Schuchmann JA, Melvin JL, Duran RJ, Coleman CR. Evaluation of local steroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1971; 52:253–255. PMID: 5090266.8. Wood MR. Hydrocortisone injections for carpal tunnel syndrome. Hand. 1980; 12:62–64. PMID: 6154006.
Article9. Kopell HP. Carpal tunnel compression median neuropathy treated nonsurgically. N Y State J Med. 1958; 58:744–745. PMID: 13517554.10. Tavares SP, Giddins GE. Nerve injury following steroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. A report of two cases. J Hand Surg Br. 1996; 21:208–209. PMID: 8732402.11. Linskey ME, Segal R. Median nerve injury from local steroid injection in carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurosurgery. 1990; 26:512–515. PMID: 2320220.
Article12. Frederick HA, Carter PR, Littler JW. Injection injuries to the median and ulnar nerves at the wrist. J Hand Surg Am. 1992; 17:645–647. PMID: 1629544.
Article13. Park GY, Kim SK, Park JH. Median nerve injury after carpal tunnel injection serially followed by ultrasonographic, sonoelastographic, and electrodiagnostic studies. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011; 90:336–341. PMID: 21765250.
Article14. Bland JD. Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2007; 36:167–171. PMID: 17534984.
Article16. Mackinnon SE, Hudson AR, Gentili F, Kline DG, Hunter D. Peripheral nerve injection injury with steroid agents. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982; 69:482–490. PMID: 7063571.
Article17. Kasten SJ, Louis DS. Carpal tunnel syndrome: a case of median nerve injection injury and a safe and effective method for injecting the carpal tunnel. J Fam Pract. 1996; 43:79–82. PMID: 8691185.18. Kim DH, Jang JE, Park BK. Anatomical basis of ulnar approach in carpal tunnel injection. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E191–E198. PMID: 23703418.19. Smith J, Wisniewski SJ, Finnoff JT, Payne JM. Sonographically guided carpal tunnel injections: the ulnar approach. J Ultrasound Med. 2008; 27:1485–1490. PMID: 18809959.20. Lindley SG, Kleinert JM. Prevalence of anatomic variations encountered in elective carpal tunnel release. J Hand Surg Am. 2003; 28:849–855. PMID: 14507518.
Article21. Propeck T, Quinn TJ, Jacobson JA, Paulino AF, Habra G, Darian VB. Sonography and MR imaging of bifid median nerve with anatomic and histologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 175:1721–1725. PMID: 11090410.
Article22. Chino N, Awad EA, Kottke FJ. Pathology of propylene glycol administered by perineural and intramuscular injection in rats. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1974; 55:33–38. PMID: 4809017.23. Sun CN, White HJ. Destruction and remyelinization of peripheral nerve after alcohol injury. Exp Pathol (Jena). 1974; 9:169–174. PMID: 4435091.24. Gentili F, Hudson AR, Hunter D, Kline DG. Nerve injection injury with local anesthetic agents: a light and electron microscopic, fluorescent microscopic, and horseradish peroxidase study. Neurosurgery. 1980; 6:263–272. PMID: 7383289.
Article25. Owen DS. Aspiration and injection of joints and soft tissues. In : Kelly WN, Harris ED, Ruddy S, Sledge CB, editors. Kelley's textbook of rheumatology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia (PA): WB Saunders;1985. p. 546–560.26. Gentili F, Hudson AR, Hunter D. Clinical and experimental aspects of injection injuries of peripheral nerves. Can J Neurol Sci. 1980; 7:143–151. PMID: 7407720.
Article27. Gentili F, Hudson AR, Kline D, Hunter D. Early changes following injection injury of peripheral nerves. Can J Surg. 1980; 23:177–182. PMID: 7363181.28. Duncan I, Sullivan P, Lomas F. Sonography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999; 173:681–684. PMID: 10470903.
Article29. Clark WK. Surgery for injection injuries of peripheral nerves. Surg Clin North Am. 1972; 52:1325–1328. PMID: 5076104.
Article30. Clark K, Williams PE Jr, Willis W, McGavran WL 3rd. Injection injury of the sciatic nerve. Clin Neurosurg. 1970; 17:111–125. PMID: 4939477.
Article31. Terzis JK, Dykes RW, Hakstian RW. Electrophysiological recordings in peripheral nerve surgery: a review. J Hand Surg Am. 1976; 1:52–66. PMID: 798755.
Article32. Marshall S, Tardif G, Ashworth N. Local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; (2):CD001554. PMID: 17443508.
Article33. Ly-Pen D, Andréu JL, de Blas G, Sánchez-Olaso A, Millán I. Surgical decompression versus local steroid injection in carpal tunnel syndrome: a one-year, prospective, randomized, open, controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:612–619. PMID: 15692981.
Article34. Ly-Pen D, Andréu JL, Millán I, de Blas G, Sánchez-Olaso A. Comparison of surgical decompression and local steroid injection in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: 2-year clinical results from a randomized trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012; 51:1447–1454. PMID: 22467087.
Article35. Andreu JL, Ly-Pen D, Millán I, de Blas G, Sánchez-Olaso A. Local injection versus surgery in carpal tunnel syndrome: Neurophysiologic outcomes of a randomized clinical trial. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013; [in press].
Article36. MacLennan A, Schimizzi A, Meier KM, Barron OA, Catalano L, Glickel S. Comparison of needle position proximity to the median nerve in 2 carpal tunnel injection methods: a cadaveric study. J Hand Surg Am. 2009; 34:875–879. PMID: 19410990.
Article37. Dubert T, Racasan O. A reliable technique for avoiding the median nerve during carpal tunnel injections. Joint Bone Spine. 2006; 73:77–79. PMID: 16242987.
Article38. Dammers JW, Veering MM, Vermeulen M. Injection with methylprednisolone proximal to the carpal tunnel: randomised double blind trial. BMJ. 1999; 319:884–886. PMID: 10506042.
Article39. Kamanli A, Bezgincan M, Kaya A. Comparison of local steroid injection into carpal tunnel via proximal and distal approach in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2011; 112:337–341. PMID: 21692409.40. Ustün N, Tok F, Yagz AE, Kizil N, Korkmaz I, Karazincir S, et al. Ultrasound-guided vs. blind steroid injections in carpal tunnel syndrome: a single-blind randomized prospective study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013; 92:999–1004. PMID: 23811617.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Caused by Persistent Median Artery and Bifid Median Nerve in an Adolescent
- Median Nerve Block for Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Report of 5 cases
- Ultrasonographic Study of Median Nerve after Carpal Tunnel Release
- Accessory Palmaris Longus Encountered during Carpal Tunnel Surgery: A Case Report
- Median Nerve Injury Caused by Brachial Plexus Block for Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery