Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jul;35(4):466-468. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.4.466.
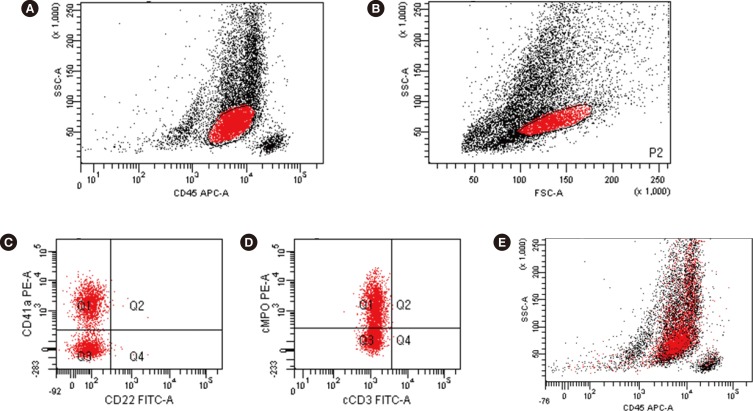
An Unusual Case of Myeloperoxidase-Positive Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. hankja@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2045873
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.4.466
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mathur NB, Joshi N, Singh T, Singh M. Congenital acute megakaryocytic leukemia. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2011; 32:165–167. PMID: 22557786.
Article2. Arber DA, Brunning RD, Orazi A, Porwit A, Peterson L, Thiele J. Acute myeloid leukemia, not otherwise specified. In : Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC;2008. p. 130–139.3. Sun T, editor. Flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and molecular genetics for hematologic neoplasms. 2012. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2012. p. 150–152.4. Pombo De Oliveira MS, Gregory C, Matutes E, Parreira A, Catovsky D. Cytochemical profile of megakaryoblastic leukaemia: a study with cytochemical methods, monoclonal antibodies, and ultrastructural cytochemistry. J Clin Pathol. 1987; 40:663–669. PMID: 3038965.
Article5. Park CJ, Cho HC, Park YS. A case of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia showing Aure rods. Korean J Hematol. 1996; 31:161–165.6. Tallman MS, Neuberg D, Bennett JM, Francois CJ, Paietta E, Wiernik PH, et al. Acute megakaryocytic leukemia: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group experience. Blood. 2000; 96:2405–2411. PMID: 11001891.7. Majhi U, Murhekar K, Sundersingh S, Rajalekshmi KR. Megakaryoblastic leukemia presenting as pancytopenia and extensive myelofibrosis in a child diagnosed by myeloid markers and CD 31. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2012; 33:59–61. PMID: 22754213.
Article8. Pusztaszeri MP, Seelentag W, Bosman FT. Immunohistochemical expression of endothelial markers CD31, CD34, von Willebrand factor, and Fli-1 in normal human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006; 54:385–395. PMID: 16234507.
Article9. Calapso P, Vitarelli E, Crisafulli C, Tuccari G. Immunocytochemical detection of megakaryocytes by endothelial markers: a comparative study. Pathologica. 1992; 84:215–223. PMID: 1437309.10. Borowitz MJ, Bene MC, Harris NL, Porwit A, Matutes E. Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage. In : Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC;2008. p. 150–155.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Re: Lee H, et al. An Unusual Case of Myeloperoxidase-Positive Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia. Ann Lab Med 2015;35:466-8
- A case of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with Down syndrome
- A case of leukemia cutis in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
- A Case of Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia
- Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia