Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jul;35(4):454-457. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.4.454.
Direct Identification of Staphylococcus aureus and Determination of Methicillin Susceptibility From Positive Blood-Culture Bottles in a Bact/ALERT System Using Binax Now S. aureus and PBP2a Tests
- Affiliations
-
- 1Hospices Civils de Lyon, Laboratoire de Bacteriologie, Centre de Biologie et de Pathologie Est, Bron, France. olivier.dauwalder@chu-lyon.fr
- 2Hospices Civils de Lyon, Centre National de Reference des Staphylocoques, Centre de Biologie et de Pathologie Est, Bron, France.
- 3International Center for Research in Infectiology, INSERM U 1111, Lyon, France.
- 4Universite de Lyon, Faculte de Medecine Lyon Est, Domaine de la Buire, Lyon, France.
- 5Research group on
, UMR 5557 Ecologie Microbienne, CNRS, Universite Lyon 1, ENVL, Universite de Lyon, Lyon, France. - 6Hospices Civils de Lyon, Laboratoire de Bacteriologie, Centre de Biologie et Pathologie Nord, Lyon, France.
- KMID: 2045870
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.4.454
Abstract
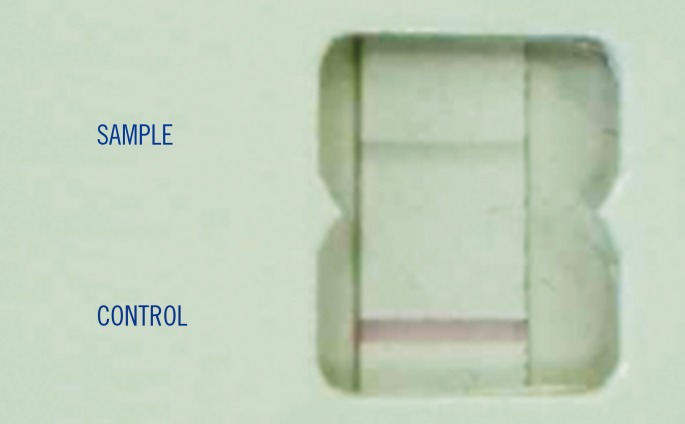
- Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia is associated with high mortality and morbidity, requiring prompt and appropriate antimicrobial treatment. Therefore, it is important to detect methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) rapidly from blood cultures. Two immunochromatographic tests, BinaxNow S. aureus and BinaxNow PBP2a, were directly applied to 79 Bact/Alert bottles that were positive for Gram positive cocci in cluster aggregations. Sensitivity and specificity for the identification of S. aureus and determination of methicillin resistance were 94% and 87%, and 100% and 100%, respectively, with less than 30 min of performance time. These tests are efficient and rapid; these tests are valuable alternatives to more sophisticated and expensive methods used in the diagnosis of MRSA bacteremia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. de Kraker ME, Wolkewitz M, Davey PG, Koller W, Berger J, Nagler J, et al. Clinical impact of antimicrobial resistance in European hospitals: excess mortality and length of hospital stay related to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:1598–1605. PMID: 21220533.
Article2. Kim SH, Kim KH, Kim HB, Kim NJ, Kim EC, Oh MD, et al. Outcome of vancomycin treatment in patients with methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 52:192–197. PMID: 17984229.3. Bates DW, Goldman L, Lee TH. Contaminant blood cultures and resource utilization. The true consequences of false-positive results. JAMA. 1991; 265:365–369. PMID: 1984535.
Article4. Romero-Gómez MP, Quiles-Melero I, Navarro C, Paño-Pardo JR, Gómez-Gil R, Mingorance J. Evaluation of the BinaxNOW PBP2a assay for the direct detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus from positive blood culture bottles. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 72:282–284. PMID: 22209514.
Article5. Carretto E, Bardaro M, Russello G, Mirra M, Zuelli C, Barbarini D. Comparison of the Staphylococcus QuickFISH BC test with the tube coagulase test performed on positive blood cultures for evaluation and application in a clinical routine setting. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:131–135. PMID: 23100336.6. Gröbner S, Dion M, Plante M, Kempf VA. Evaluation of the BD GeneOhm StaphSR assay for detection of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates from spiked positive blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:1689–1694. PMID: 19369439.7. Lagacé-Wiens PR, Adam HJ, Karlowsky JA, Nichol KA, Pang PF, Guenther J, et al. Identification of blood culture isolates directly from positive blood cultures by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry and a commercial extraction system: analysis of performance, cost, and turnaround time. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:3324–3328. PMID: 22875888.8. Alere. BinaxNOW® Staphylococcus aureus Card. Updated on Dec 16, 2009. www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K090964.pdf.9. Dhiman N, Trienski TL, DiPersio LP, DiPersio JR. Evaluation of the BinaxNOW Staphylococcus aureus test for rapid identification of Gram-positive cocci from VersaTREK blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:2939–2942. PMID: 23804393.10. Yossepowitch O, Dan M, Kutchinsk A, Gottesman T, Schwartz-Harari O. A cost-saving algorithm for rapid diagnosis of Staphylococcus aureus and susceptibility to oxacillin directly from positive blood culture bottles by combined testing with BinaxNOW® S. aureus and Xpert MRSA/SA Assay. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014; 78:352–355. PMID: 24503507.11. Spencer DH, Sellenriek P, Burnham CA. Validation and implementation of the GeneXpert MRSA/SA blood culture assay in a pediatric setting. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011; 136:690–694. PMID: 22031306.
Article12. Qian Q, Eichelberger K, Kirby JE. Rapid identification of Staphylococcus aureus directly from Bactec blood culture broth by the BinaxNOW S. aureus test. J Clin Microbiol. 2014; 52:319–320. PMID: 24153135.13. Corso A, Soloaga R, Faccone D, Gagetti P, Corbella S, Iglesias M, et al. Improvement of a latex agglutination test for the evaluation of oxacillin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004; 50:223–225. PMID: 15541610.
Article14. Laurent F, Chardon H, Haenni M, Bes M, Reverdy ME, Madec JY, et al. MRSA harboring mecA variant gene mecC, France. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012; 18:1465–1467. PMID: 22932400.15. Eigner U, Weizenegger M, Fahr AM, Witte W. Evaluation of a rapid direct assay for identification of bacteria and the mecA and van genes from positive-testing blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:5256–5262. PMID: 16207992.16. Szabados F, Kaase M, Anders A, Gatermann SG. Identical MALDI TOF MS-derived peak profiles in a pair of isogenic SCCmec-harboring and SCCmec-lacking strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect. 2012; 65:400–405. PMID: 22750235.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Direct Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Blood Cultures Using Three Non-Molecular Methods: PBP2a Latex Agglutination, PBP2a Rapid Immunochromatographic Assay and MRSA-Chromogenic Medium
- Growth Dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a Function of Time to Detection in BacT/Alert 3D Blood Culture Bottles with Various Preincubation Conditions
- Comparison of BACTEC Plus Aerobic/F Media and BacT/Alert FA Media to Detect Bacteria in Blood Culture Bottles Containing Peak Therapeutic Levels of Antimicrobials
- Comparison of the BACTEC Peds Plus Pediatric Blood Culture Bottle to the BacT/Alert PF Pediatric Blood Culture Bottle for Culturing Blood from Pediatric Patients
- Evaluation of Positive Rate of Aerobic BacT/Alert Blood Culture Bottles by Antibiotic Usage and Inoculated Blood Volume