J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 May;64(5):491-496. 10.3348/jksr.2011.64.5.491.
Desmoplastic Fibroma of Bone: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Korea. hdhdoc@naver.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2040818
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.64.5.491
Abstract
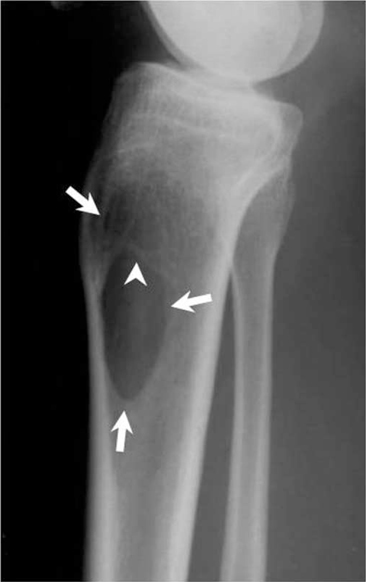
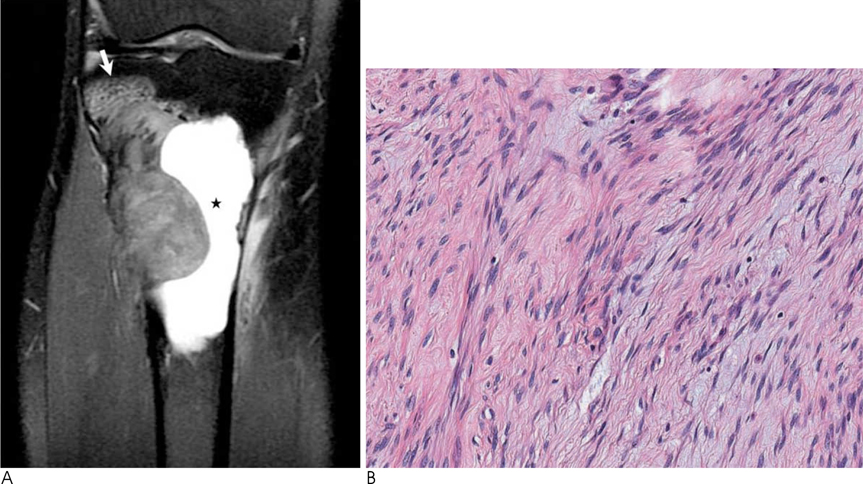
- Desmoplastic fibroma of bone is a rare benign primary bone tumor that histologically resembles the extra-abdominal desmoid tumor of soft tissues. It is a nonmetastasizing, but locally aggressive tumor that is similar to a desmoid tumor of the soft tissues, and so it is considered "semimalignant". According to a previous report on a series of bone tumors, the incidence rate of desmoplastic fibroma was 0.1-0.3%. Its rarity results in radiologists having a tendency of overlooking the possibility of desmoplastic fibroma of bone during the imaging readings. We report on the imaging findings of desmoplastic fibroma of bone with a review of the relevant literature.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jaffe HL. Tumors and tumorous conditions of the bones and joints. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger;1958. p. 298–303.2. Fornasico V, Pritzker KPH, Bridge JA. Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. In : Fletcher CDM, Unni KK, Merten SF, editors. Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC Press;2002. p. 288.3. Inwards CY, Unni KK, Beabout JW, Sim FH. Desmoplastic fibroma of bone. Cancer. 1991; 68:1978–1983.4. Mirra JM, Picci P, Gold RH. Bone tumors: clinical, radiologic, and pathologic correlations. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger;1989. p. 735–747.5. Crim JR, Gold RH, Mirra JM, Eckardt JJ, Bassett LW. Desmoplastic fibroma of bone: radiographic analysis. Radiology. 1989; 172:827–832.6. Taconis WK, Schutte HE, van der Heul RO. Desmoplastic fibroma of bone: a reported of 18 cases. Skeletal Radiol. 1994; 23:283–288.7. Bohm P, Krober S, Greschniok A, Laniado M, Kaiserling E. Desmoplastic fibroma of the bone. A reported of two patients, review of the literature, and therapeutic implications. Cancer. 1996; 78:1011–1023.8. Frick MA, Sundaram M, Unni KK, Inwards CY, Fabbri N, Tretani F, et al. Imaging findings in desmoplastic fibroma of bone: distinctive T2 chracteristic. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:1762–1767.9. Vanhoenacker FM, Hauben E, De Beuckeleer LH, Willemen D, Van Marck E, De Schepper AM. Desmoplastic fibroma of bone: MRI features. Skeletal Radiol. 2000; 29:171–175.10. Sundaram M, McGuire MH, Schajowicz F. Soft-tissue masses: histologic basis for decreased signal (short T2) on T2-weighted MR images. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987; 148:1247–1767.