J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Dec;79(Suppl 1):S58-S61. 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.Suppl1.S58.
Cholelithiasis with Mucosal Dysplasia of the Gallbladder in a 2-year-old Child
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea. goodnews@gnah.co.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 2040555
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.79.Suppl1.S58
Abstract
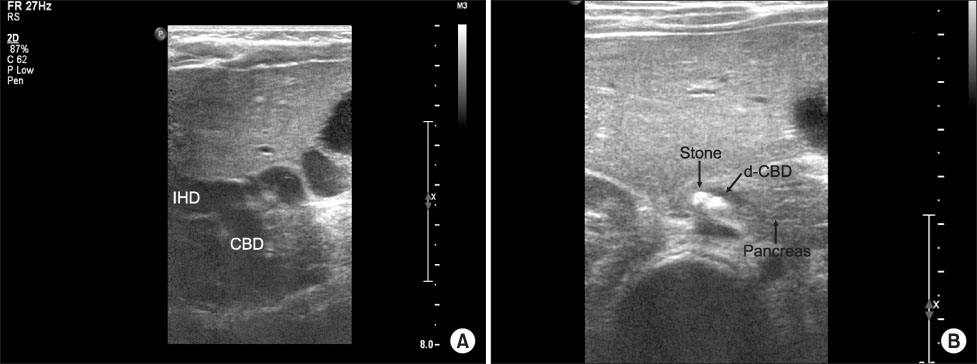
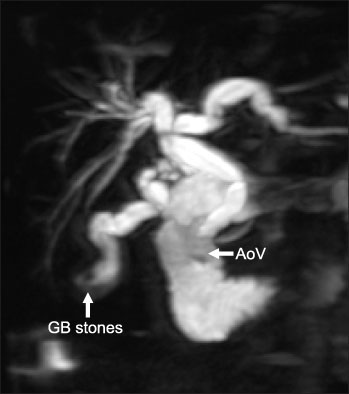
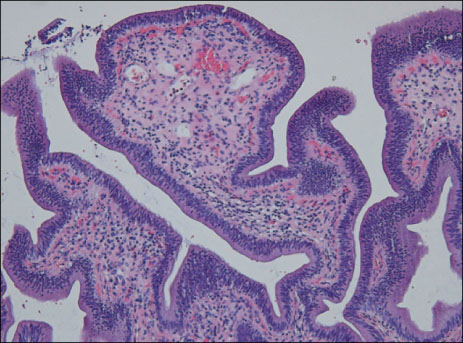
- Traditionally, it has been emphasized that hemolytic disease was the primary cause of gallstones (cholelithiasis) in most young patients. In recent years, gallstones and common bile duct calculi have been increasingly diagnosed in infants and children, unrelated to hemolytic diseases. On the matter, the World Health Organization (WHO) classified intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) of gall bladder as one of the precursor lesions of invasive cancer. The following article describes the case of a 2-year-old girl who had a laparoscopic cholecystectomy due to cholelithiasis and the pathologic diagnosis was chronic cholecystitis with diffuse, mild mucosal dysplasia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Albores-Saavedra J, Scoazec J, Wittekind C, Stripa B, Menke HR, Soehendra N. Stanley RH, Lauri AA, editors. Tumors of the gallbladder and extrahepatic bile ducts. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Digestive System. 1999. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC;211–213.2. Roa I, de Aretxabala X, Araya JC, Roa J. Preneoplastic lesions in gallbladder cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2006. 93:615–623.3. Lugo-Vicente HL. Trends in management of gallbladder disorders in children. Pediatr Surg Int. 1997. 12:348–352.4. Kumar R, Nguyen K, Shun A. Gallstones and common bile duct calculi in infancy and childhood. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000. 70:188–191.5. Robertson JF, Carachi R, Sweet EM, Raine PA. Cholelithiasis in childhood: a follow-up study. J Pediatr Surg. 1988. 23:246–249.6. Gilliland TM, Traverso LW. Modern standards for comparison of cholecystectomy with alternative treatments for symptomatic cholelithiasis with emphasis on long-term relief of symptoms. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1990. 170:39–44.7. St Peter SD, Keckler SJ, Nair A, Andrews WS, Sharp RJ, Snyder CL, et al. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the pediatric population. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2008. 18:127–130.8. Bailey PV, Connors RH, Tracy TF Jr, Sotelo-Avila C, Lewis JE, Weber TR. Changing spectrum of cholelithiasis and cholecystitis in infants and children. Am J Surg. 1989. 158:585–588.9. Duarte I, Llanos O, Domke H, Harz C, Valdivieso V. Metaplasia and precursor lesions of gallbladder carcinoma. Frequency, distribution, and probability of detection in routine histologic samples. Cancer. 1993. 72:1878–1884.10. Kozuka S, Tsubone N, Yasui A, Hachisuka K. Relation of adenoma to carcinoma in the gallbladder. Cancer. 1982. 50:2226–2234.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cholelithiasis as a Risk Factor for Gallbladder Cancer
- Hyperplasia, Metaplasia, and Dysplasia of the Gallbladder Correlation to Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma
- Agenesis of the Gallbladder
- A Case of Gallbladder Stones Associated with Anti-E Antibody Hemolytic Disease in a Neonate
- Gallstone formation and gallbladder mucosal changes in mice fed a lithogenic diet