J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2015 Mar;17(1):7-12. 10.7461/jcen.2015.17.1.7.
CT Fluoroscopy-guided Aspiration of Intracerebral Hematomas: Technique and Outcomes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. storynlemon@gmail.com
- KMID: 1963143
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.1.7
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The authors evaluated the feasibility and targeting accuracy of CT fluoroscopy (CTF)-guided catheter placement and aspiration of intracerebral hematoma (ICH)s.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nine patients (mean age, 63.3 +/- 15.3 years) were treated by CTF-guided hematoma aspiration under local anesthesia. The targeting errors in the lesion center, volume of the aspirated hematoma, accuracy of the final catheter position, procedure time, and clinical outcomes were evaluated.
RESULTS
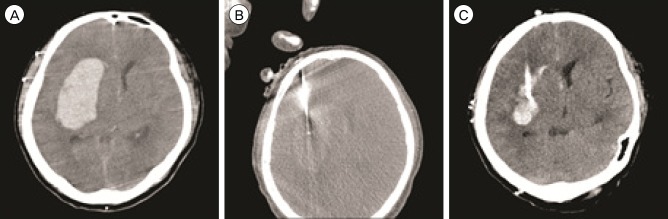
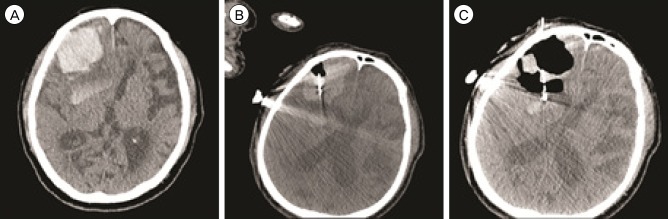
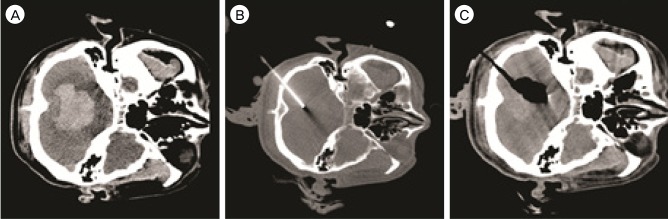
All catheters were successfully placed in the center of the hematoma. The mean volume of the aspirated hematoma was 20.6 +/- 8.8 mL (pre-treatment, 44.7 +/- 20.1 mL; post-treatment, 24.1 +/- 13.8 mL). The average procedure time was 25.1 minutes (range, 18-32 minutes). In one case with a scanty residual hematoma, the catheter was removed at the end of the procedure. In the remaining eight cases, the catheter was left in the residual hematoma for drainage and all catheter tips were accurately located in the final position. There were no procedure-related complications, including rebleeding and infection.
CONCLUSION
CTF-guided ICH aspiration is a feasible, quick, and accurate procedure which could substitute for stereotactic methods. The accurate catheter position provided by real-time observation enables an effective aspiration and drainage of hematomas.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Carlson SK, Bender CE, Classic KL, Zink FE, Quam JP, Ward EM, et al. Benefits and safety of CT fluoroscopy in interventional radiologic procedures. Radiology. 2001; 5. 219(2):515–520. PMID: 11323481.
Article2. Katada K, Kato R, Anno H, Ogura Y, Koga S, Ida Y, et al. Guidance with real-time CT fluoroscopy: early clinical experience. Radiology. 1996; 9. 200(3):851–856. PMID: 8756943.
Article3. Mapstone TB, Ratcheson RA. Techniques of ventricular puncture. In : Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS, editors. Neurosurgery. New York: McGrow-Hill;1996. p. 179–180.4. Montes JM, Wong JH, Fayad PB, Awad IA. Stereotactic computed tomographic-guided aspiration and thrombolysis of intracerebral hematoma : protocol and preliminary experience. Stroke. 2000; 4. 31(4):834–840. PMID: 10753984.5. Morgan T, Zuccarello M, Narayan R, Keyl P, Lane K, Hanley D. Preliminary findings of the minimally-invasive surgery plus rtPA for intracerebral hemorrhage evacuation (MISTIE) clinical trial. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2008; 105:147–151. PMID: 19066101.
Article6. Murphy K, Nussbaum DA, Gailloud P. CT fluoroscopy: novel application for the treatment of ventricular pathologies. Neuroradiology. 2007; 4. 49(4):373–378. PMID: 17393194.
Article7. Niizuma H, Otsuki T, Johkura H, Nakazato N, Suzuki J. CT-guided stereotactic aspiration of intracerebral hematoma--result of a hematoma-lysis method using urokinase. Appl Neurophysiol. 1985; 48(1-6):427–430. PMID: 3915660.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Stereotactic Aspiration of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma using Multiple Catheters
- Analysis of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematomas Confirmed by CT
- Role of Stereotactic Surgery for Treatment of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematomas
- Stereotatic Aspiration of Simultaneous Bilateral Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Case Report
- The Fluid-Blood Level in a Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma