J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2005 Sep;12(3):229-232. 10.4184/jkss.2005.12.3.229.
Percutaneous Drainage of Epidural abscess in Lumbar Spin: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu Korea. bong@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1941689
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2005.12.3.229
Abstract
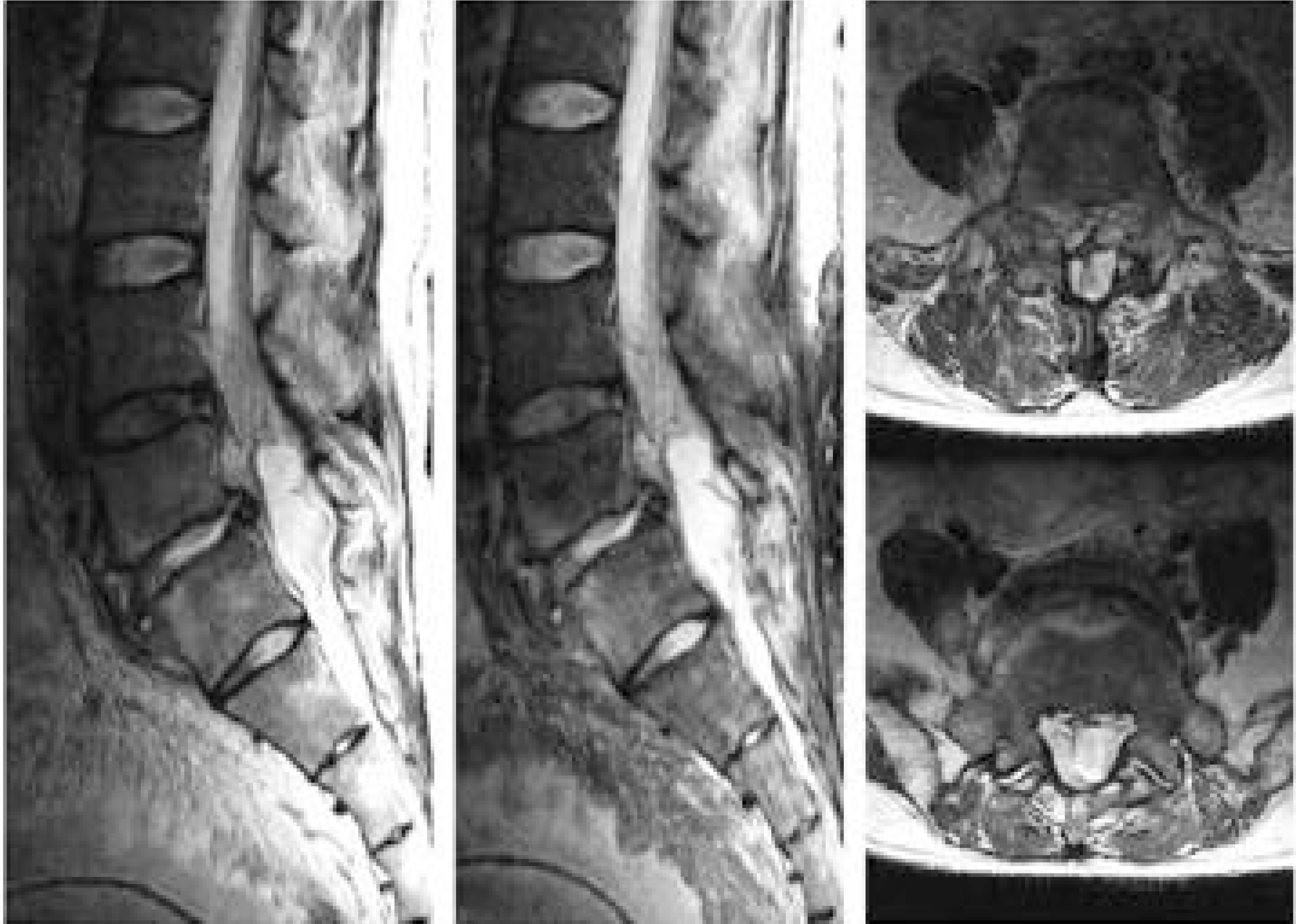
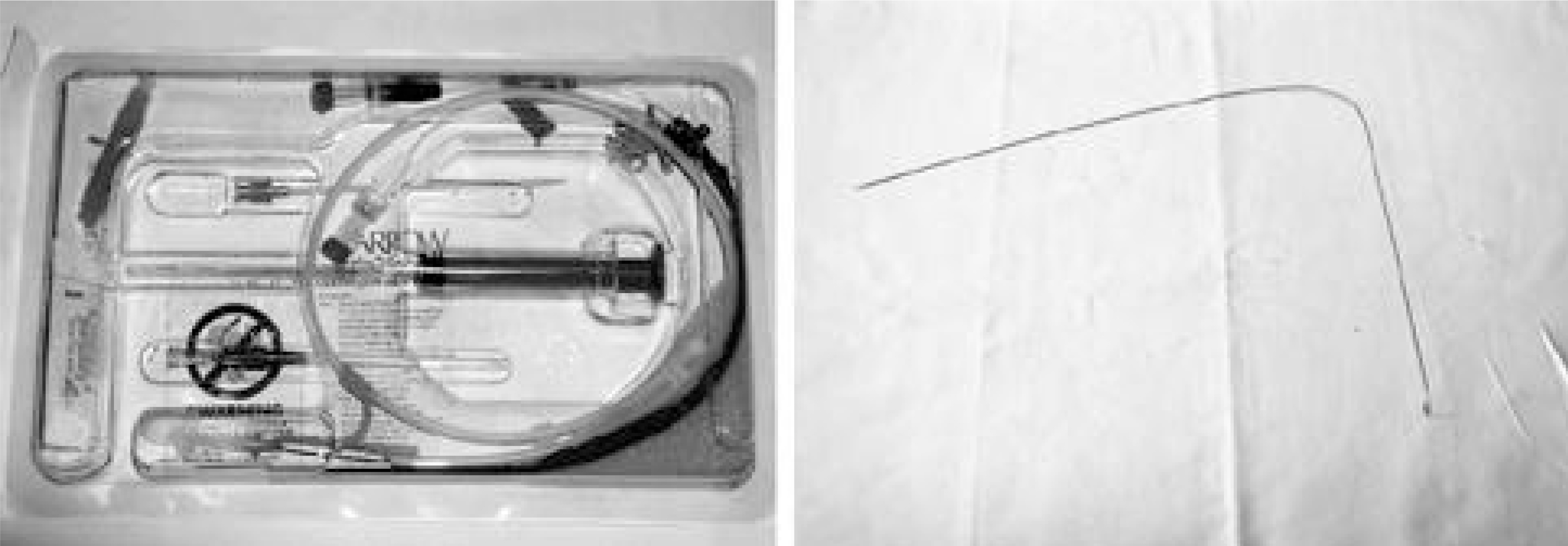
- The choice of treatment of an epidural abscess is surgical decompression accompanied by an adequate parenteral antibiotics injection. However, in selected patients, unable to endure a surgical procedure due to a medical problem, percutaneous drainage using a spring wire guide & CVP catheter through the sacral hiatus, under fluoroscopic monitoring, is thought to be a good alternative choice for surgical decompression.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Lyu RK, Chen CJ, Tang LM, Chen ST. Spinal epidural abscess successfully treated with percutaneous, computed tomography-guided, needle aspiration and parenteral antibiotic therapy: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 51(2):509–12. discussion 512. 2002.
Article2). Nussbaum ES, Rigamonti D, Standiford H, Numaguchi Y, Wolf AL, Robinson WL. Spinal epidural abscess: a report of 40 cases and review. Surg Neurol. 38(3):225–31. 1992.
Article3). Hlavin ML, Kaminski HJ, Ross JS, Ganz E. S pina l epidural abscess: a ten-year perspective. Neurosurgery. 27(2):177–84. 1990.4). Tabo E, Ohkuma Y, Kimura S, Nagaro T, Arai T. Successful percutaneous drainage of epidural abscess with epidural needle and catheter. Anesthesiology. 80(6):1393–5. 1994.
Article5). Darouiche RO, Hamill RJ, Greenberg SB, Weathers SW, Musher DM. Bacterial spinal epidural abscess. Review of 43 cases and literature survey. Medicine (Balti - more). 71(6):369–85. 1992.6). Mackenzie AR, Laing RB, Smith CC, Kaar GF, Smith F W. Spinal epidural abscess: the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 65(2):209–12. 1998.
Article7). Rigamonti D, Liem L, Sampath P, Knoller N, Nam-aguchi Y, Schreibman DL, Sloan MA, Wolf A, Zeid-man S. Spinal epidural abscess: contemporary trends in etiology, evaluation, and management. Surg Neurol. 52(2):189–96. discussion 197. 1999.
Article8). Hanigan WC, Asner NG, Elwood PW. Magnetic resonance imaging and the nonoperative treatment of spinal epidural abscess. Surg Neurol. 34(6):408–13. 1990.
Article9). Walter RS, King JC Jr, Manley J, Rigamonti D. Spinal epidural abscess in infancy: successful percutaneous drainage in a nine-month-old and review of the literature. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 10(11):860–4. 1991.
Article10). Cwikiel W. Percutaneous drainage of abscess in psoas compartment and epidural space. Case report and review of the literature. Acta Radiol. 32(2):159–61. 1991.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pediatric Lumbar Epidural Abscess Combined with Cauda Equina Syndrome: Case Report
- Pyogenic Spinal Epidural Abscess: A Case Report
- The Epidural and Psoas Abscess Recognized after Lumbar Epidural Block: A case report
- Successful Treatment of Epidural Abscess with Percutaneous Drainage: A case report
- Cervico-thoraco-lumbar Spinal Epidural Abscess and Psoas Abscess Successfully Treated with Parenteral Antibiotic Therapy and Percutaneous Drainage: A Case Report