Korean J Perinatol.
2014 Mar;25(1):17-21. 10.14734/kjp.2014.25.1.17.
A Case of Pai Syndrome: First Reported Case in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Cheil General Hospital & Women's Health Care Center, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ykleeped@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1917228
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2014.25.1.17
Abstract
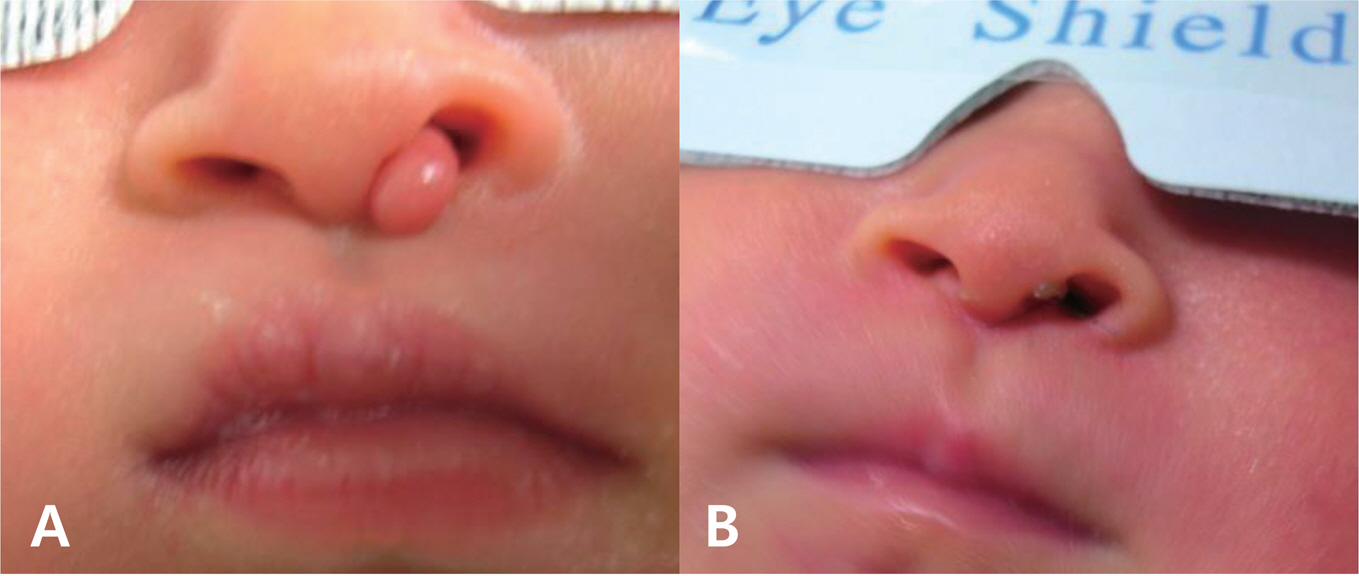
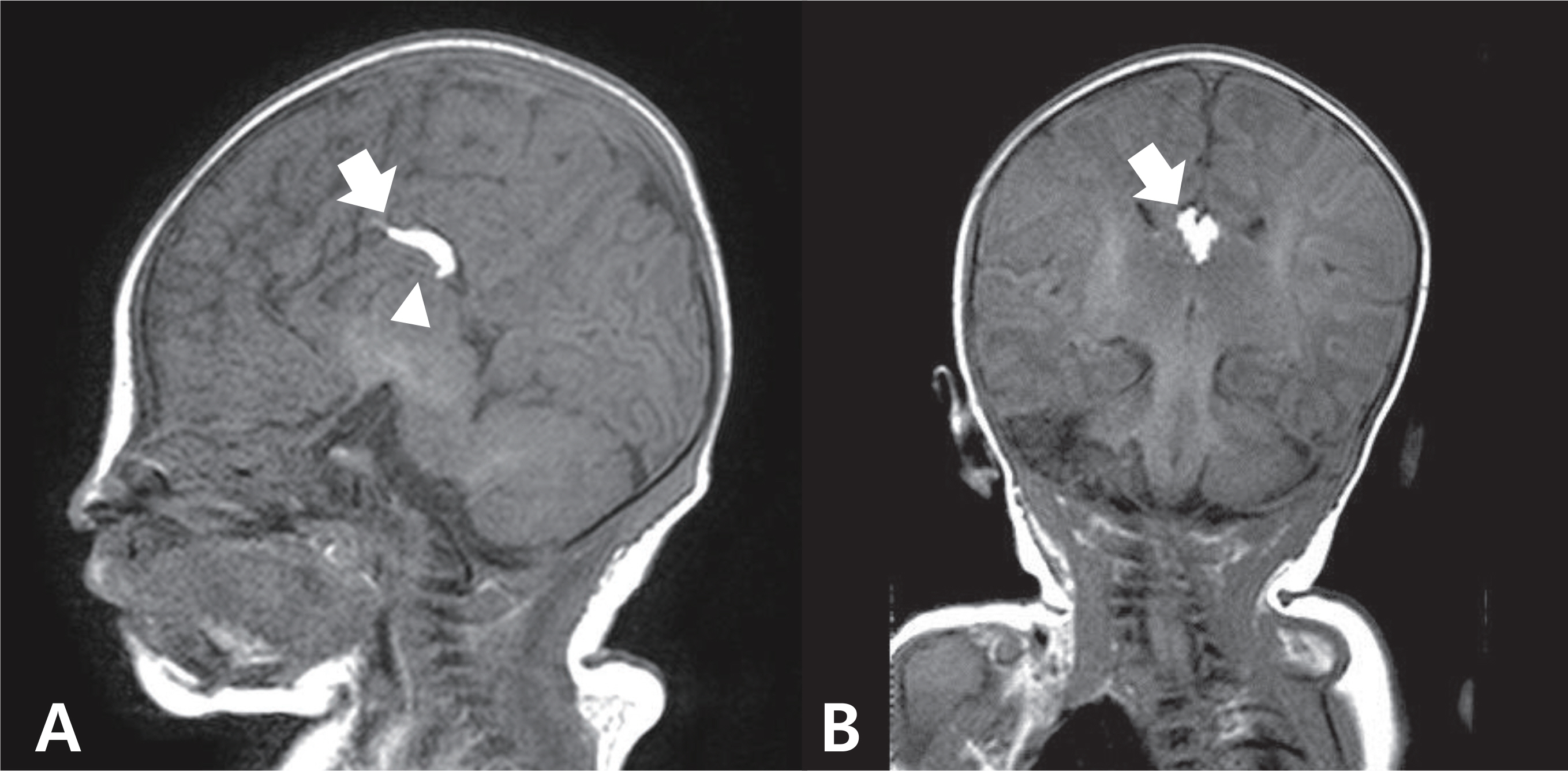
- Pai syndrome is a rare disorder, first described in 1987. Diagnostic criteria are the presence of the nasal polyp and one of the following: midline cleft lip, congenital polyp of mid-anterior alveolar process, and pericallosal lipoma. Thirty-six cases of Pai syndrome have been described so far. We report 1 case of Pai syndrome accompanied by congenital nasal polyp and callosal lipoma with partial agenesis of corpus callosum, the first time in Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.Lederer D., Wilson B., Lefesvre P., Poorten VV., Kirkham N., Mitra D, et al. Atypical findings in three patients with Pai syndrome and literature review. Am J Med Genet A. 2012. 158A:2899–904.
Article2.Pai GS., Levkoff AH., Leithiser RE Jr. Median cleft of the upper lip associated with lipomas of the central nervous system and cutaneous polyps. Am J Med Genet. 1987. 26:921–4.
Article3.Castori M., Rinaldi R., Bianchi A., Caponetti A., Assumma M., Grammatico P. Pai syndrome: first patient with agenesis of the corpus callosum and literature review. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2007. 79:673–9.
Article4.Al-Mazrou KA., Al-Rekabi A., Alorainy IA., Al-Kharfi T., Al-Serhani AM. Pai syndrome: a report of a case and review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011. 61:149–53.
Article5.Vaccarella F., Pini Prato A., Fasciolo A., Pisano M., Carlini C., Seymandi PL. Phenotypic variability of Pai syndrome: report of two patients and review of the literature. Int J Oral Max-illofac Surg. 2008. 37:1059–64.
Article6.Chousta A., Ville D., James I., Foray P., Bisch C., Depardon P, et al. Pericallosal lipoma associated with Pai syndrome: prenatal imaging findings. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008. 32:708–10.
Article7.Savasta S., Chiapedi S., Perrini S., Tognato E., Corsano L., Chiara A. Pai syndrome: a further report of a case with bifid nose, lipoma, and agenesis of the corpus callosum. Childs Nerv Syst. 2008. 24:773–6.
Article8.Guion-Almeida ML., Mellado C., Beltrán C., Richieri-Costa A. Pai syndrome: report of seven South American patients. Am J Med Genet A. 2007. 143A:3273–9.
Article9.Masuno M., Imaizumi K., Fukushima Y., Tanaka Y., Ishii T., Nakamura M, et al. Median cleft of upper lip and pedunculated skin masses associated with de novo reciprocal translocation 46,X,t(X;16)(q28;q11.2). J Med Genet. 1997. 34:952–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of the superior mesenteric artery syndrome
- Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Type 1 Gene Polymorphism in Patients with Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome
- A case of type VI Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- A Case of Gianotti-Crosti Syndrome Associated with HBs Antigenemia
- Apert Syndrome A Case Report and Analysis of the Reported Cases in Korea