Prog Med Phys.
2013 Dec;24(4):284-289. 10.14316/pmp.2013.24.4.284.
A Dosimetric Comparision of IMRT and VMAT in Synchronous Bilateral Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Eulji University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Physics, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea. skkim3@ynu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1910571
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2013.24.4.284
Abstract
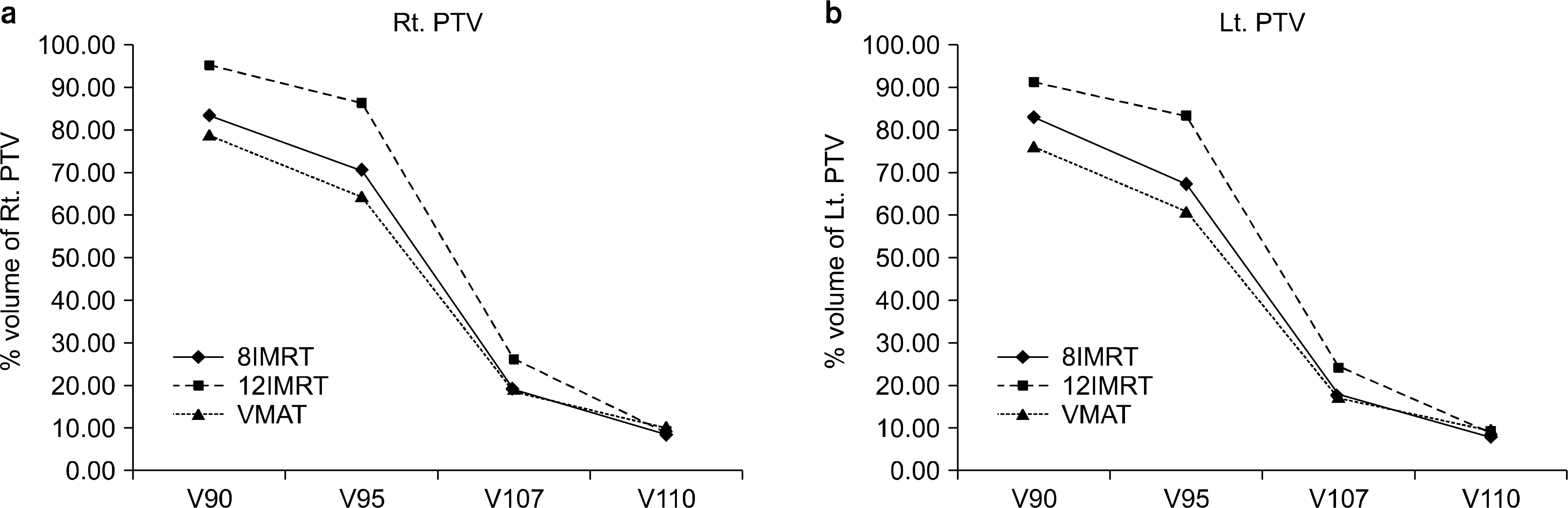
- A study was performed comparing dosimetric characteristics of volumetric modulated arc and intensity modulated radiatio therapy on patients with bilateral breast cancer. For 5 patients, 3 plans were made for each patient; IMRT beams 8 and 12 of the beam intensity modulated radiation therapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy plan. The average PTVs volumes and D98 for 12-IMRT were 51.04+/-0.57 Gy (right), 50.80+/-1.07 Gy (left), 42.94+/-16.16 Gy (right), 42.56+/-2.09 Gy (left). HI (D5~D95) and CI90,95, even 12-IMRT has shown excellent results. In OAR, 3 plans showed excellent results. But the lowest dose of 12-IMRT. 12-IMRT achieved similar PTV coverage and sparing of organs at risk than 8-IMRT and VMAT.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fisher B, Anderson S, Redmond CK, et al. Reanalysis and results after 12 years of followup in a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy with lumpectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 333(22):1456–1461. 1995.
Article2. Fogliataa A, Nicolinia G, Alberb M, et al. IMRT for breast. A planning study. Radiother Oncol. 76(3):300–310. 2005.3. Nicolini G, Clivio A, Fogliata A, et al. Simultaneous integrated boost radiotherapy for bilateral breast: a treatment planning and dosimetric comparison for volumetric modulated arc and fixed field intensity modulated therapy. Rad Oncol. 4(1):27. 2009.
Article4. Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Collaborative Working Group. Intensity modulated radiotherapy: current status and issues of interest. Int J Radiation Oncology Biol Phys. 51(4):880–917. 2001.5. Otto K. Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med Phys. 35(1):310–317. 2008.
Article6. Semenenko VA, Reitzet B, et al. Evaluation of a commercial biologically based IMRT treatment planning system. Med Phys. 35(12):5851–5860. 2008.
Article7. Lafond C, Gassa F, Odin C, et al. Comparison between two treatment planning systems for volumetric modulated arc therapy optimization for prostate cancer. Eur J Med Phys. 30(1):1–8. 2013.
Article8. Martha MM, Di Y, Inga G, Alvaro M. Clinical applications of volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int J Radiation Oncology Biol Phys. 77(2):608–616. 2010.9. Clivio A, Fogliata A, Franzetti-Pellanda A, et al. Volumetricmodulated arc radiotherapy for carcinomas of the anal canal: A treatment planning comparison with fixed field IMRT. Radiother Oncol. 92(1):118–124. 2009.
Article10. Verbakel WF, Cuijpers JP, Hoffmans D, et al. Volumetric intensity-modulated arc therapy vs. conventional IMRT in headandneck cancer: a comparative planning and dosimetric study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 74(1):252–259. 2009.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of jaw tracking in intensity-modulated and volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy for head and neck cancers: a dosimetric study
- Dosimetric Evaluation of Low-Dose Spillage Volumes for Head and Neck Cancer Using Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy and Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy Treatment Techniques
- Dosimetric and Radiobiological Evaluation of Dose Volume Optimizer (DVO) and Progressive Resolution Optimizer (PRO) Algorithm against Photon Optimizer on IMRT and VMAT Plan for Prostate Cancer
- Dosimetric comparative study of 3DCRT, IMRT, VMAT, Ecomp, and Hybrid techniques for breast radiation therapy
- Analysis on the Dosimetric Characteristics of Tangential Breast Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy