J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2014 Mar;19(1):19-28. 10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.1.19.
Arthroscopically assisted Cancellous Bone Grafting and Percutaneous K-Wires Fixation for the Treatment of Scaphoid Nonunions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dason Orthopaedic Clinic, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Chen and Woo's Institute for Hand Surgery and Reconstructive Microsurgery, W Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Prince of Wales Hospital, Chinese University, Hong Kong.
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungbuk National Universiry Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Chungju, Korea.
- 5Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. trueyklee@naver.com
- KMID: 1896923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.1.19
Abstract
- PURPOSE
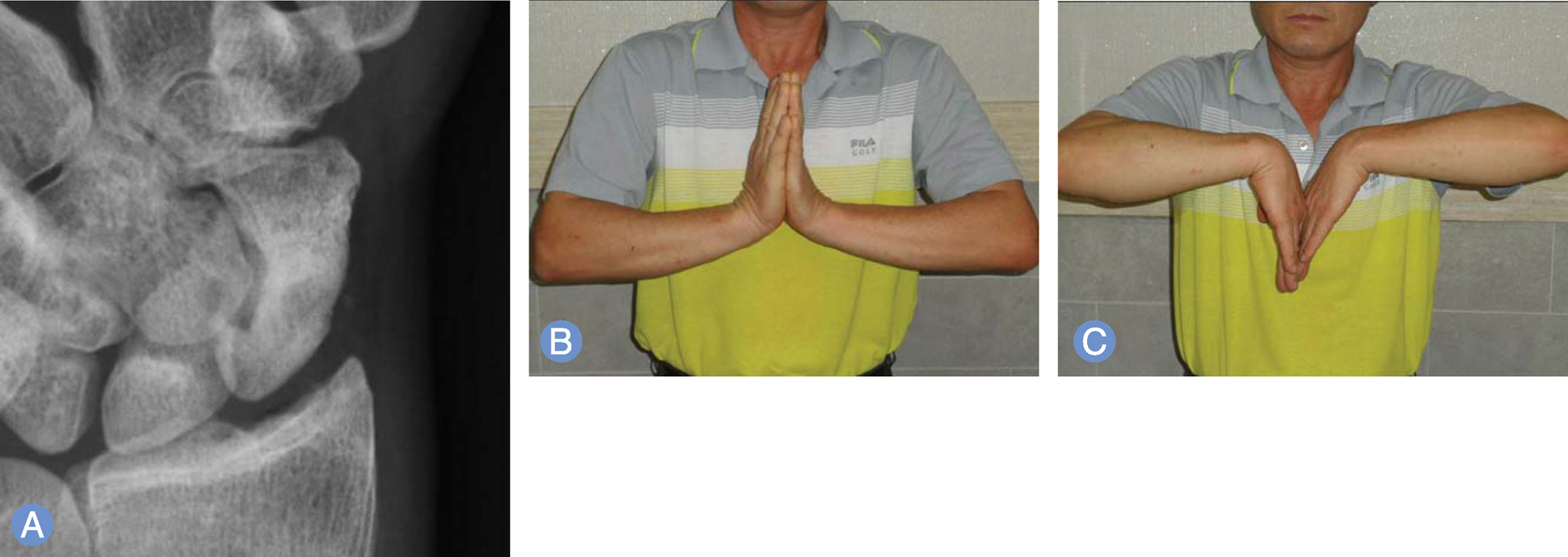
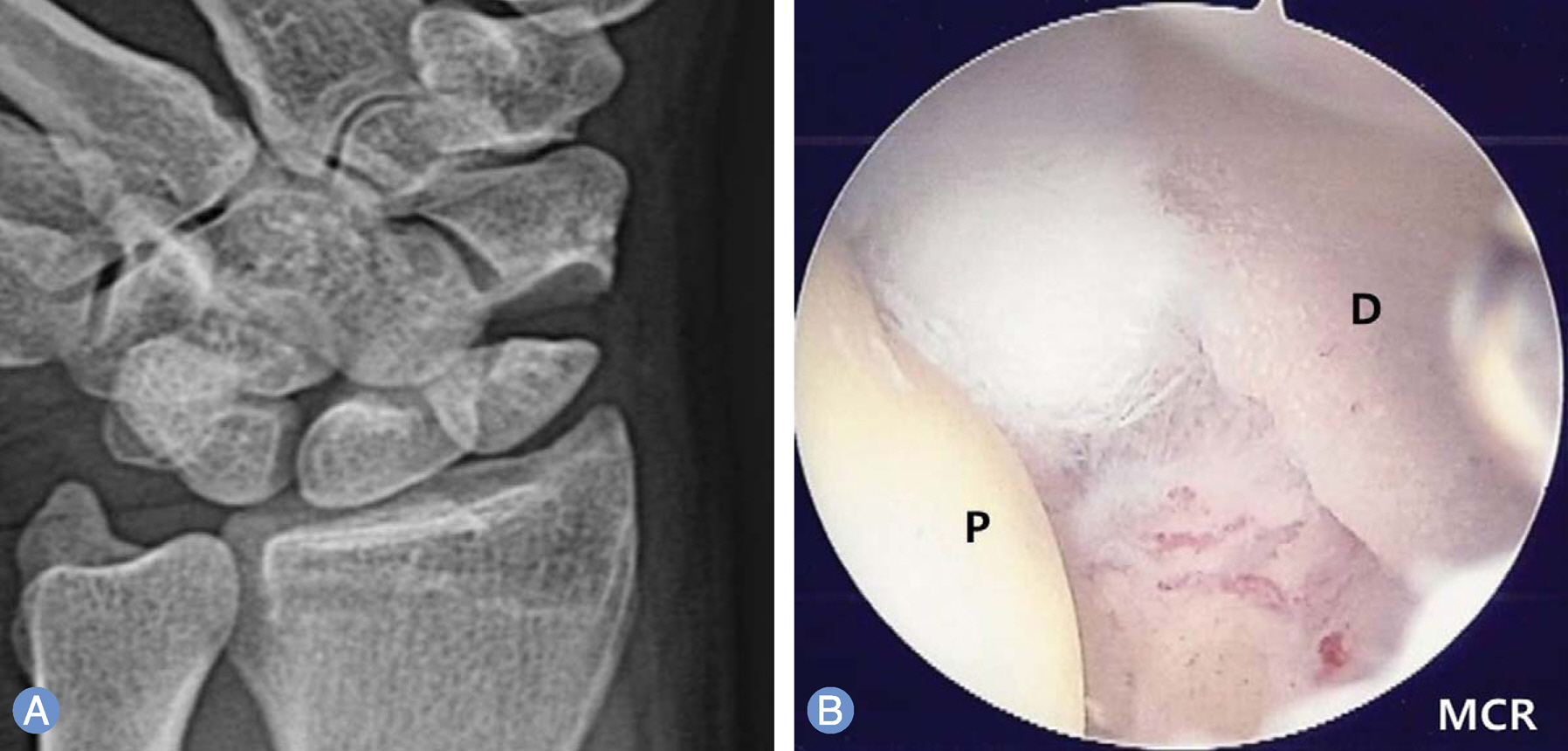
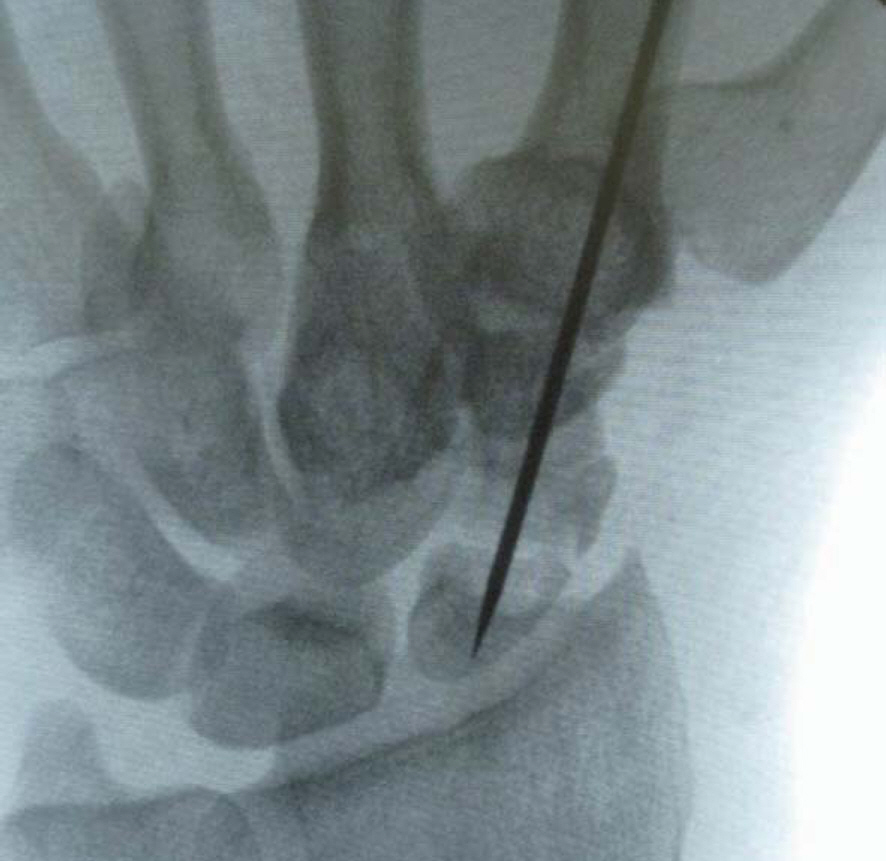
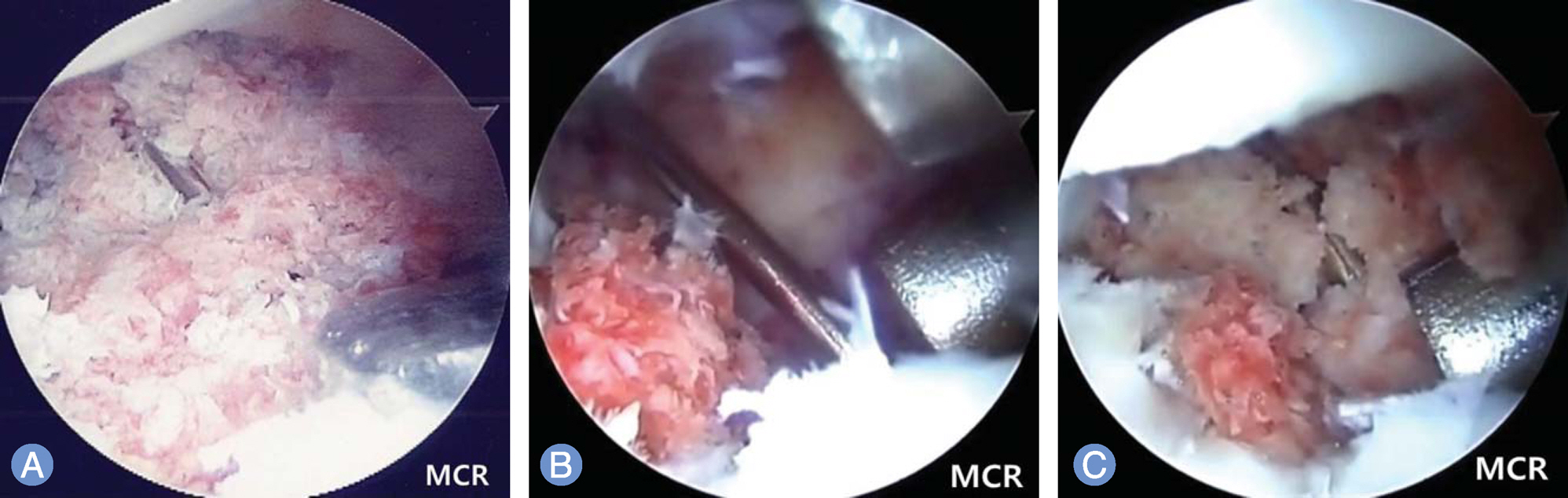
The purpose of this study was to analyze the clinical results of patients with scaphoid nonunions treated with arthroscopically assisted bone grafting and percutaneous K-wires fixation.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed 20 patients with a scaphoid nonunions which was treated with arthroscopically assisted bone grafting and percutaneous K-wires fixation from November 2008 to July 2012. Time from injury to treatment was 74 months (range, 3-480 months) in average. Functional outcome was evaluated using the modified Mayo wrist score and visual analogue scale (VAS) for pain, which were measured before operation and at the last follow up.
RESULTS
All nonunions were healed successfully. The average radiologic union time was 9.7 weeks (range, 7-14 weeks). The average VAS score improved from 6.3 (range, 4-8) preoperatively to 1.6 (range, 0-3) at the last follow up. The average modified Mayo wrist score increased from 62.5 preoperatively to 85.7 at the last follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Arthroscopically assisted bone grafting and percutaneous K-wires fixation is an effective treatment method for a scaphoid nonunion. It may provide more biological environment than open surgery as a minimally invasive procedure.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Result of Percutaneous Screw Fixation without Bone Grafting for Scaphoid Waist Nonunion under Local Anesthesia
Jung-Kwon Cha, Ji-Kang Park, Seung-Myoung Choi, Jae-Young Yang
J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2017;22(2):89-95. doi: 10.12790/jkssh.2017.22.2.89.
Reference
-
1. Christodoulou LS, Kitsis CK, Chamberlain ST. Internal fixation of scaphoid non-union: a comparative study of three methods. Injury. 2001; 32:625–30.
Article2. Schuind F, Haentjens P, Van Innis F, Vander Maren C, Garcia-Elias M, Sennwald G. Prognostic factors in the treatment of carpal scaphoid nonunions. J Hand Surg Am. 1999; 24:761–76.
Article3. Barton NJ. Experience with scaphoid grafting. J Hand Surg Br. 1997; 22:153–60.
Article4. Munk B, Larsen CF. Bone grafting the scaphoid nonunion: a systematic review of 147 publications including 5,246 cases of scaphoid nonunion. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004; 75:618–29.5. Chang MA, Bishop AT, Moran SL, Shin AY. The outcomes and complications of 1,2-intercompartmental supraretinacular artery pedicled vascularized bone grafting of scaphoid nonunions. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31:387–96.
Article6. Whipple TL. The role of arthroscopy in the treatment of intra-articular wrist fractures. Hand Clin. 1995; 11:13–8.
Article7. Taras JS, Sweet S, Shum W, Weiss LE, Bartolozzi A. Percutaneous and arthroscopic screw fixation of scaphoid fractures in the athlete. Hand Clin. 1999; 15:467–73.
Article8. Shih JT, Lee HM, Hou YT, Tan CM. Results of arthroscopic reduction and percutaneous fixation for acute displaced scaphoid fractures. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21:620–6.
Article9. Wong WY, Ho PC. Minimal invasive management of scaphoid fractures: from fresh to nonunion. Hand Clin. 2011; 27:291–307.
Article10. Lee YK, Woo SH, Ho PC. Arthroscopic bone grafting and percutaneous k-wires fixation for the treatment of scaphoid nonunion: surgical technique. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2010; 15:93–7.11. Capo JT, Orillaza NS Jr, Slade JF 3rd. Percutaneous management of scaphoid nonunions. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2009; 13:23–9.
Article12. Chu PJ, Shih JT. Arthroscopically assisted use of injectable bone graft substitutes for management of scaphoid nonunions. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:31–7.
Article13. Slade JF III, Merrell GA, Geissler WB. Fixation of acute and selected nonunion scaphoid fractures. Geissler W, editor. Wrist arthroscopy. New York, NY: Springer;2005. p. 112–24.14. Geissler WB, Freeland AE, Savoie FH, McIntyre LW, Whipple TL. Intracarpal soft-tissue lesions associated with an intra-articular fracture of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78:357–65.
Article15. Palmer AK. Triangular fibrocartilage complex lesions: a classification. J Hand Surg Am. 1989; 14:594–606.
Article16. Green DP. The effect of avascular necrosis on Russe bone grafting for scaphoid nonunion. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:597–605.
Article17. Slade JF 3rd, Dodds SD. Minimally invasive management of scaphoid nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 445:108–19.
Article18. Slade JF 3rd, Geissler WB, Gutow AP, Merrell GA. Percutaneous internal fixation of selected scaphoid nonunions with an arthroscopically assisted dorsal approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85(Suppl 4):20–32.
Article19. Zaidemberg C, Siebert JW, Angrigiani C. A new vascularized bone graft for scaphoid nonunion. J Hand Surg Am. 1991; 16:474–8.
Article20. Mathoulin C, Haerle M. Vascularized bone graft from the palmar carpal artery for treatment of scaphoid nonunion. J Hand Surg Br. 1998; 23:318–23.
Article21. Harpf C, Gabl M, Reinhart C, et al. Small free vascularized iliac crest bone grafts in reconstruction of the scaphoid bone: a retrospective study in 60 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 108:664–74.
Article22. Lim TK, Kim HK, Koh KH, Lee HI, Woo SJ, Park MJ. Treatment of avascular proximal pole scaphoid nonunions with vascularized distal radius bone grafting. J Hand Surg Am. 2013; 38:1906–12.e1.23. Kim JS, Yoon JO, Kim E, Lee CC, Kim JM. Pure cancellous chip bone graft and K-wire fixation for undisplaced scaphoid nonunion. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2008; 13:177–81.24. Robbins RR, Ridge O, Carter PR. Iliac crest bone grafting and Herbert screw fixation of nonunions of the scaphoid with avascular proximal poles. J Hand Surg Am. 1995; 20:818–31.25. Herbert TJ, Fisher WE. Management of the fractured scaphoid using a new bone screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984; 66:114–23.
Article26. Wozasek GE, Moser KD. Percutaneous screw fixation for fractures of the scaphoid. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:138–42.
Article27. Trail IA, Stanley JK. Scaphoid nonunions: predictive factors. Slutsky DJ, editor. Principles and practice of wrist surgery. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier;2010. p. 233–8.28. Gutow AP. Percutaneous fixation of scaphoid fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007; 15:474–85.
Article29. Ritter K, Giachino AA. The treatment of pseudoarthrosis of the scaphoid by bone grafting and three methods of internal fixation. Can J Surg. 2000; 43:118–24.30. Chen CY, Chao EK, Lee SS, Ueng SW. Osteosynthesis of carpal scaphoid nonunion with interpositional bone graft and Kirschner wires: a 3- to 6-year follow-up. J Trauma. 1999; 47:558–63.
Article31. Takami H, Takahashi S, Ando M. Scaphoid nonunion treated by open reduction, anterior inlay bone grafting, and Kirschner-wire fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2000; 120:134–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arthroscopic Bone Grafting and Kirschner-Wires Fixation for Scaphoid Nonunion
- Arthroscopic Bone Grafting and Percutaneous K-Wires Fixation for the Treatment of Scaphoid Nonunion: Surgical Technique
- Revision Osteosynthesis after Failed Surgery for Scaphoid Nonunion
- Operative Treatment of the Carpal Scaphoid Nonunions
- Pure Cancellous Iliac Bone grafting for the Treatment of Scaphoid Waist Nonunions with Humpback Deformity