Korean J Urol.
2012 Oct;53(10):699-704. 10.4111/kju.2012.53.10.699.
Impact of Tamsulosin on Ureter Stone Expulsion in Korean Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. drboss@snubh.org
- KMID: 1856989
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.10.699
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Using meta-analysis, the study's aim was to evaluate the efficacy of tamsulosin, an alpha-blocker, in the treatment of ureteral stones with or without shockwave lithotripsy (SWL) in Korean patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
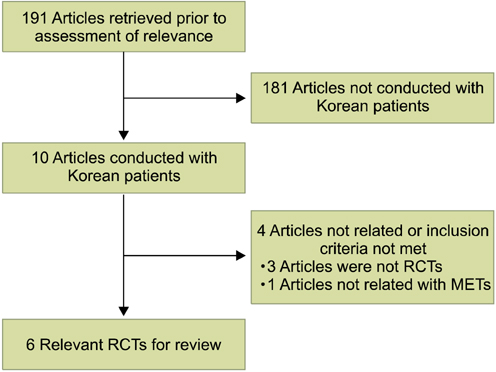
Relevant randomized controlled studies published through June 2011 were identified in a search of MEDLINE, KoreaMed, and the Korean Medical Database. No language restriction was applied. Only randomized controlled trials conducted with Korean patients were eligible for the analysis. The primary outcome assessed was the stone clearance rate. Two reviewers independently assessed the quality of the study and extracted the data. Meta-analysis was conducted by using R, version 2.13.0.
RESULTS
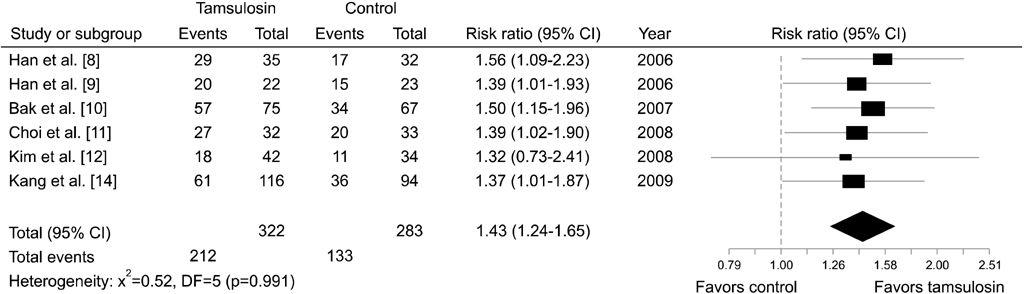
A total of 6 articles were selected as being suitable for evaluation. Pooling of the trials demonstrated a 43% higher expulsion rate for tamsulosin treatment compared to a control group (risk ratio [RR], 1.43; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.24 to 1.65). Similar results were obtained in all subgroup analyses according to stone location (upper: RR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.68, lower: RR, 1.50; 95% CI, 1.20 to 1.88) or concomitant SWL (yes: RR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.14 to 1.68, no: RR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.21 to 1.83).
CONCLUSIONS
This meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies provides a high level of evidence supporting the suggestion that treatment with tamsulosin augments the stone expulsion rate for ureter stones with or without SWL in a Korean population. However, a high-quality, large-scale, multicenter, randomized controlled trial is warranted to fully support this hypothesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ramello A, Vitale C, Marangella M. Epidemiology of nephrolithiasis. J Nephrol. 2000. 13:Suppl 3. S45–S50.2. Stamatelou KK, Francis ME, Jones CA, Nyberg LM, Curhan GC. Time trends in reported prevalence of kidney stones in the United States: 1976-1994. Kidney Int. 2003. 63:1817–1823.3. Lee HN, Yoon HN, Shim BS. The trend change of incidence and treatment of urolithiasis between the 1980s and 2000s. Korean J Urol. 2007. 48:40–44.4. Preminger GM, Tiselius HG, Assimos DG, Alken P, Buck AC, Gallucci M, et al. 2007 Guideline for the management of ureteral calculi. Eur Urol. 2007. 52:1610–1631.5. Seitz C, Liatsikos E, Porpiglia F, Tiselius HG, Zwergel U. Medical therapy to facilitate the passage of stones: what is the evidence? Eur Urol. 2009. 56:455–471.6. Singh A, Alter HJ, Littlepage A. A systematic review of medical therapy to facilitate passage of ureteral calculi. Ann Emerg Med. 2007. 50:552–563.7. Zhu Y, Duijvesz D, Rovers MM, Lock TM. alpha-Blockers to assist stone clearance after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: a meta-analysis. BJU Int. 2010. 106:256–261.8. Han MC, Park YY, Shim BS. Effect of tamsulosin on the expectant treatment of lower ureteral stones. Korean J Urol. 2006. 47:708–711.9. Han MC, Jeong WS, Shim BS. Additive expulsion effect of tamsulosin after shock wave lithotripsy for upper ureteral stones. Korean J Urol. 2006. 47:813–817.10. Bak CW, Yoon SJ, Chung H. Effects of an alpha-blocker and terpene mixture for pain control and spontaneous expulsion of Ureter Stone. Korean J Urol. 2007. 48:517–521.11. Choi NY, Ahn SH, Han JH, Jang IH. The effect of tamsulosin and nifedipine on expulsion of ureteral stones after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Korean J Urol. 2008. 49:150–154.12. Kim TH, Oh SY, Moon YT. The effect of tamsulosin on expulsion of ureteral stones after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Korean J Urol. 2008. 49:1100–1104.13. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996. 17:1–12.14. Kang DI, Cho WY, Kim TH, Chung JM, Park J, Yoon JH, et al. Effect of tamsulosin 0.2 mg on the short-term treatment of urinary stones: multicenter, prospective, randomized study. Korean J Urol. 2009. 50:586–590.15. Morita T, Ando M, Kihara K, Oshima H. Function and distribution of autonomic receptors in canine ureteral smooth muscle. Neurourol Urodyn. 1994. 13:315–321.16. Park HK, Choi EY, Jeong BC, Kim HH, Kim BK. Localizations and expressions of alpha-1A, alpha-1B and alpha-1D adrenoceptors in human ureter. Urol Res. 2007. 35:325–329.17. Cervenakov I, Fillo J, Mardiak J, Kopecny M, Smirala J, Lepies P. Speedy elimination of ureterolithiasis in lower part of ureters with the alpha 1-blocker--Tamsulosin. Int Urol Nephrol. 2002. 34:25–29.18. Sigala S, Dellabella M, Milanese G, Fornari S, Faccoli S, Palazzolo F, et al. Evidence for the presence of alpha1 adrenoceptor subtypes in the human ureter. Neurourol Urodyn. 2005. 24:142–148.19. Zheng S, Liu LR, Yuan HC, Wei Q. Tamsulosin as adjunctive treatment after shockwave lithotripsy in patients with upper urinary tract stones: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2010. 44:425–432.20. Kobayashi M, Naya Y, Kino M, Awa Y, Nagata M, Suzuki H, et al. Low dose tamsulosin for stone expulsion after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: efficacy in Japanese male patients with ureteral stone. Int J Urol. 2008. 15:495–498.21. Kaneko T, Matsushima H, Morimoto H, Tsuzaka Y, Homma Y. Efficacy of low dose tamsulosin in medical expulsive therapy for ureteral stones in Japanese male patients: a randomized controlled study. Int J Urol. 2010. 17:462–465.22. Dellabella M, Milanese G, Muzzonigro G. Medical-expulsive therapy for distal ureterolithiasis: randomized prospective study on role of corticosteroids used in combination with tamsulosin-simplified treatment regimen and health-related quality of life. Urology. 2005. 66:712–715.23. Porpiglia F, Vaccino D, Billia M, Renard J, Cracco C, Ghignone G, et al. Corticosteroids and tamsulosin in the medical expulsive therapy for symptomatic distal ureter stones: single drug or association? Eur Urol. 2006. 50:339–344.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Tamsulosin on the Expectant Treatment of Lower Ureteral Stones
- A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial of the Efficacy of Tamsulosin After Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for a Single Proximal Ureteral Stone
- Effects of an alpha-blocker and Terpene Mixture for Pain Control and Spontaneous Expulsion of Ureter Stone
- Randomized Controlled Trial to Compare the Safety and Efficacy of Naftopidil and Tamsulosin as Medical Expulsive Therapy in Combination With Prednisolone for Distal Ureteral Stones
- Comparison and Efficacy of Low-Dose and Standard-Dose Tamsulosin and Alfuzosin in Medical Expulsive Therapy for Lower Ureteral Calculi: Prospective, Randomized, Comparative Study