Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Jul;58(1):58-60. 10.4166/kjg.2011.58.1.58.
Suspected Pulmonary Involvement of Autoimmune Pancreatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sensass@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1792817
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.58.1.58
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Autoimmune Diseases/*diagnosis/drug therapy/immunology
Azathioprine/therapeutic use
Common Bile Duct/pathology
Emphysema
Fibrosis
Humans
Immunoglobulin G/blood
Immunosuppressive Agents/therapeutic use
Lung/*radiography
Male
Middle Aged
Pancreatitis/*diagnosis/drug therapy/immunology
Stents
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
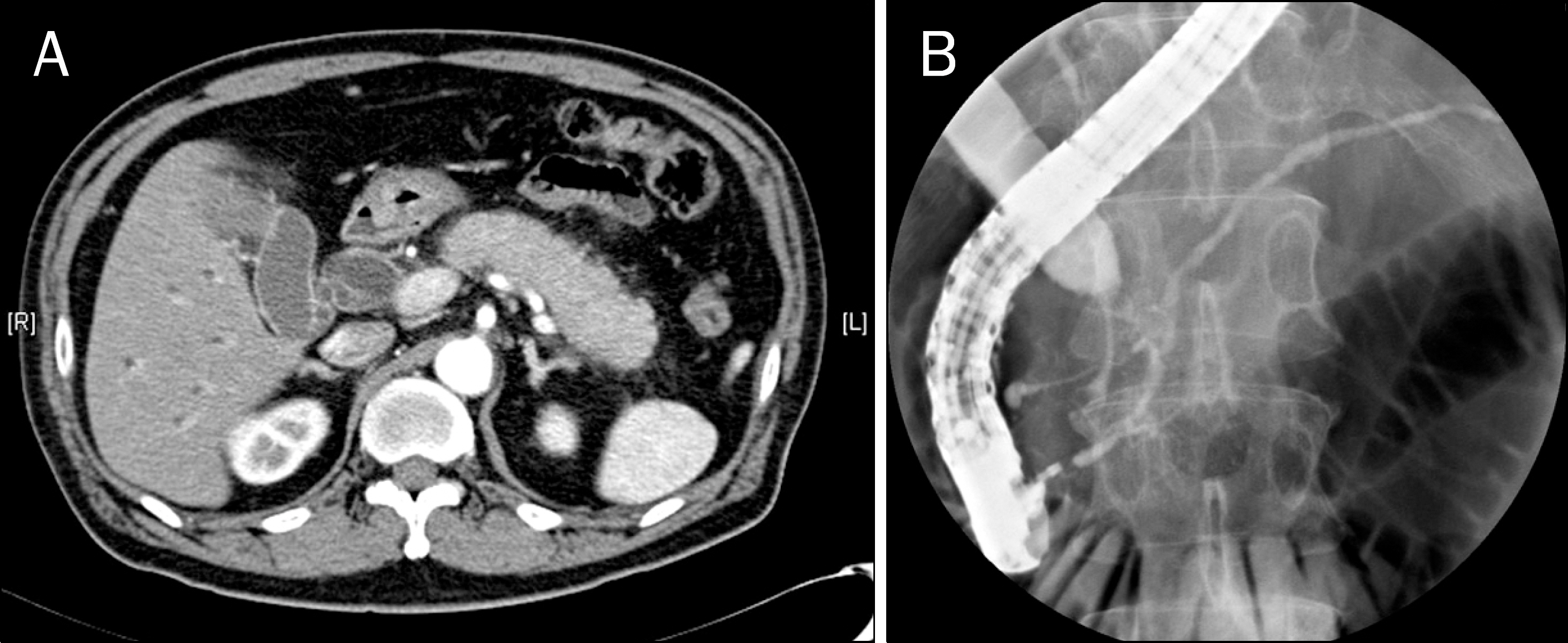
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738.
Article2. Hamano H, Kawa S, Ochi Y, et al. Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet. 2002; 359:1403–1404.3. Kim KP, Kim MH, Song MH, Lee SS, Seo DW, Lee SK. Autoimmune chronic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:1605–1616.
Article4. Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, Watanabe S, Shiratori K, Hayashi N. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995; 40:1561–1568.5. Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with and without hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor, and sclerosing pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis: do they belong to a spectrum of sclerosing pancreatitis? Am J Surg Pathol. 2004; 28:1193–1203.6. Taniguchi T, Ko M, Seko S, et al. Interstitial pneumonia associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2004; 53:770.7. Tsushima K, Tanabe T, Yamamoto H, et al. Pulmonary involvement of autoimmune pancreatitis. Eur J Clin Invest. 2009; 39:714–722.
Article8. Yoo JW, Roh JH, Lim CM, et al. Two cases of pulmonary involvement of immunoglobulin G4 related autoimmune disease. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2009; 67:359–363.
Article9. Sandanayake NS, Church NI, Chapman MH, et al. Presentation and management of post-treatment relapse in autoimmune pancreatitis/immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 7:1089–1096.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastric Involvement in Autoimmune Pancreatitis
- A Case of Pancreatitis associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case of Systemic Amyloidosis with Pancreatic Involvement Mimicking Autoimmune Pancreatitis
- A Case of Autoimmune Pancreatitis Combined with Extensive Involvement of Biliary Tract
- A Case of Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Eosinophilic Infiltration that Demonstrated Multiple Masses on Endoscopic Ultrasonography