Clin Endosc.
2013 Jan;46(1):91-94. 10.5946/ce.2013.46.1.91.
A Case of Spontaneous Esophagopleural Fistula Successfully Treated by Endoscopic Stent Insertion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. mhs1357@cnuh.co.kr
- KMID: 1792647
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.1.91
Abstract
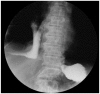
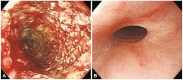
- The most common cause of esophagorespiratory fistulas (ERFs) is associated with malignancy. The use of self-expandable metal stents is effective for the treatment of malignant ERFs, but benign ERF is rare, which is why its optimal treatment is not defined yet. There have been few reports describing benign esophagopleural fistula and its treatments in South Korea. Here, we report a rare case of spontaneous esophagopleural fistula, which was successfully treated by endoscopic placement of a membrane covered metal stent.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shin JH, Song HY, Ko GY, Lim JO, Yoon HK, Sung KB. Esophagorespiratory fistula: long-term results of palliative treatment with covered expandable metallic stents in 61 patients. Radiology. 2004; 232:252–259. PMID: 15166325.
Article2. Wychulis AR, Ellis FH Jr, Andersen HA. Acquired nonmalignant esophagotracheobronchial fistula: report of 36 cases. JAMA. 1966; 196:117–122. PMID: 5952106.
Article3. Duranceau A, Jamieson GG. Malignant tracheoesophageal fistula. Ann Thorac Surg. 1984; 37:346–354. PMID: 6201144.
Article4. Angorn IB. Intubation in the treatment of carcinoma of the esophagus. World J Surg. 1981; 5:535–541. PMID: 6172904.
Article5. Kim KR, Shin JH, Song HY, et al. Palliative treatment of malignant esophagopulmonary fistulas with covered expandable metallic stents. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:W278–W282. PMID: 19770295.
Article6. Coleman FP. Acquired non-malignant esophagorespiratory fistula. Am J Surg. 1957; 93:321–328. PMID: 13394811.
Article7. Wesselhoeft CW Jr, Keshishian JM. Acquired nonmalignant esophagotracheal and esophagobronchial fistulas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1968; 6:187–195. PMID: 4918289.
Article8. Spalding AR, Burney DP, Richie RE. Acquired benign bronchoesophageal fistulas in the adult. Ann Thorac Surg. 1979; 28:378–383. PMID: 507984.
Article9. Vandenplas Y, Helven R, Derop H, et al. Endoscopic obliteration of recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula. Dig Dis Sci. 1993; 38:374–377. PMID: 8425452.
Article10. Lopes MF, Pires J, Nogueria Brandão A, Reis A, Morais Leitão L. Endoscopic obliteration of a recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula with enbucrilate and polidocanol in a child. Surg Endosc. 2003; 17:657. PMID: 12582778.
Article11. Truong S, Böhm G, Klinge U, Stumpf M, Schumpelick V. Results after endoscopic treatment of postoperative upper gastrointestinal fistulas and leaks using combined Vicryl plug and fibrin glue. Surg Endosc. 2004; 18:1105–1108. PMID: 15156390.
Article12. van Bodegraven AA, Kuipers EJ, Bonenkamp HJ, Meuwissen SG. Esophagopleural fistula treated endoscopically with argon beam electrocoagulation and clips. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 50:407–409. PMID: 10462666.
Article13. Raymer GS, Sadana A, Campbell DB, Rowe WA. Endoscopic clip application as an adjunct to closure of mature esophageal perforation with fistulae. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 1:44–50. PMID: 15017516.
Article14. Adler DG, McAfee M, Gostout CJ. Closure of an esophagopleural fistula by using fistula tract coagulation and an endoscopic suturing device. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54:652–653. PMID: 11677492.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Esophageal Stent in Postpneumonectomy Esophagopleural Fistula
- A Case of Esophagopleural Fistula Treated by Endoscopic Injection of Histoacryl in Boerhaave's Syndrome
- Double Bypass of Esophagus and Descending Thoracic Aorta for the Treatment of Esophagopleural and Aortopleural Fistula
- A Case of Ureteral Fistula through the Intervertebral Space
- A Case of Esophageal Perforation Cured by Conservative Management after Stent Insertion