Korean J Lab Med.
2007 Jun;27(3):210-215. 10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.3.210.
Evaluation of the OC-SENSOR neo System for Testing Fecal Occult Blood
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. mnkim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1781486
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.3.210
Abstract
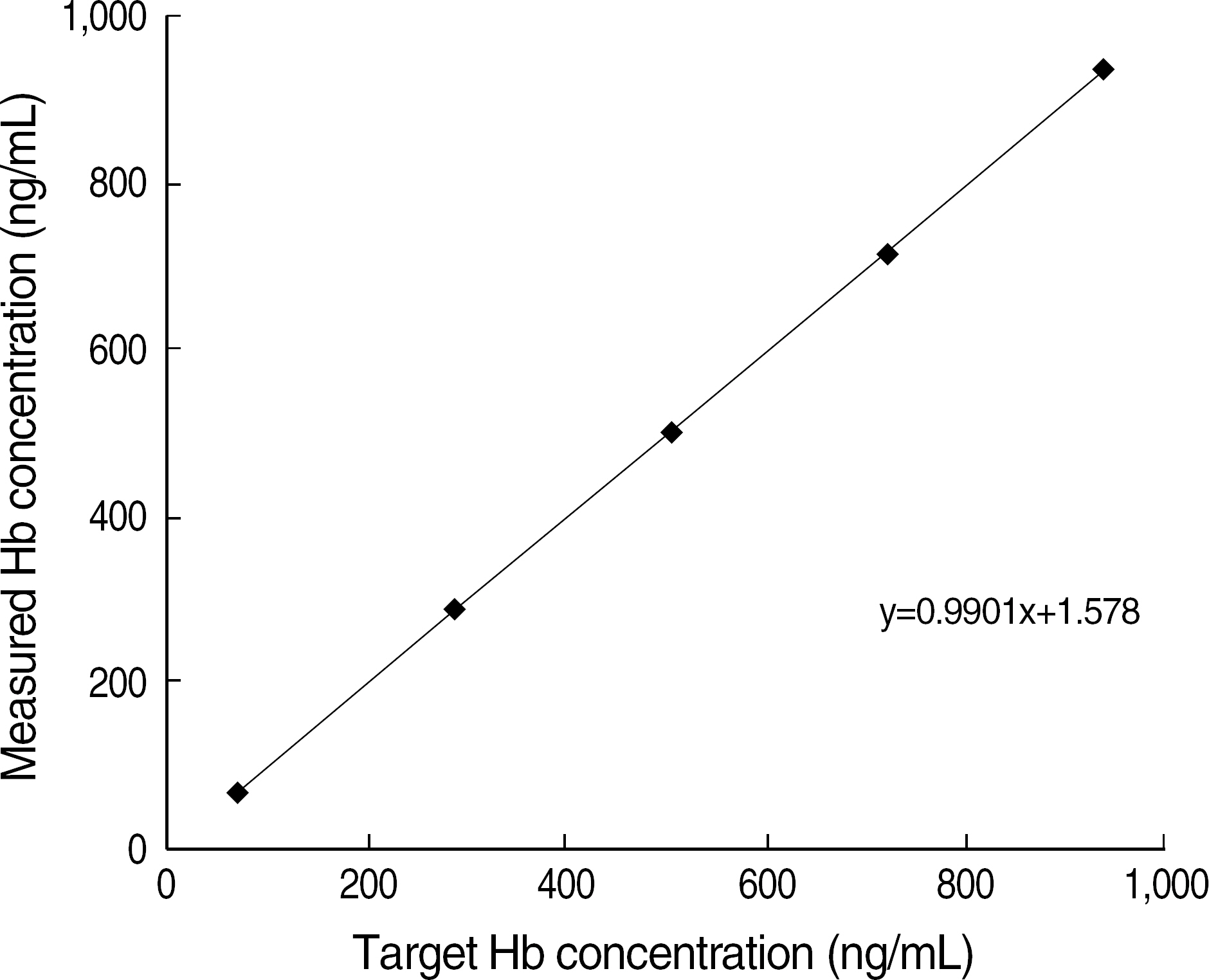
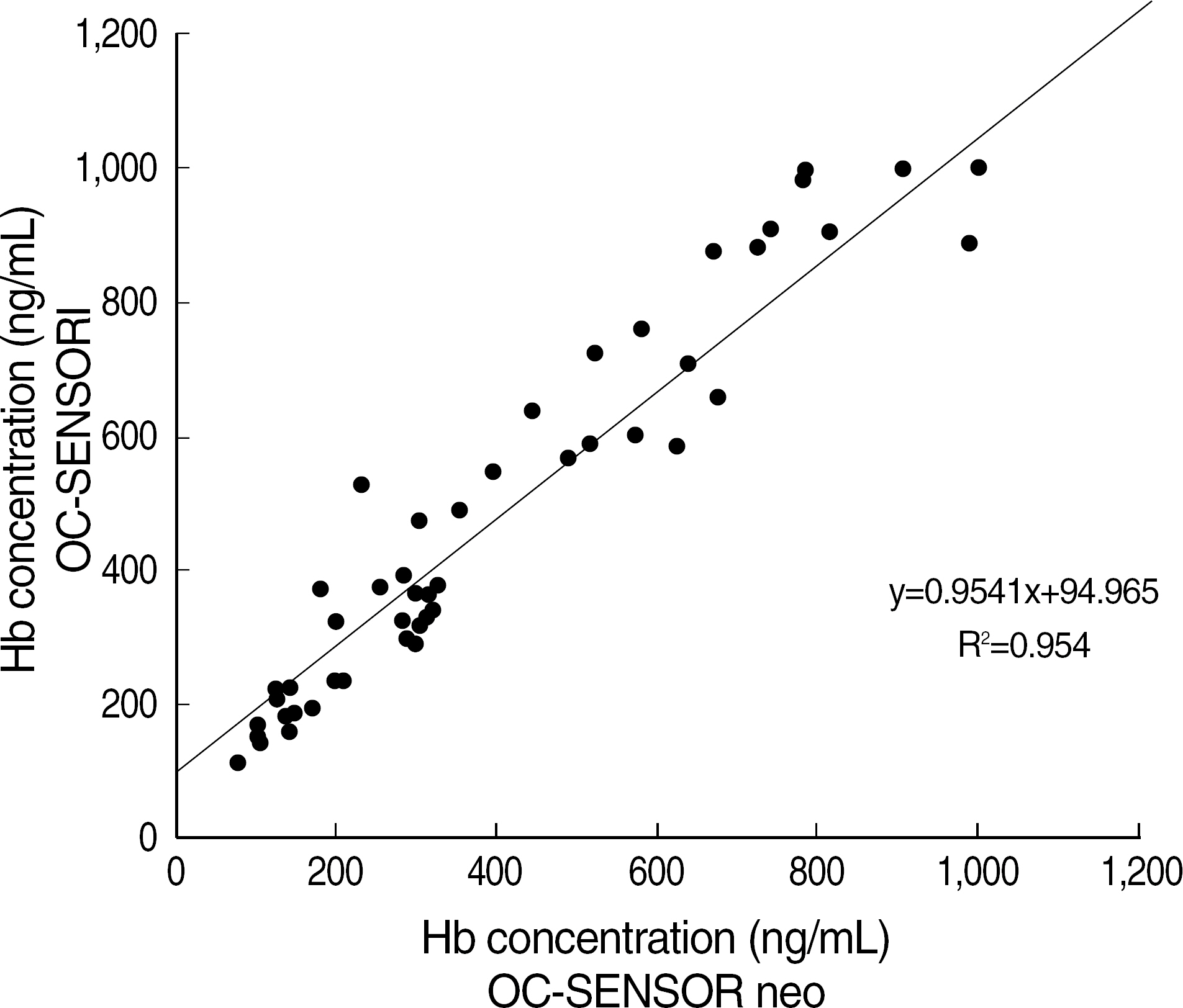
- BACKGROUND: Fecal occult blood tests (FOBTs) have been widely used as a means of colorectal cancer screening. Automated FOBTs using immunologic principles have the advantages such as quantitation, high specificity, and high throughput. We evaluated a newly-introduced automated FOBT analyzer, OC-SENSOR neo (OC neo) (Eiken Chemical Co., Japan). METHODS: The precision, linearity, and carry-over rate of OC neo were assessed with specimens prepared in accordance with the guidelines of CLSI. We performed a parallel test between OC neo and OC-SENSOR I (OC I) (Eiken Chemical Co.) using 300 consecutive stool specimens and 60 OC I-positive specimens. The results were analyzed with SPSS version 13.0 (SPSS Inc., USA). RESULTS: The coefficients of variation (CV) of within-run, between-run, and between-day using OCControl L (Eiken Chemical Co.) of ca. 150 ng/mL were 3.5-7.8%, 4.5-8.8% and 4.9-5.0%, respectively. The linear regression coefficient and carry-over rate with the range of 67.8-939.4 ng/mL were 0.9998 (P<0.001), and 0.1%, respectively. Correlation coefficient between OC neo and OC I was R(2)=0.954 (P<0.001) for 60 OC I-positive specimens. The positive and negative interpretations of 300 consecutive specimens by OC neo were completely consistent with those of OC I. CONCLUSIONS: Because OC neo showed an excellent performance and a good correlation with OC I, OC neo warrants to be a reliable quantitative FOBT system for high volume laboratories.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Performance Evaluation of SENTiFIT 270 and FOB Gold Reagent for Detecting Fecal Occult Blood
Da Young Kang, Dokyun Kim, Keonhan Kim, In-Ho Jang, Seok Hoon Jeong
Ann Clin Microbiol. 2019;22(2):29-34. doi: 10.5145/ACM.2019.22.2.29.Performance Evaluation of Two Automated Quantitative Fecal Occult Blood Tests
Ari Ahn, Jeongeun Kim, Young Jin Ko, Heungsup Sung, Mi-Na Kim
Lab Med Online. 2016;6(4):233-239. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2016.6.4.233.
Reference
-
References
1. Kim DW, Bang YJ, Heo DS, Kim NK. Colorectal cancer in Korea: characteristics and trends. Tumori. 2002; 88:262–5.
Article2. Helm J, Choi J, Sutphen R, Barthel JS, Albrecht TL, Chirikos TN. Current and evolving strategies for colorectal cancer screening. Cancer Control. 2003; 10:193–204.
Article3. Anwar R. Screening for colorectal cancer in the UK. Dig Liver Dis. 2006; 38:279–82.
Article4. Bromer MQ, Weinberg DS. Screening for colorectal cancer-now and the near future. Semin Oncol. 2005; 32:3–10.
Article5. Winawer SJ, Fletcher RH, Miller L, Godlee F, Stolar MH, Mulrow CD, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: clinical guidelines and rationale. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:594–642.
Article6. Suggested technique for fecal occult blood testing and interpretation in colorectal cancer screening. American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 1997; 126:808–10.7. Mandel JS, Bond JH, Church TR, Snover DC, Bradley GM, Schuman LM, et al. Reducing mortality from colorectal cancer by screening for fecal occult blood. Minnesota Colon Cancer Control Study. N Engl J Med. 1993; 328:1365–71.8. Hardcastle JD, Chamberlain JO, Robinson MH, Moss SM, Amar SS, Balfour TW, et al. Randomised controlled trial of faecal-occult-blood screening for colorectal cancer. Lancet. 1996; 348:1472–7.
Article9. Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, Jorgensen OD, Sondergaard O. Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet. 1996; 348:1467–71.
Article10. Mandel JS, Church TR, Bond JH, Ederer F, Geisser MS, Mongin SJ, et al. The effect of fecal occult-blood screening on the incidence of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:1603–7.
Article11. Steinmetz J, Spyckerelle Y, Gueguen R, Dupre C. Colorectal cancer screening in Health Examination Centers. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2006; 30:832–7.
Article12. Walsh JM, Terdiman JP. Colorectal cancer screening: scientific review. JAMA. 2003; 289:1288–96.13. Levin B. Screening for Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Control. 1996; 3:20–5.
Article14. Han WS, Choi YM, Lee DH. Comparison of guaiac method with latex method for the fecal occult blood test. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1996; 16:318–23.15. Vilkin A, Rozen P, Levi Z, Waked A, Maoz E, Birkenfeld S, et al. Performance characteristics and evaluation of an automated-developed and quantitative, immunochemical, fecal occult blood screening test. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:2519–25.
Article16. Horiuchi Y, Masubuchi J, Oikawa S, Matsuda R, Hishinuma A, Ieiri T. Evaluation of fully automated fecal occult blood analyzer OC-SENSOR neo and OC-SENSOR II. Jap Assoc Clin Lab Auto. 2003; 28:40–6.17. Touzuka S, Aoyama K, Kamino T. Fundamental study on fully automated fecal occult blood immunochemical analyzer, OC-SENSOR neo. Med Exam Equip-Reag. 2002; 25:121–5.18. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures; A statistical approach; Approved guideline. Document EP6-A. Vilanova, PA: National Commitee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2003.19. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; Approved guideline-Second edition. Document EP5-A2.Vilanova, PA: National Commitee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2004.20. Pesce MA. Laboratory antomation. In. Kaplan LA, Pesce AJ, editors. Clinical Chemistry. 4th ed.Baltimore: Mosby;2003. :294.21. Hong SB, Kim HS, Park HS, Lee DH. Evaluation of the HM-JACK Automatic Analyzer for Fecal Occult Blood Test. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2002; 24:221–4.22. Kim DC, Cho SS, Song J, Kim EC, Kim JQ. Evaluation of the OC-SENSOR for Immunological Fecal Occult Blood Test. Korean J Clin Pathol Qual Control. 1998; 20:281–8.23. Imperiale TF. Quantitative immunochemical fecal occult blood tests: is it time to go back to the future? Ann Intern Med. 2007; 146:309–11.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the OC-SENSOR (Automatic Measuring Apparatus) for Immunological Fecal Occult Blood Test
- Evaluation of the Ez step FOBTM for Fecal Occult Blood Test
- Performance Evaluation of the HM-JACKarc Analyser for Fecal Occult Blood Test
- Performance Evaluation of Two Automated Quantitative Fecal Occult Blood Tests
- Evaluation of the HM-JACK Automatic Analyzer for Fecal Occult Blood Test