J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Jun;21(3):425-429. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.425.
Polycystin-1 Expression in Fetal, Adult and Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leekyubeck@yahoo.co.kr
- 4Graduate School of Biotechnology, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Biology, College of Natural Sciences, Kyungpook National University, Deagu, Korea.
- KMID: 1778422
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.425
Abstract
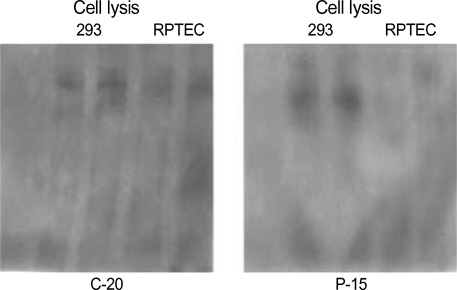
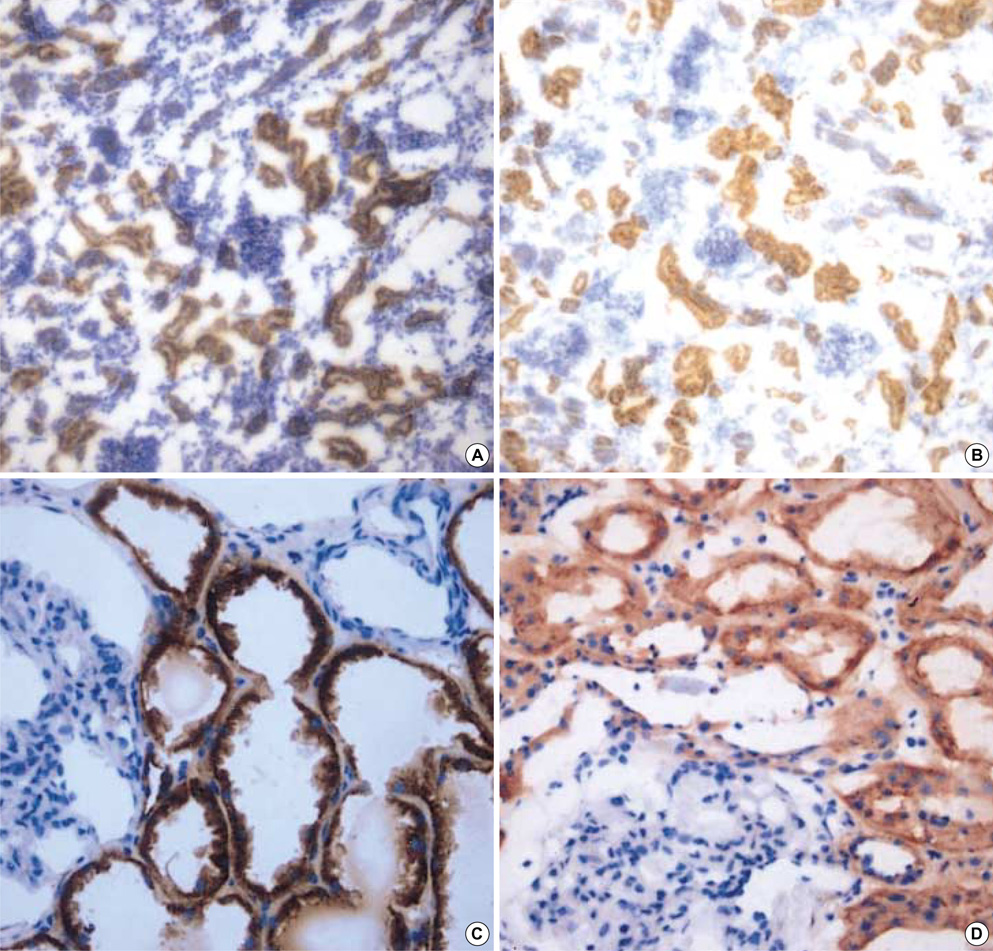
- The mutation of the PKD1 gene causes autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), and the PKD1 gene encodes polycystin-1 (PC-1). PC-1 is thought to be a cell-cell/matrix adhesion receptor molecule at the cell surface that is widely expressed in the kidney. However, there are controversies about the role of PC-1 protein and its expression when using different antibodies to detect it. We used two PC-1 antibodies; C-20 (Santa Cruz, sc-10372) as the C-terminal antibody, and P-15 (Santa Cruz, sc-10307) as the N-terminal antibody. We evaluated the PC-1 expression by performing immunoblotting on the human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells and the renal proximal tubular epithelial cell (RPTEC) lysates. We characterized the expression of PC-1 in the fetal, adult and polycystic kidneys tissues by performing immunohistochemistry. We confirmed the PC-1 expression in the HEK 293 cells and the RPTEC lysates, but the expression was very low. The PC-1 proteins were diffusely expressed in the tubular epithelial cells cytoplasm in the fetal and adult kidneys, and the PC-1 expression was more prominent in the proximal tubules of the fetal kidney. In the ADPKD kidney, the PC-1 proteins were heterogenously and weakly expressed in the tubular or cyst lining epithelial cells. Our data suggests that the development of the kidney may regulate the expression of PC-1, and an altered PC-1 expression may contribute to cyst formation in ADPKD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gabow PA. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:332–342.
Article2. The European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell. 1994. 77:881–894.3. Mochizuki T, Wu G, Hayashi T, Xenophontos SL, Veldhuisen B, Saris JJ, Raynolds DM, Cai Y, Gabow PA, Pierides A, Kimberling WJ, Breuning MH, Deltas CC, Peters DJ, Somlo S. PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes an integral membrane protein. Science. 1996. 272:1339–1342.
Article4. Hughes J, Ward CJ, Peral B, Aspinwall R, Clark K, San Millan JL, Gamble V, Harris PC. PKD1 gene encodes a novel protein with multiple cell recognition domains. Nature Gent. 1995. 10:151–160.5. The International Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. Polycystic kidney disease: The complete structure of the PKD1 gene and its protein. Cell. 1995. 81:289–298.6. Hanaoka K, Qian F, Boletta A, Bhunia AK, Piontek K, Tiokas L, Sukhatme VP, Guggino WB, Germino GG. Co-assembly of polycystin-1 and -2 produces unique cation-permeable currents. Nature. 2000. 408:990–994.
Article7. Newby LJ, Streets AJ, Zhao Y, Harris PC, Ward CJ, Ong AC. Identification, characterization, and localization of a novel kidney polycystin-1-polycystin-2 complex. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:20763–20773.
Article8. Nauta J, Goedbloed MA, van den Ouweland AM, Nellist M, Hoogeveen AT. Immunological detection of polycystin-1 in human kidney. Histochem Cell Biol. 2000. 113:303–311.
Article9. Ong AC. Polycystin expression in the kidney and other tissues: Complexity, consensus and controversy. Exp Nephrol. 2000. 8:208–214.
Article10. Kim H, Bae Y, Jeong W, Ahn C, Kang S. Depletion of PKD1 by an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide induces premature G1/s-phase transition. Eur J Hum Genet. 2003. 12:433–440.
Article11. Van Adelsberg J, Chamberlain S, D'Agati V. Polycystin expression is temporally spatially regulated during renal development. Am J Physiol. 1997. 272:602–609.12. Geng L, Segal Y, Peissel B, Deng N, Pei Y, Carone F, Rennke HG, Glucksmann-Kuis AM, Schneider MC, Ericsson M, Reeders ST, Zhou J. Identification and localization of polycystin, the PKD1 gene product. J Clin Invest. 1996. 98:2674–2682.
Article13. Geng L, Segal Y, Pavlova A, Barros EJ, Lohning C, Lu W, Nigam SK, Frischauf AM, Reeders ST, Zhou J. Distribution and developmentally regulated expression of murine polycystin. Am J Physiol. 1997. 272:451–459.
Article14. Ong AC, Harris PC, Davies DR, Pritchard L, Rossetti S, Biddolph S, Vaux DJ, Migone N, Ward CJ. Polycystin-1 expression in PKD1, early onset PKD1 and TSC2/PKD1 cystic tissue. Kidney Int. 1999. 56:1324–1333.15. Leeuwen IS, Dauwerse JG, Baelde HJ, Leonhard WN, Wal A, Ward CJ, Verbeek S, DeRuiter MC, Breunig MH, Heer E, Peters DJM. Lowering of Pkd1 expression is sufficient to cause polycystic kidney disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2004. 13:3069–3077.
Article16. Roitbak T, Ward CJ, Harris PC, Bacallao R, Ness SA, Ness AW. A polycystin-1 multiprotein complex is disrupted in polycystic kidney disease cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. 15:1334–1346.
Article17. Yoder BK, Hou X, Guay-Woodford LM. The polycystic kidney disease proteins, polycystin-1, polycystin-2, polaris, and cystin, are colocalized in renal cilia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002. 13:2508–2516.
Article18. Nauli SM, Alenghat FJ, Luo Y, Williams E, Vassilev P, Li X, Elia AE, Lu W, Brown EM, Quinn SJ, Ingber DE, Zhou J. Polycystins 1 and 2 mediate mechanosensation in the primary cilium of kidney cells. Nature Genetics. 2003. 33:129–137.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cyst growth, polycystins, and primary cilia in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- A Case of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Hemodialyzed
- A Case of Transitional Cell Carcinoma Associated with Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Pathogenesis and New Treatment of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Prenatal Diagnosis of a Fatal Case of Fetal Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease