Yonsei Med J.
2013 Jan;54(1):220-224. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.220.
Change in Electromyographic Activity of Wrist Extensor by Cylindrical Brace
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. acebhs@gmail.com
- KMID: 1776942
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.220
Abstract
- PURPOSE
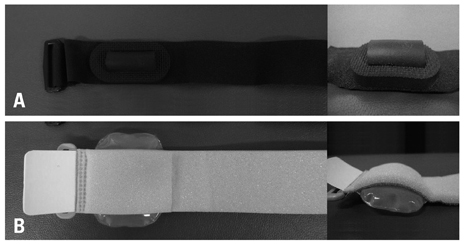
To verify the effect of a newly-developed cylindrical type forearm brace, which was designed to give focal counterforce perpendicularly on the muscle belly of the wrist extensor.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
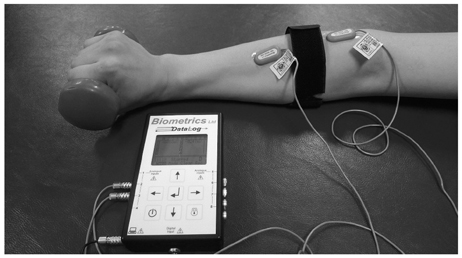
The dominant hands of 24 (12 males, 12 females) healthy subjects were tested. Two types of forearm braces (focal cylindrical type and broad pneumatic type) were examined. The braces were applied at the extensor carpi radialis brevis, 5 to 7 cm distal to the lateral epicondyle. Two surface electrodes were attached to the proximal and distal parts of the brace. By quantitative electromyography, the mean amplitudes of voluntary extensor carpi radialis brevis contraction before and after applying each brace were recorded and analyzed.
RESULTS
The mean amplitudes of the focal cylindrical brace and broad pneumatic brace were reduced significantly compared to no brace (p<0.05), with a larger reduction for the cylindrical brace than the pneumatic brace (p<0.05). There was no significant difference between the proximal and distal mean amplitudes with each brace.
CONCLUSION
A cylindrical type brace decreased electromyographic activity in the wrist extensor more effectively than did the pneumatic type brace.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Faro F, Wolf JM. Lateral epicondylitis: review and current concepts. J Hand Surg Am. 2007. 32:1271–1279.
Article2. Jobe FW, Ciccotti MG. Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis of the Elbow. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1994. 2:1–8.
Article3. Regan W, Wold LE, Coonrad R, Morrey BF. Microscopic histopathology of chronic refractory lateral epicondylitis. Am J Sports Med. 1992. 20:746–749.
Article4. Nirschl RP, Ashman ES. Elbow tendinopathy: tennis elbow. Clin Sports Med. 2003. 22:813–836.
Article5. Bales CP, Placzek JD, Malone KJ, Vaupel Z, Arnoczky SP. Microvascular supply of the lateral epicondyle and common extensor origin. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007. 16:497–501.
Article6. Alfredson H, Ljung BO, Thorsen K, Lorentzon R. In vivo investigation of ECRB tendons with microdialysis technique--no signs of inflammation but high amounts of glutamate in tennis elbow. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000. 71:475–479.
Article7. Galliani I, Burattini S, Mariani AR, Riccio M, Cassiani G, Falcieri E. Morpho-functional changes in human tendon tissue. Eur J Histochem. 2002. 46:3–12.
Article8. Kalichman L, Bannuru RR, Severin M, Harvey W. Injection of botulinum toxin for treatment of chronic lateral epicondylitis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 40:532–538.
Article9. Bisset L, Paungmali A, Vicenzino B, Beller E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials on physical interventions for lateral epicondylalgia. Br J Sports Med. 2005. 39:411–422.
Article10. Meyer NJ, Pennington W, Haines B, Daley R. The effect of the forearm support band on forces at the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis: a cadaveric study and review of literature. J Hand Ther. 2002. 15:179–184.
Article11. Assendelft WJ, Hay EM, Adshead R, Bouter LM. Corticosteroid injections for lateral epicondylitis: a systematic overview. Br J Gen Pract. 1996. 46:209–216.12. Sölveborn SA, Buch F, Mallmin H, Adalberth G. Cortisone injection with anesthetic additives for radial epicondylalgia (tennis elbow). Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. (316):99–105.
Article13. Price R, Sinclair H, Heinrich I, Gibson T. Local injection treatment of tennis elbow--hydrocortisone, triamcinolone and lignocaine compared. Br J Rheumatol. 1991. 30:39–44.
Article14. Stonecipher DR, Catlin PA. The effect of a forearm strap on wrist-extensor strength*. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1984. 6:184–189.
Article15. Wadsworth C, Nielsen DH, Burns LT, Krull JD, Thompson CG. Effect of the counterforce armband on wrist extension and grip strength and pain in subjects with tennis elbow. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1989. 11:192–197.
Article16. Anderson MA, Rutt RA. The effects of counterforce bracing on forearm and wrist muscle function. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1992. 15:87–91.
Article17. Luginbühl R, Brunner F, Schneeberger AG. No effect of forearm band and extensor strengthening exercises for the treatment of tennis elbow: a prospective randomised study. Chir Organi Mov. 2008. 91:35–40.
Article18. Chan HL, Ng GY. Effect of counterforce forearm bracing on wrist extensor muscles performance. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2003. 82:290–295.
Article19. Cyriax JH. The pathology and treatment of tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg. 1936. 18:921–940.20. Verhaar J, Walenkamp G, Kester A, van Mameren H, van der Linden T. Lateral extensor release for tennis elbow. A prospective long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993. 75:1034–1043.
Article21. Rayan GM, Coray SA. V-Y slide of the common extensor origin for lateral elbow tendonopathy. J Hand Surg Am. 2001. 26:1138–1145.
Article22. Das D, Maffulli N. Surgical management of tennis elbow. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2002. 42:190–197.23. Tasto JP, Cummings J, Medlock V, Hardesty R, Amiel D. Microtenotomy using a radiofrequency probe to treat lateral epicondylitis. Arthroscopy. 2005. 21:851–860.
Article24. Ng GY, Chan HL. The immediate effects of tension of counterforce forearm brace on neuromuscular performance of wrist extensor muscles in subjects with lateral humeral epicondylosis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2004. 34:72–78.
Article25. Groppel JL, Nirschl RP. A mechanical and electromyographical analysis of the effects of various joint counterforce braces on the tennis player. Am J Sports Med. 1986. 14:195–200.
Article26. Faes M, van Elk N, de Lint JA, Degens H, Kooloos JG, Hopman MT. A dynamic extensor brace reduces electromyographic activity of wrist extensor muscles in patients with lateral epicondylalgia. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006. 36:170–178.
Article27. Jansen CW, Olson SL, Hasson SM. The effect of use of a wrist orthosis during functional activities on surface electromyography of the wrist extensors in normal subjects. J Hand Ther. 1997. 10:283–289.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous Rupture of 3rd, 4th, and 5th Extensor Digitorum Tendons in an Amateur Golfer: A Case Report
- The Changes of Electromyographic Activity of Upper Extremity and Physiologic Cost Index According to Forward and Reverse Wheelchair Propulsion Methods
- Extensor Digitorum Brevis Manus
- Calcific Tendinitis of the Common Extensor Tendon: A Case Report
- Intratendinous Ganglion: A Case Report