Korean J Gastroenterol.
2012 Oct;60(4):253-257. 10.4166/kjg.2012.60.4.253.
Massive Life-threatening Lower Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage Caused by an Internal Hemorrhoid in a Patient Receiving Antiplatelet Therapy: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. songhj@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 1775810
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2012.60.4.253
Abstract
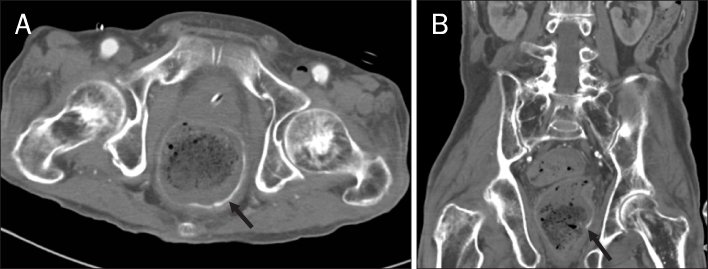
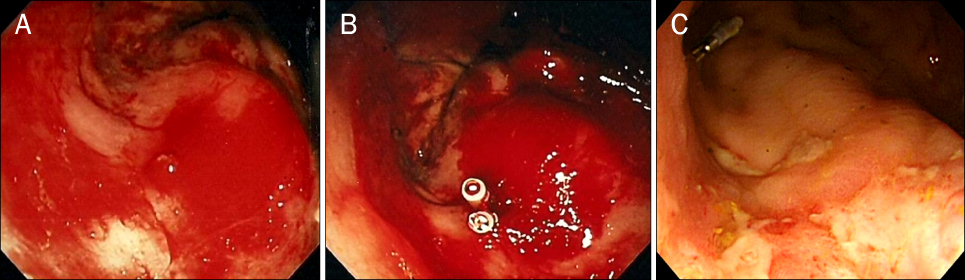
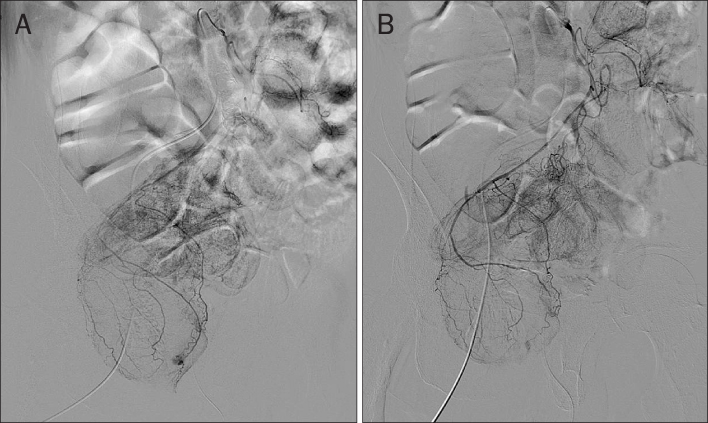
- A Dieulafoy lesion in the rectum is a very rare and it can cause massive lower gastrointestinal bleeding. An 83-year-old man visited our hospital. He had chronic constipation and had taken aspirin for about 10 years because of a previous brain infarction. He was admitted because of a recent brain stroke. On the third hospital day, he had massive hematochezia and suddenly developed hypovolemic shock. Abdominal computed tomography showed active arterial bleeding on the left side of the mid-rectum. Emergency sigmoidoscopy showed an exposed vessel with blood spurting from the rectal wall. The active bleeding was controlled successfully by an injection of epinephrine and two hemoclippings. On the fourth day after the procedure, he had massive recurrent hematochezia, and his vital signs were unstable. Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery band ligation was performed urgently at two sites. However, he rebled on the third postoperative day. Selective inferior mesenteric angiography revealed an arterial pseudoaneurysm in a branch of the superior rectal artery, as the cause of rectal bleeding, and this was embolized successfully. We report a rare case of life-threatening rectal bleeding caused by a Dieulafoy lesion combined with pseudoaneurysm of the superior rectal artery which was treated successfully with embolization.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged, 80 and over
Aneurysm/radiography
Angiography
Aspirin/therapeutic use
Brain Infarction/drug therapy/prevention & control
Embolization, Therapeutic
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage/*diagnosis/etiology/therapy
Hemorrhoids/*complications
Humans
Male
Mesenteric Artery, Inferior/radiography
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors/therapeutic use
Rectal Diseases/complications/diagnosis/therapy
Rectum/blood supply
Sigmoidoscopy
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee EW, Laberge JM. Differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004. 7:112–122.2. Syed MI, Chaudhry N, Shaikh A, Morar K, Mukerjee K, Damallie E. Catheter-directed middle hemorrhoidal artery embolization for life-threatening rectal bleeding. Can J Gastroenterol. 2007. 21:117–123.3. Ruiz-Tovar J, Díe-Trill J, López-Quindós P, Rey A, López-Hervás P, Devesa JM. Massive low gastrointestinal bleeding due to a Dieulafoy rectal lesion. Colorectal Dis. 2008. 10:624–625.4. Baig MK, Lewis M, Stebbing JF, Marks CG. Multiple microaneurysms of the superior hemorrhoidal artery: unusual recurrent massive rectal bleeding: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003. 46:978–980.5. Chang WC, Liu CH, Hsu HH, et al. Intra-arterial treatment in patients with acute massive gastrointestinal bleeding after endoscopic failure: comparisons between positive versus negative contrast extravasation groups. Korean J Radiol. 2011. 12:568–578.6. Hokama A, Takeshima Y, Toyoda A, et al. Images of interest. Gastrointestinal: rectal Dieulafoy lesion. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005. 20:1303.7. Sueyoshi E, Sakamoto I, Nakashima K, Minami K, Hayashi K. Visceral and peripheral arterial pseudoaneurysms. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 185:741–749.8. Gupta V, Kumar S, Kumar P, Chandra A. Giant pseudoaneurysm of the splenic artery. JOP. 2011. 12:190–193.9. Ozdil B, Akkiz H, Sandikci M, Kece C, Cosar A. Massive lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage secondary to rectal hemorrhoids in elderly patients receiving anticoagulant therapy: case series. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. 55:2693–2694.10. Whitlow CB. Endoscopic treatment for lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2010. 23:31–36.11. Nelson RS, Ewing BM, Ternent C, Shashidharan M, Blatchford GJ, Thorson AG. Risk of late bleeding following hemorrhoidal banding in patients on antithrombotic prophylaxis. Am J Surg. 2008. 196:994–999.12. Van Rosendaal GM, Sutherland LR, Verhoef MJ, et al. Defining the role of fiberoptic sigmoidoscopy in the investigation of patients presenting with bright red rectal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000. 95:1184–1187.13. Jang JW, Chae HS, Shin JH, et al. A case of rectal bleeding treated by endoscopic band ligation. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2001. 22:229–232.14. Lee KW, Chae HS, Park YB, et al. A case of rectal varix bleeding treated with endoscopic variceal ligation. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2003. 26:52–55.15. Yoshikumi Y, Mashima H, Suzuki J, et al. A case of rectal Dieulafoy's ulcer and successful endoscopic band ligation. Can J Gastroenterol. 2006. 20:287–290.16. Odelowo OO, Mekasha G, Johnson MA. Massive life-threatening lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage following hemorrhoidal rubber band ligation. J Natl Med Assoc. 2002. 94:1089–1092.17. Bat L, Melzer E, Koler M, Dreznick Z, Shemesh E. Complications of rubber band ligation of symptomatic internal hemorrhoids. Dis Colon Rectum. 1993. 36:287–290.18. Guy GE, Shetty PC, Sharma RP, Burke MW, Burke TH. Acute lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: treatment by superselective embolization with polyvinyl alcohol particles. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992. 159:521–526.19. Berczi V, Gopalan D, Cleveland TJ. Embolization of a hemorrhoid following 18 hours of life-threatening bleeding. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008. 31:183–185.20. Nomura S, Kawahara M, Yamasaki K, Nakanishi Y, Kaminishi M. Massive rectal bleeding from a Dieulafoy lesion in the rectum: successful endoscopic clipping. Endoscopy. 2002. 34:237.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Massive Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding from the Appendix
- Life-Threatening Lower Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage in Pediatric Crohn's Disease
- Embolization of a Life-Threatening Hemorrhage from Meckel's Diverticulum in an Adult
- Endoscopic Band Ligation to Treat a Massive Hemorrhoidal Hemorrhage Following a Transrectal Ultrasound-Guided Prostate Biopsy
- Gastric Submucosal Hematoma after Endoscopic Hemostasis in Patient with Dual Antiplatelet Therapy