Korean J Radiol.
2014 Feb;15(1):140-144. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.140.
Growing Heterotopic Calcification in the Prevertebral Space of a Cervical Spine as a Late Complication of Irradiation: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul 133-792, Korea. radsh@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1711489
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.140
Abstract
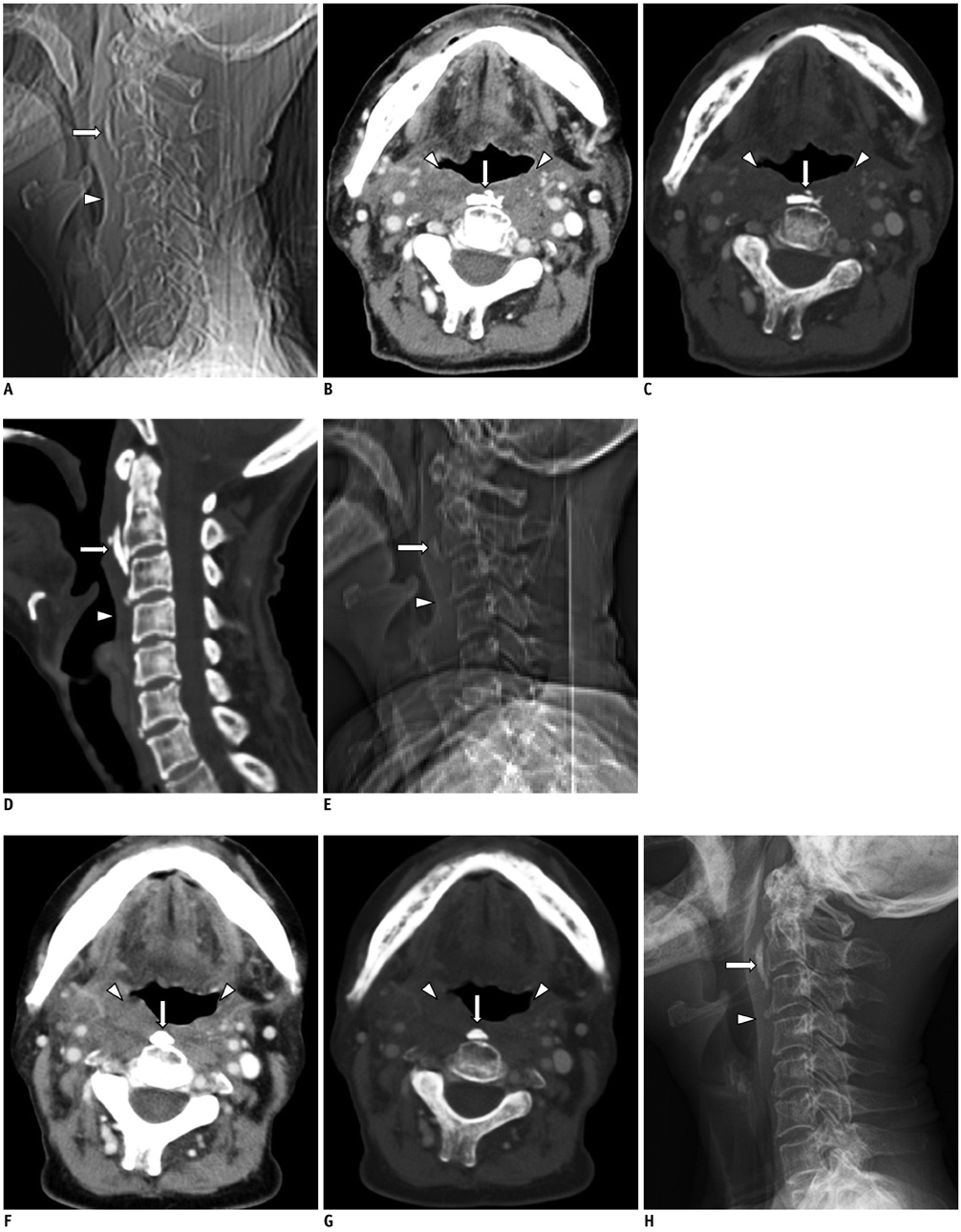
- Heterotopic calcification following head and neck irradiation has rarely been reported. It usually develops as a late complication of radiotherapy in patients with malignancies, including breast cancer, lymphoma, and genitourinary malignancies. The occurrence of heterotopic calcification in the prevertebral space of the cervical spine has not been described as a late complication of irradiation. Here, we report a case of prevertebral heterotopic calcification in a patient with history of chemotherapy and radiotherapy for tonsil cancer 21 years ago.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Carl UM, Hartmann KA. Heterotopic calcification as a late radiation effect: report of 15 cases. Br J Radiol. 2002; 75:460–463.2. Amin R, Hamilton-Wood C, Silver D. Subcutaneous calcification following chest wall and breast irradiation: a late complication. Br J Radiol. 2002; 75:279–282.3. Zaka Z, Fodor J, Udvarhelyi N, Orosz Z, Kásler M. Subcutaneous calcification as a delayed complication of radiotherapy: a case report and review of the literature. Pathol Oncol Res. 2008; 14:485–488.4. Vainright JR, Diaconis JN, Haney PJ. Presternal soft tissue calcifications following mediastinal radiotherapy for Hodgkin's disease. Chest. 1987; 91:136–137.5. Wyman SM, Weber AL. Calcification in intrathoracic nodes in Hodgkin's disease. Radiology. 1969; 93:1021–1024.6. Plzak J, Kalitova P, Urbanova M, Betka J. Subcutaneous calcification in the pectoralis major flap: a late complication of radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 2011; 84:e221–e223.7. O'Brien EJ, Frank CB, Shrive NG, Hallgrímsson B, Hart DA. Heterotopic mineralization (ossification or calcification) in tendinopathy or following surgical tendon trauma. Int J Exp Pathol. 2012; 93:319–331.8. Mavrogenis AF, Soucacos PN, Papagelopoulos PJ. Heterotopic ossification revisited. Orthopedics. 2011; 34:177.9. Rabin BM, Meyer JR, Berlin JW, Marymount MH, Palka PS, Russell EJ. Radiation-induced changes in the central nervous system and head and neck. Radiographics. 1996; 16:1055–1072.10. Lee S, Joo KB, Lee KH, Uhm WS. Acute retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis in an unusual location: a case Report in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and atlantoaxial subluxation. Korean J Radiol. 2011; 12:504–509.11. Mizuno J, Nakagawa H, Song J. Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine: a report of seven cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:1375–1379.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cervical Prevertebral Hematoma - a Rare Complication of Acupuncture Therapy: A Case Report
- Migration of Penrose Drain Following Anterior Cervical Spinal Surgery
- Prevertebral Soft Tissue Swelling After Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
- Acute Calcific Prevertebral Tendinitis without Differentiated by Simple X-ray
- Negative Pressure Pulmonary Edema Associated with Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery