Korean J Radiol.
2014 Feb;15(1):54-60. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.54.
Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking a Mass: Report of Three Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu 700-712, Korea. kjh2603@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu 700-712, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu 700-712, Korea.
- KMID: 1711477
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.54
Abstract
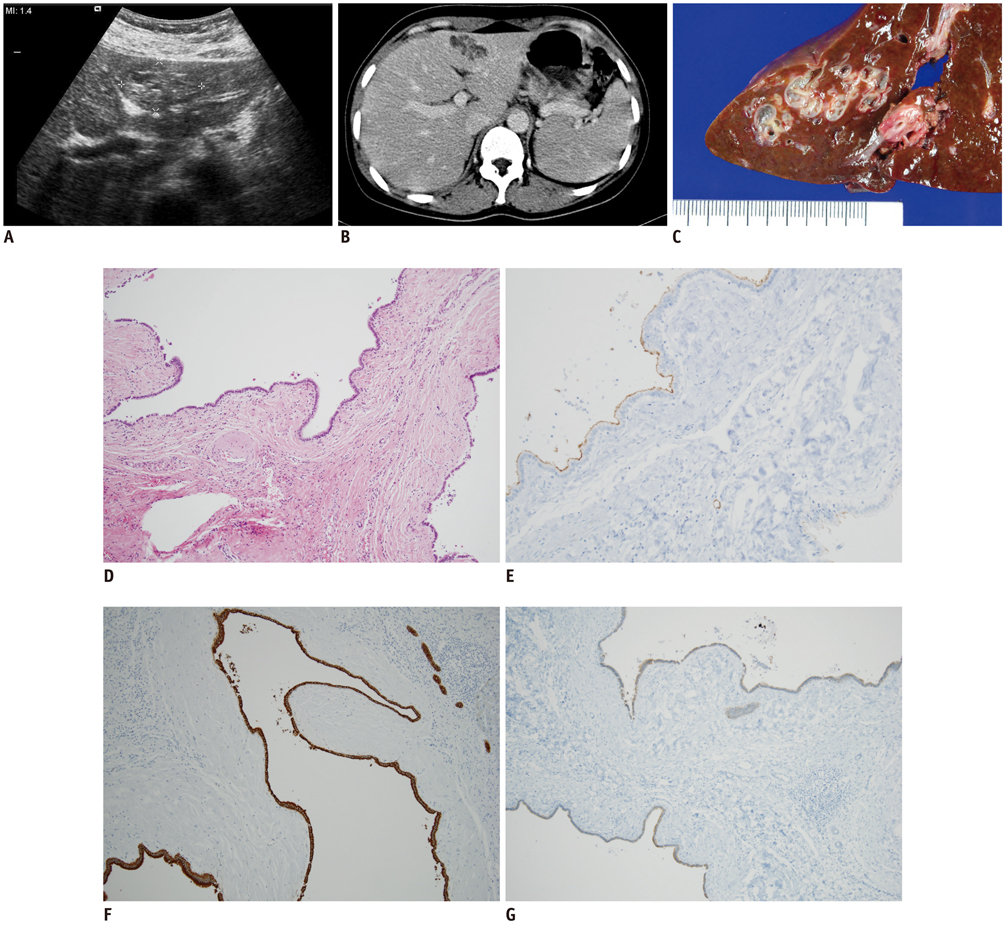
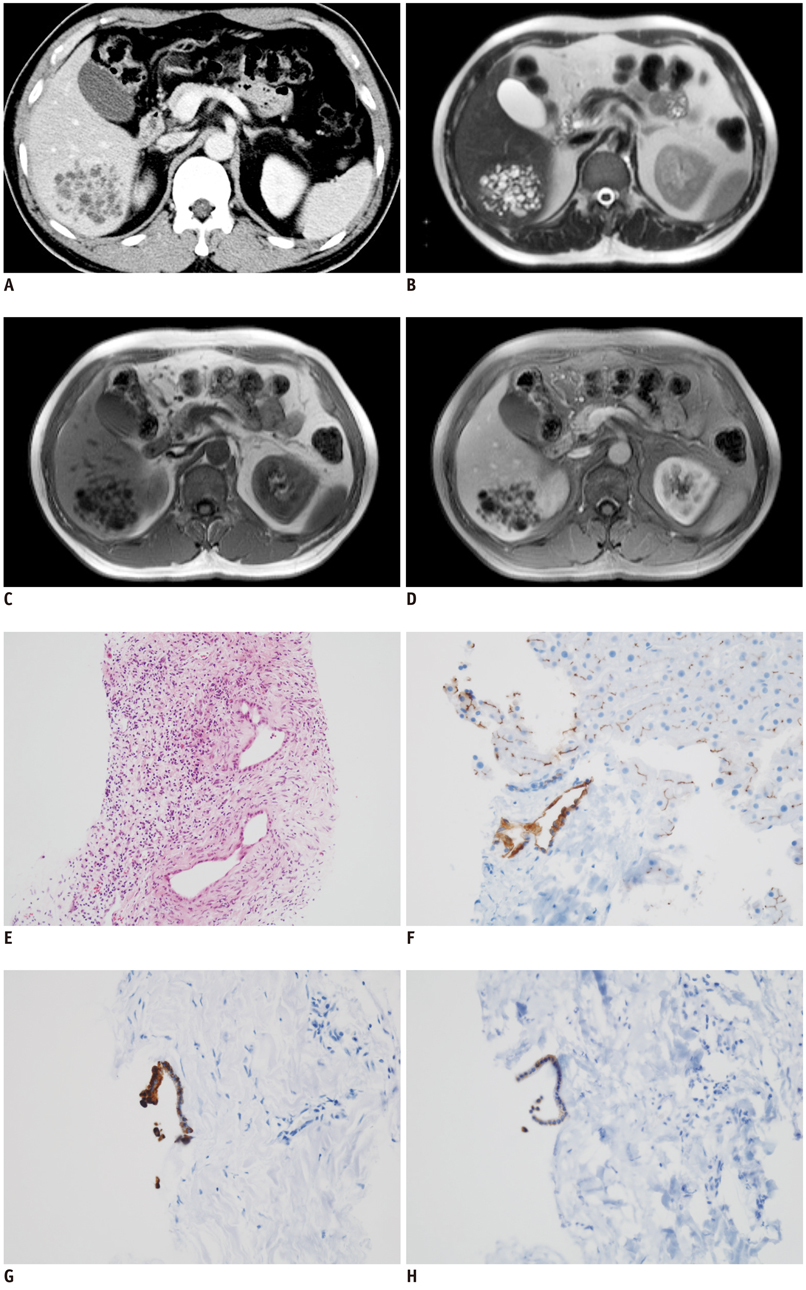
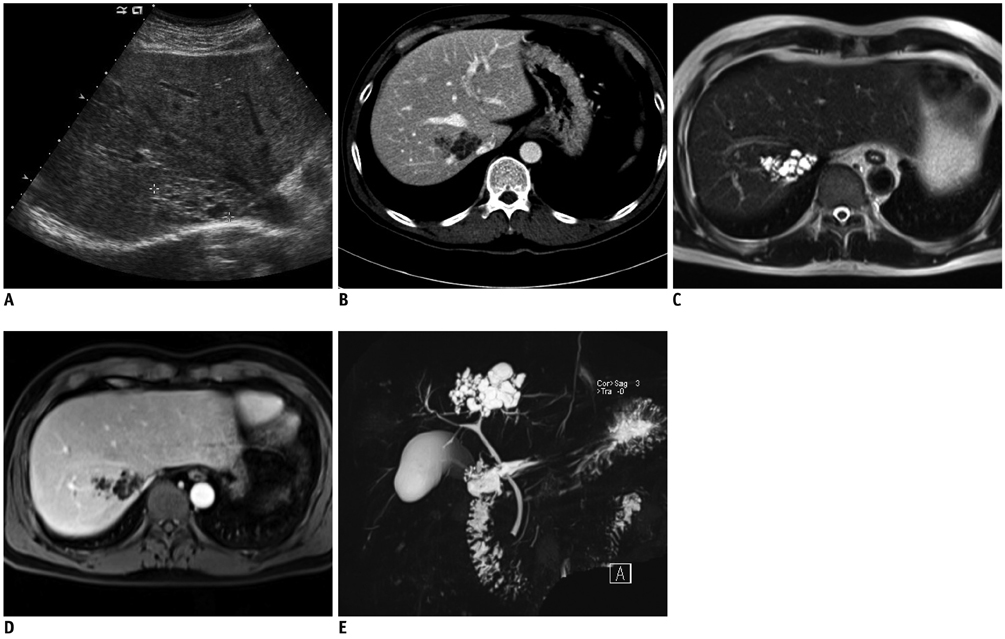
- Hepatobiliary fibropolycystic diseases are a unique group of entities involving the liver and biliary tract, which are caused by abnormal embryologic development of the ductal plates at various stages. We experienced strange hepatobiliary fibropolycystic diseases with a complex mass composed of malformed ducts and biliary cysts, which did not belong to, and were different from, previously known malformations. They were unique in imaging and histologic features. We herein report three cases of monosegmental hepatobiliary fibropolycystic disease mimicking a mass.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Vilgrain V, Vullierme MP, Marin D, Lagalla R. Fibropolycystic liver disease: CT and MR imaging findings. Radiographics. 2005; 25:659–670.2. Levy AD, Rohrmann CA Jr, Murakata LA, Lonergan GJ. Caroli's disease: radiologic spectrum with pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 179:1053–1057.3. Terada T, Moriki T. Monolobar hepatobiliary fibropolycystic disease. Pathol Oncol Res. 2011; 17:159–165.4. Terada T, Moriki T. Monolobar ductal plate malformation disease of the liver. Pathol Int. 2010; 60:407–412.5. Desmet VJ. Congenital diseases of intrahepatic bile ducts: variations on the theme "ductal plate malformation". Hepatology. 1992; 16:1069–1083.6. Summerfield JA, Nagafuchi Y, Sherlock S, Cadafalch J, Scheuer PJ. Hepatobiliary fibropolycystic diseases. A clinical and histological review of 51 patients. J Hepatol. 1986; 2:141–115.7. Veigel MC, Prescott-Focht J, Rodriguez MG, Zinati R, Shao L, Moore CA, et al. Fibropolycystic liver disease in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2009; 39:317–327. quiz 420-421.8. Lee HK, Park SJ, Yi BH, Lee AL, Moon JH, Chang YW. Imaging features of adult choledochal cysts: a pictorial review. Korean J Radiol. 2009; 10:71–80.9. Venkatanarasimha N, Thomas R, Armstrong EM, Shirley JF, Fox BM, Jackson SA. Imaging features of ductal plate malformations in adults. Clin Radiol. 2011; 66:1086–1093.10. Choi BI, Yeon KM, Kim SH, Han MC. Caroli disease: central dot sign in CT. Radiology. 1990; 174:161–163.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fibropolycystic disease: A case report
- Two Cases of Monosegmental Pedicle Screw Fixation for Thoraco-lumbar Fracture(Three-column Injury), and a Review of the Literature
- Hilar Choledochal Cyst Mimicking Biliary Atresia on Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy: a Case Report
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Lung Disease Mimicking Lung Cancer: Two Case Reports
- Comparison of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion in Monosegmental Vacuum Phenomenon within an Intervertebral Disc