Ann Lab Med.
2013 Nov;33(6):441-448. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.6.441.
Development of a Document Management System for the Standardization of Clinical Laboratory Documents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Center for Diagnostic Oncology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. dhlee@ncc.re.kr
- 2Department of Information Technology Team, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Rehabilitation Clinic, Center for Clinical Specialty, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1711318
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.6.441
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Documentation is very important; a considerable number of documents exist for use in accreditation inspection. However, most laboratories do not effectively manage the processes of documentation, organization, and storage. The purpose of this study was to facilitate the establishment of a strategically effective and sustainably standardized document management system.
METHODS
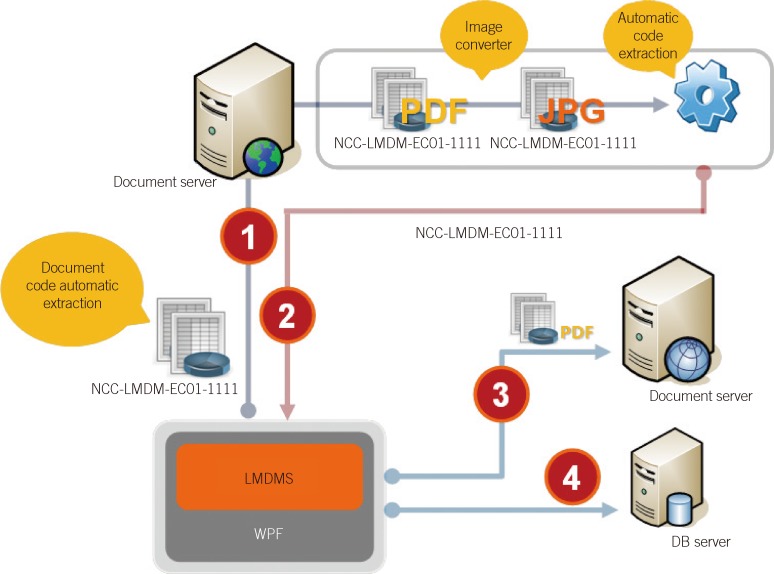
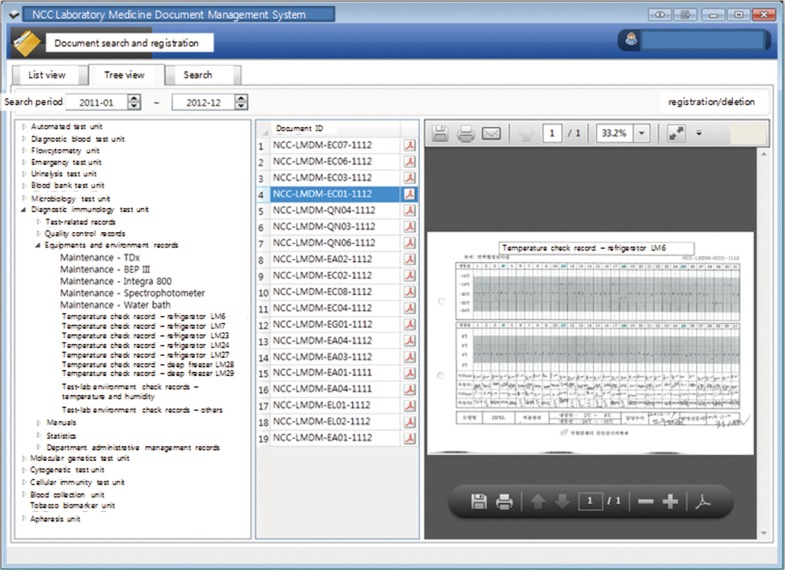
A document code formatting system was modified by comparing the document list data received from 3 major university hospitals. In addition, a questionnaire regarding document code standardization was created and sent to 268 institutes to establish document classifications and generate a standard coding scheme. A computerized document management system was developed.
RESULTS
Only 32% (8 out of 25 institutes) answered that they were able to identify all of the document types and their numbers. In total, 76% of institutes (19 out of 25) answered that a systematic document management system was necessary. Disorganized document files were systemized by classifying them into 8 major groups according to their characteristics: patient test records (T), test quality control (Q), manuals (M), equipment and environment management (E), statistics (S), division administration (A), department administration (R), and others (X).
CONCLUSIONS
Our documentation system may serve as a basis for the standardization of documents and the creation of a document management system for all hospital laboratories.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wagner LR. The College of American Pathologists, 1946-1996: laboratory standards. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1997; 121:536–541. PMID: 9167614.2. Lee WG, Kwak YS, Lee DH, Hwang YS, Lee KN. Clinical pathology laboratory inspection and accreditation in Korea I: development of the system and its trial. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2001; 21:86–92.3. Lee WG, Kwak YS, Lee DH, Hwang YS, Lee KN. Laboratory inspection and accreditation in Korea II: analysis of the first round inspection. Korean J Lab Med. 2003; 23:363–369.4. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Laboratory documents: developement and control; Approved guideline. GP2-A5. 5th ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2006.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Document Repository System for Electronic Health Record
- Introduction of Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing Subcommittee Meeting
- Evaluation of Co-occurring Terms in Clinical Documents Using Latent Semantic Indexing
- PhactaManager: A Clinical Trial Management System Incorporating an XML Layer as a Database-Independent Processing Platform
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 15189