Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2008 Sep;1(3):161-165. 10.3342/ceo.2008.1.3.161.
Functional Benefit after Modification of Radial Forearm Free Flap for Soft Palate Reconstruction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Hallym University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ys20805@chol.com
- 2Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Hallym University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1486088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2008.1.3.161
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
To compare the velopharyngeal function, swallowing and speech of the conventional and modified radial forearm free flap (RFFF) for soft palate reconstruction.
METHODS
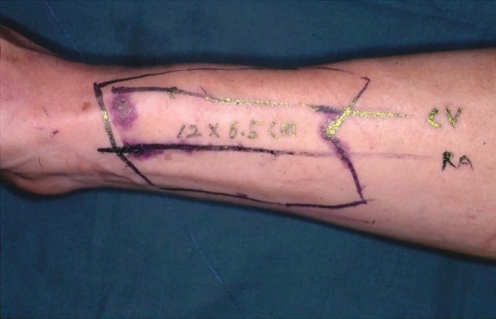
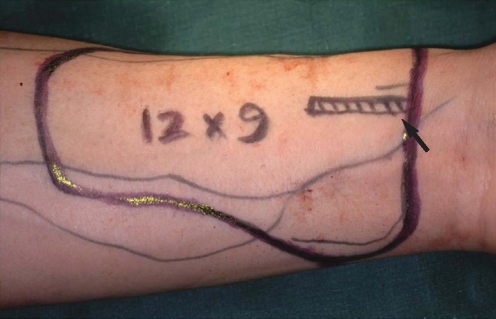
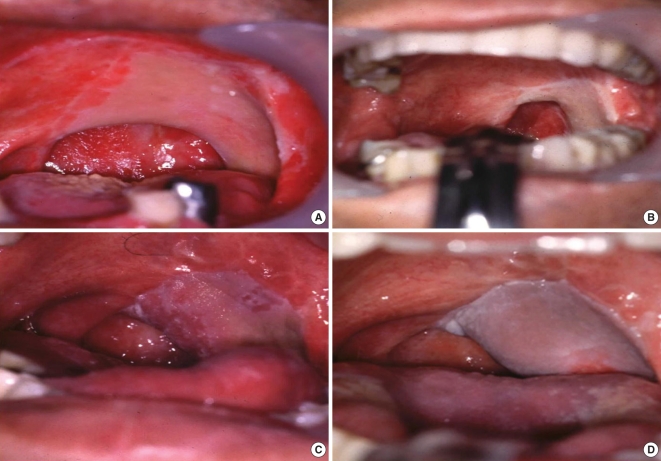
Retrospective clinical study. Twenty-eight patients who underwent oropharyngeal reconstruction with RFFF were divided into two groups: 10 patients had conventional folded RFFF and 18 patients underwent modified method.
RESULTS
The average speech intelligibility score in modified RFFF group was 8.0+/-2.4, and 6.2+/-2.2 in conventional RFFF group (P<0.05). The nasalance was 27.4+/-7.8% in modified group and 38.6+/-2.7% in conventional group during no nasal passage reading and 43.6+/-7.3% in modified group, 55.2+/-7.6% in conventional group during high nasal passage reading (P<0.05). The subjective swallowing functional score was 2.8 in modified group and 2.1 in conventional group.
CONCLUSION
The speech assessment and nasalance demonstrate a more favorable outcome in modified group than conventional group.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brown JS, Zuydam AC, Jones DC, Rogers SN, Vaughan ED. Functional outcome in soft palate reconstruction using a radial forearm free flap in conjunction with a superiorly based pharyngeal flap. Head Neck. 1997; 9. 19(6):524–534. PMID: 9278761.
Article2. Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Logemann JA, Colangelo LA. Speech and swallowing in irradiated and nonirradiated postsurgical oral cancer patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998; 5. 118(5):616–624. PMID: 9591859.
Article3. Hirose J. General rules for clinical and pathological studies on head and neck cancer: Japan society for head neck cancer. 1991. 2nd ed. Tokyo: Kinbara;p. 101. Japanese.4. Hassan SJ, Weymuller EA Jr. Assessment of quality of life in head and neck cancer patients. Head Neck. 1993; Nov–Dec. 15(6):485–496. PMID: 8253555.
Article5. Sinha UK, Young P, Hurvitz K, Crockett DM. Functional outcomes following palatal reconstruction with a folded radial forearm free flap. Ear Nose Throat J. 2004; 1. 83(1):45–48. PMID: 14986758.
Article6. Kimata Y, Uchiyama K, Sakuraba M, Ebihara S, Hayashi R, Haneda T, et al. Velopharyngeal function after microsurgical reconstruction of lateral and superior oropharyngeal defects. Laryngoscope. 2002; 6. 112(6):1037–1042. PMID: 12160270.
Article7. Miura T, Haji T, Kishimoto S. Flap selection for a mesopharyngeal reconstruction: articulartory and deglutitory evaluations. Jpn J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994; 11. 37(11):1265–1272. Japanese.8. Seikaly H, Rieger J, Wolfaardt J, Moysa G, Harris J, Jha N. Functional outcomes after primary oropharyngeal cancer resection and reconstruction with the radial forearm free flap. Laryngoscope. 2003; 5. 113(5):897–904. PMID: 12792330.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reconstruction of Hard Palatal Defect using Staged Operation of the Prelaminated Radial Forearm Free Flap
- Design of Radial Forearm Free Flap for Oropharyngeal Reconstruction
- Radial forearm free flap in a patient with an unusual radial artery variation: a case report
- Correction of Orbital Hypoplasia Using A Radial Forearm Osteocutaneous Free Flap
- FUNCTIONAL EFFECTS OF RADIAL FOREARM FREE FLAP USED FOR RECONSTRUCTION IN THE TONSILLAR REGION