Anat Cell Biol.
2012 Mar;45(1):57-61. 10.5115/acb.2012.45.1.57.
Abnormal patterns of the renal veins
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Medicine, Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences, Sanandaj, Iran. hadi_anjam@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran.
- 3Department of Urology, Moradi Hospital, School of Medicine, Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences, Rafsanjan, Iran.
- KMID: 1447454
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2012.45.1.57
Abstract
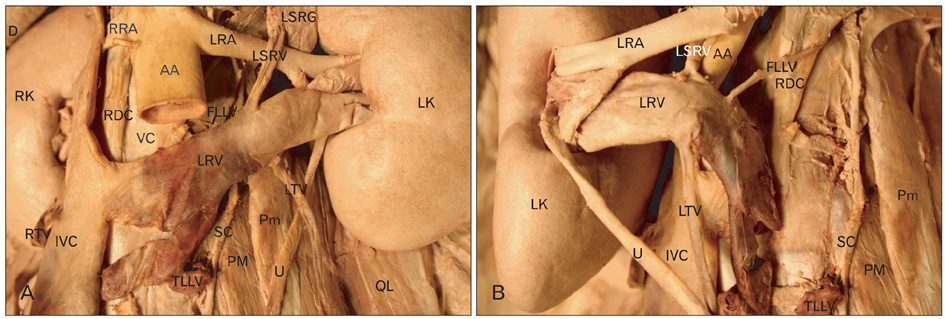
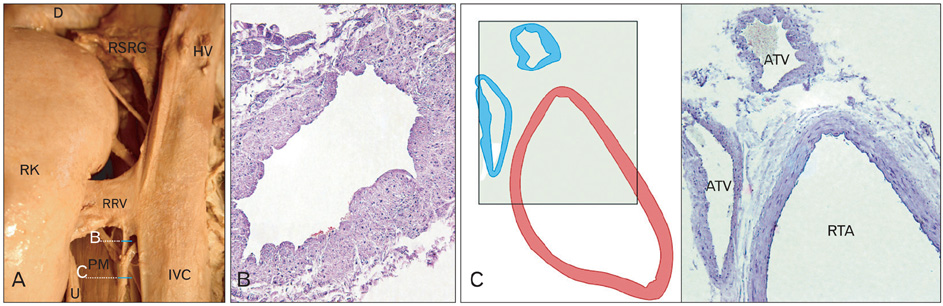
- Knowledge of the renal vascular anatomy may greatly contribute to the success of surgical, invasive and radiological procedures of the retroperitoneal region. Here, morphometric and histological studies of a human cadaveric specimen presented a complex, anomalous pattern of renal veins. The left renal vein had an oblique retro-aortic course and received two lumbar veins. It bifurcated near its drainage point into the inferior vena cava. The right renal vein received the right testicular vein. In addition, the left kidney was located at a low position. The spleen was enlarged. The present case is unique and provides information that may help surgeons or angiologists to apply safer interventions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Multiple renal veins clogging the hilum of the right kidney
Satheesha B Nayak, Narendra Pamidi, Vasanthakumar Packirisamy, Soumya Kodimajalu Vasudeva
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(1):141-144. doi: 10.5115/acb.22.109.
Reference
-
1. Satyapal KS, Kalideen JM, Haffejee AA, Singh B, Robbs JV. Left renal vein variations. Surg Radiol Anat. 1999. 21:77–81.2. Senecail B, Bobeuf J, Forlodou P, Nonent M. Two rare anomalies of the left renal vein. Surg Radiol Anat. 2003. 25:465–467.3. Malcic-Gürbüz J, Akalin A, Gümüşcü B, Cavdar S. Clinical implications of concomitant variations of the testicular, suprarenal and renal veins: a case report. Ann Anat. 2002. 184:35–39.4. Benedetti E, Troppmann C, Gillingham K, Sutherland DE, Payne WD, Dunn DL, Matas AJ, Najarian JS, Grussner RW. Short- and long-term outcomes of kidney transplants with multiple renal arteries. Ann Surg. 1995. 221:406–414.5. Jetti R, Jevoor P, Vollala VR, Potu BK, Ravishankar M, Virupaxi R. Multiple variations of the urogenital vascular system in a single cadaver: a case report. Cases J. 2008. 1:344.6. Kumar S, Neyaz Z, Gupta A. The utility of 64 channel multidetector CT angiography for evaluating the renal vascular anatomy and possible variations: a pictorial essay. Korean J Radiol. 2010. 11:346–354.7. Bass JE, Redwine MD, Kramer LA, Huynh PT, Harris JH Jr. Spectrum of congenital anomalies of the inferior vena cava: cross-sectional imaging findings. Radiographics. 2000. 20:639–652.8. Field S, Saxton H. Venous anomalies complicating left adrenal catheterization. Br J Radiol. 1974. 47:219–225.9. Macchi V, Parenti A, De Caro R. Pivotal role of the sub-supracardinal anastomosis in the development and course of the left renal vein. Clin Anat. 2003. 16:358–361.10. Arslan H, Etlik O, Ceylan K, Temizoz O, Harman M, Kavan M. Incidence of retro-aortic left renal vein and its relationship with varicocele. Eur Radiol. 2005. 15:1717–1720.11. Holden A, Smith A, Dukes P, Pilmore H, Yasutomi M. Assessment of 100 live potential renal donors for laparoscopic nephrectomy with multi-detector row helical CT. Radiology. 2005. 237:973–980.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Normal variations of renal vessels based upon the study of 240 living-donor nephrectomies
- Case Report on Horseshoe Kidney
- Angiographic analysis of renal artery and vein in 85 candidates of renal transplant dornor
- Common Variations of Renal Vessels in Donor Kidneys
- Multi-Detector CT Findings of Double Retroaortic Left Renal Veins