J Korean Surg Soc.
2011 Dec;81(6):427-430. 10.4174/jkss.2011.81.6.427.
Histologic confirmation of huge pancreatic lipoma: a case report and review of literatures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. seohi71@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 4Diagnostic Radiology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 1445774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.6.427
Abstract
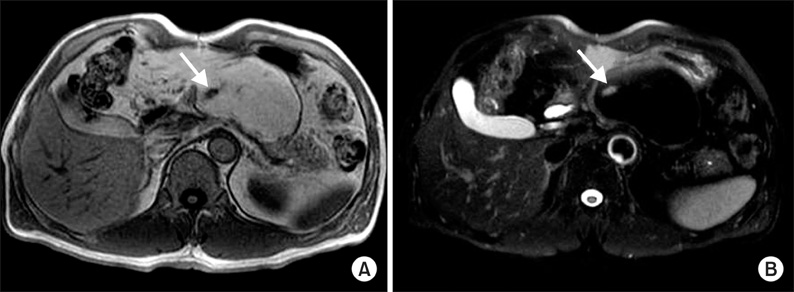
- Pancreatic lipomas are commonly diagnosed based on radiologic images, although the prevalence of lipomas has not been established. Histologic confirmation of pancreatic lipomas is extremely rare because surgical treatment is unnecessary in most cases. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology has been suggested to avoid unnecessary surgery to distinguish between a lipoma and a well-differentiated liposarcoma; however, surgery would be needed when the tumor is associated with symptoms or difficult to distinguish from a liposarcoma. We present a case of a pancreatic lipoma in a 54-year-old male patient that was histologically-confirmed by subtotal pancreatectomy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bigard MA, Boissel P, Regent D, Froment N. Intrapancreatic lipoma. First case in the literature. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1989. 13:505–507.2. De Jong SA, Pickleman J, Rainsford K. Nonductal tumors of the pancreas. The importance of laparotomy. Arch Surg. 1993. 128:730–734.3. Boglino C, Inserra A, Silvano A, Ciprandi G, Boldrini R, Caione P. Intrapancreatic lipoma: a case report. Pediatr Med Chir. 1993. 15:397–399.4. Merli M, Fossati GS, Alessiani M, Spada M, Gambini D, Viezzoli A, et al. A rare case of pancreatic lipoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996. 43:734–736.5. Di Maggio EM, Solcia M, Dore R, Preda L, La Fianza A, Rodino C, et al. Intrapancreatic lipoma: first case diagnosed with CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996. 167:56–57.6. Raut CP, Fernandez-del Castillo C. Giant lipoma of the pancreas: case report and review of lipomatous lesions of the pancreas. Pancreas. 2003. 26:97–99.7. Di Matteo FM, Shimpi L, Pandolfi M, Rabitti C, Fabio C, Gabbrielli A, et al. EUS diagnosis of pancreatic lipoma: a case report. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006. 64:146–148.8. Celis Zapata J, Berrospi Espinoza F, Valencia Mariñas HD, Sánchez Lihón J, Abad Licham M, Farías Mejía I. Pancreatic lipoma: presentation of a case and review of literature. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2008. 28:56–59.9. Suzuki R, Irisawa A, Hikichi T, Shibukawa G, Takagi T, Wakatsuki T, et al. Pancreatic lipoma diagnosed using EUS-FNA. A case report. JOP. 2009. 10:200–203.10. Karaosmanoglu D, Karcaaltincaba M, Akata D, Ozmen M, Akhan O. Pancreatic lipoma computed tomography diagnosis of 17 patients and follow-up. Pancreas. 2008. 36:434–436.