J Korean Surg Soc.
2012 Dec;83(6):397-402. 10.4174/jkss.2012.83.6.397.
Laparoscopic colectomy of colonic intussusceptions in adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. kgiseup@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 1437542
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.83.6.397
Abstract
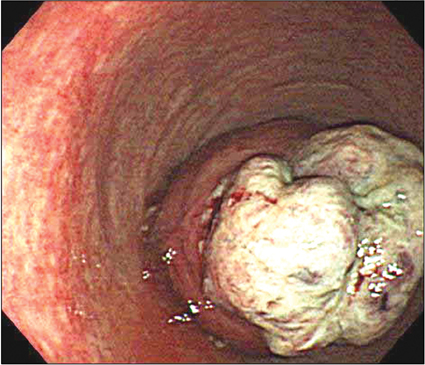
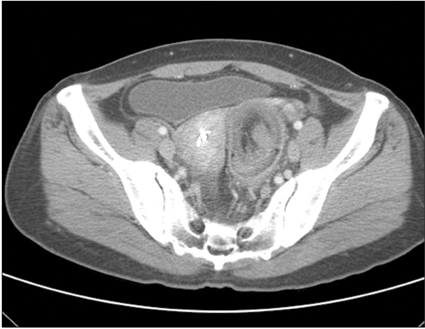
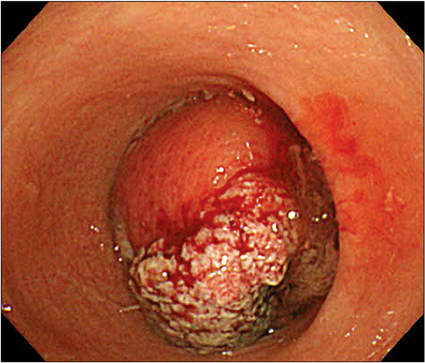
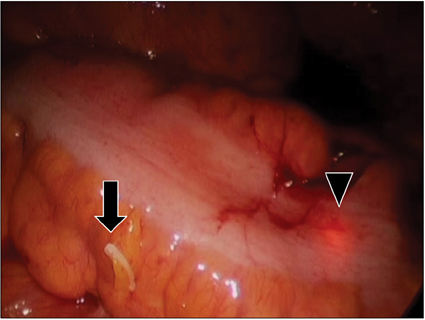
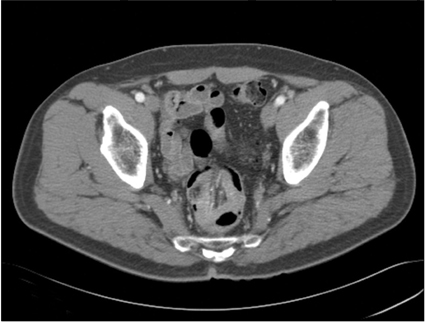
- Adult intussusception is a rare entity. Most adult intussusceptions require surgical intervention because they have a high rate of pathologic leading point. Mandatory laparotomy and en bloc resection is recommended in colonic intussusceptions due to the possibility of malignancy. We report herein 3 cases of adult colonic intussusceptions. The intussusceptions were located in the sigmoid and rectum, which were managed by laparoscopic colectomy. Case 1 was managed by laparoscopic anterior resection and diverting ileostomy combined with perineal reduction. Perineal approach facilitated laparoscopic reduction. In case 2, intraoperative colonoscopy was performed to determine the distal resection margin. Intraoperative colonoscopy showed edematous bowel mucosa as well as leading point after reduction of intussusceptions. Case 3 showed asymptomatic transient rectorectal colonic intussusceptions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Azar T, Berger DL. Adult intussusception. Ann Surg. 1997. 226:134–138.2. Nagorney DM, Sarr MG, McIlrath DC. Surgical management of intussusception in the adult. Ann Surg. 1981. 193:230–236.3. Eisen LK, Cunningham JD, Aufses AH Jr. Intussusception in adults: institutional review. J Am Coll Surg. 1999. 188:390–395.4. Fleshman J, Sargent DJ, Green E, Anvari M, Stryker SJ, Beart RW Jr, et al. Laparoscopic colectomy for cancer is not inferior to open surgery based on 5-year data from the COST Study Group trial. Ann Surg. 2007. 246:655–662.5. Park KJ, Choi HJ, Kim SH, Han SY, Hong SH, Cho JH, et al. Sigmoidorectal intussusception of adenoma of sigmoid colon treated by laparoscopic anterior resection after spongeon-the-stick-assisted manual reduction. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:146–149.6. Greenley CT, Ahmed B, Friedman L, Deitte L, Awad ZT. Laparoscopic management of sigmoidorectal intussusception. JSLS. 2010. 14:137–139.7. Kim KH, Lee IK, Lee YS, Kim DH, Park JK, An CH, et al. Analysis of the Diagnostic Maneuver and Timing of Operation in Adult Intussusception. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007. 73:419–423.8. Chang CC, Chen YY, Chen YF, Lin CN, Yen HH, Lou HY. Adult intussusception in Asians: clinical presentations, diagnosis, and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 22:1767–1771.9. Agha FP. Intussusception in adults. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986. 146:527–531.10. Catalano O. Transient small bowel intussusception: CT findings in adults. Br J Radiol. 1997. 70:805–808.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic Colectomy of Splenic Flexure for Giant Lipomas Causing Symptoms: Report on Two Cases
- Current Status of Laparoscopic Colectomy for Colon Cancer
- Laparoscopic transverse colectomy using a new articulating instrument
- Laparoscopic Surgery for Colorectal Cancer
- Current Status of Single-port Colectomy in Korea