Korean J Radiol.
2012 Dec;13(6):827-831. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.827.
Intrahepatic Portosystemic Venous Shunt: Successful Embolization Using the Amplatzer Vascular Plug II
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon 301-721, Korea. starzan@chollian.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon 301-721, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon 301-721, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Konyang University Hospital, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon 371-718, Korea.
- KMID: 1397518
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.827
Abstract
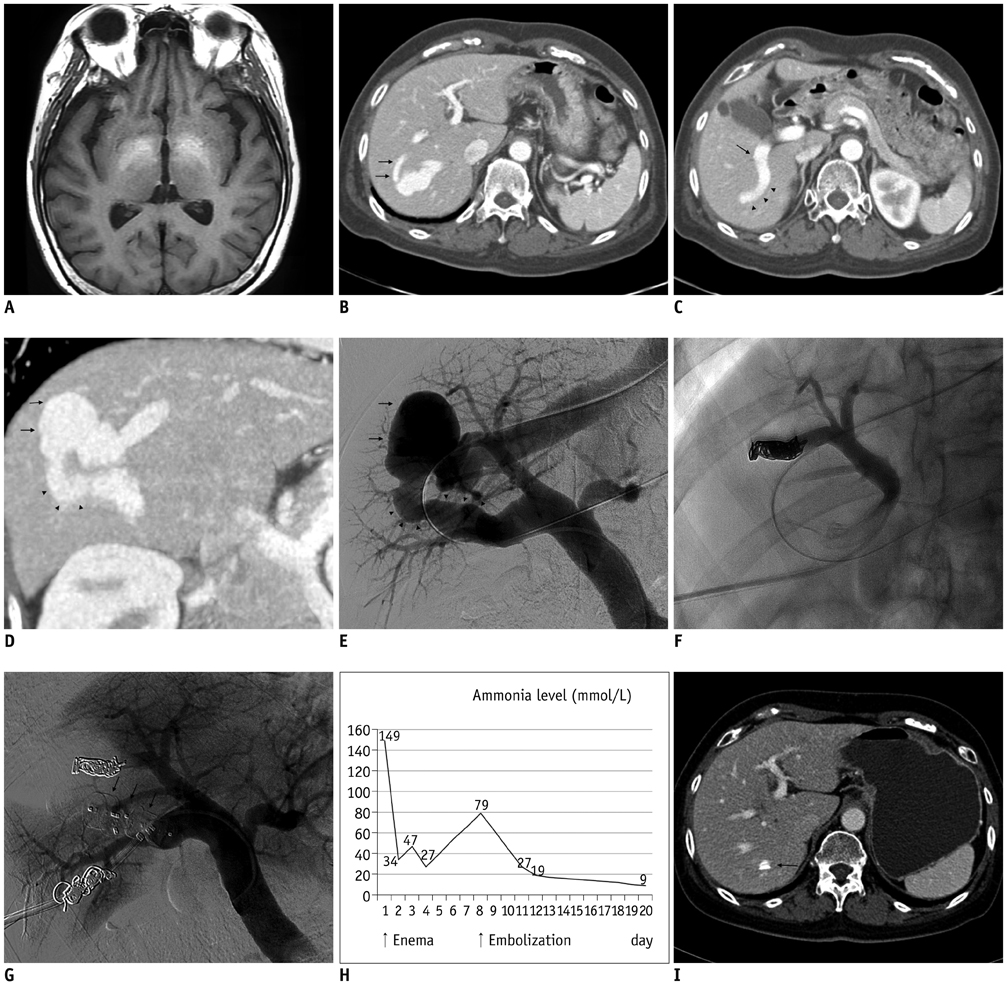
- A 67-year-old woman presented with memory impairment and behavioral changes. Brain MRI indicated hepatic encephalopathy. Abdominal CT scans revealed an intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt that consisted of two shunt tracts to the aneurysmal sac that communicated directly with the right hepatic vein. The large tract was successfully occluded by embolization using the newly available AMPLATZERTM Vascular Plug II and the small tract was occluded by using coils. The patient's symptoms disappeared after shunt closure and she remained free of recurrence at the 3-month follow-up evaluation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tsitouridis I, Sotiriadis C, Michaelides M, Dimarelos V, Tsitouridis K, Stratilati S. Intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunts: radiological evaluation. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009. 15:182–187.2. Hiraoka A, Kurose K, Hamada M, Azemoto N, Tokumoto Y, Hirooka M, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy due to intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt successfully treated by interventional radiology. Intern Med. 2005. 44:212–216.3. Oguz B, Akata D, Balkanci F, Akhan O. Intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt: diagnosis by colour/power Doppler imaging and three-dimensional ultrasound. Br J Radiol. 2003. 76:487–490.4. Tanoue S, Kiyosue H, Komatsu E, Hori Y, Maeda T, Mori H. Symptomatic intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt: embolization with an alternative approach. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 181:71–78.5. Boixadera H, Tomasello A, Quiroga S, Cordoba J, Perez M, Segarra A. Successful embolization of a spontaneous mesocaval shunt using the Amplatzer Vascular Plug II. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010. 33:1044–1048.6. Zhu X, Tam MD, Pierce G, McLennan G, Sands MJ, Lieber MS, et al. Utility of the Amplatzer Vascular Plug in splenic artery embolization: a comparison study with conventional coil technique. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2011. 34:522–531.7. Ringe KI, Weidemann J, Rosenthal H, Keberle M, Chavan A, Baus S, et al. Transhepatic preoperative portal vein embolization using the Amplatzer Vascular Plug: report of four cases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007. 30:1245–1247.8. Rovira A, Alonso J, Córdoba J. MR imaging findings in hepatic encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. 29:1612–1621.9. Hegde AN, Mohan S, Lath N, Lim CC. Differential diagnosis for bilateral abnormalities of the basal ganglia and thalamus. Radiographics. 2011. 31:5–30.10. Lee SA, Lee YS, Lee KS, Jeon GS. Congenital intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt and liver mass in a child patient: successful endovascular treatment with an amplatzer vascular plug (AVP). Korean J Radiol. 2010. 11:583–586.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Congenital Intrahepatic Portosystemic Venous Shunt and Liver Mass in a Child Patient: Successful Endovascular Treatment with an Amplatzer Vascular Plug (AVP)
- Treating Sudden Onset Hepatic Encephalopathy with Coil Embolization in a Patient with a Congenital Intrahepatic Portosystemic Venous Shunt: A Case Report
- Intrahepatic Portosystemic Venous Shunt Presenting as a Cystic Mass in a Patient without Liver Cirrhosis: A Case Report
- A Case of Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy Secondary to Spontaneous Intrahepatic Portosystemic Venous Shunt
- Gastric Variceal Rebleeding by Aberrant Left Gastric Vein after Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: A Case Report