J Vet Sci.
2011 Dec;12(4):325-331. 10.4142/jvs.2011.12.4.325.
Evaluation of IGF-I levels and serum protein profiles of diabetic cats and dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Ondokuz Mayis, 55139 Samsun, Turkey. gciftci@omu.edu.tr
- KMID: 1365015
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2011.12.4.325
Abstract
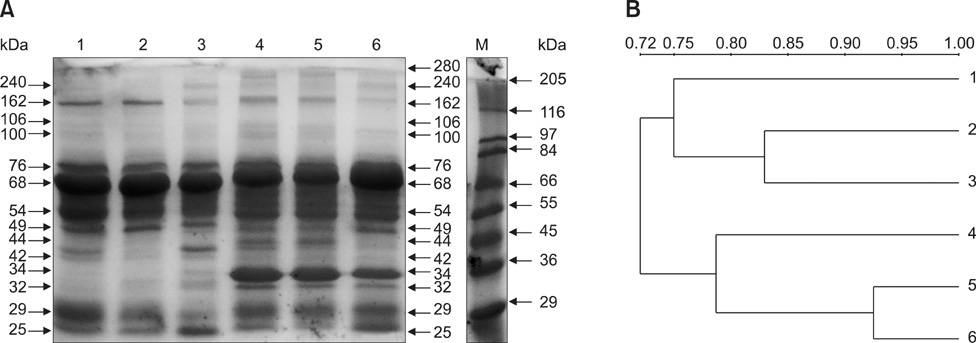
- In this study, we measured the insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I levels and evaluated the serum protein profiles of diabetic, insulin-treated, and healthy cats and dogs. The total IGF-I concentrations were 33.74 +/- 3.4 ng/mL for normal, 25.8 +/- 4.5 ng/mL for diabetic, and 180.4 +/- 31.4 ng/mL for insulin-treated cats. IGF-I concentrations were 46.4 +/- 6.6 ng/mL for normal, 25.1 +/- 4.1 ng/mL for diabetic, and 303.0 +/- 61.3 ng/mL for insulin-treated dogs. Total serum protein profiles were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Fourteen bands ranging from 25 to 240 kDa in size were observed for cats, and 17 bands ranging from 25 to 289 kDa were observed for dogs. The densities of the bands differed among control, diabetic, and insulin-treated animals. In conclusion, we found that serum protein profiles and IGF-I concentrations were altered in both diabetic and insulin-treated animals. When judiciously interpreted in the light of other clinical and laboratory data, the techniques used in our study provide a valuable modality for measuring the severity of diabetes mellitus in dogs and cats.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Asada T, Takakura S, Ogawa T, Iwai M, Kobayashi M. Overexpression of glucose transporter protein 5 in sciatic nerve of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett. 1998. 252:111–114.
Article2. Aytuğ N. İmren HY, editor. Metabolizma hastalıkları. Kedi ve Köpek Hastalıkları. 1998. Ankara: Medisan Yayınları;345–346.3. Bach LA, Rechler MM. Insulin-like growth factors and diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1992. 8:229–257.
Article4. Bach MA, Chin E, Bondy CA. The effects of subcutaneous insulin-like growth factor-I infusion in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994. 79:1040–1045.
Article5. Banting FG, Best CH. Pancreatic extracts. 1922. J Lab Clin Med. 1990. 115:254–272.6. Baxter RC. Characterization of the acid-labile subunit of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988. 67:265–272.
Article7. Bereket A, Lang CH, Wilson TA. Alterations in the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res. 1999. 31:172–181.
Article8. Berg RIM, Nelson RW, Feldman EC, Kass PH, Pollard R, Refsal KR. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I concentration in cats with diabetes mellitus and acromegaly. J Vet Intern Med. 2007. 21:892–898.
Article9. Blum WF. Ranke MB, editor. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Diagnostics of Endocrine Function in Children and Adolescents. 1996. Heidelberg: Barth Verlag;190–218.
Article10. Boulware SD, Tamborlane WV, Rennert NJ, Gesundheit N, Sherwin RS. Comparison of the metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin. Dose-response relationships in healthy young and middle-aged adults. J Clin Invest. 1994. 93:1131–1139.
Article11. Brismar K, Fernqvist-Forbes E, Wahren J, Hall K. Effect of insulin on the hepatic production of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), IGFBP-3, and IGF-I in insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994. 79:872–878.
Article12. Candiano G, Bruschi M, Musante L, Santucci L, Ghiggeri GM, Carnemolla B, Orecchia P, Zardi L, Righetti PG. Blue silver: a very sensitive colloidal Coomassie G-250 staining for proteome analysis. Electrophoresis. 2004. 25:1327–1333.
Article13. Dai J, Baxter RC. Regulation in vivo of the acid-labile subunit of the rat serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex. Endocrinology. 1994. 135:2335–2341.
Article14. Dunger DB, Acerini CL. IGF-I and diabetes in adolescence. Diabetes Metab. 1998. 24:101–107.15. Eigenmann JE, Becker M, Kammermann B, Leemann W, Heimann R, Zapf J, Froesch ER. Decrease of non-suppressible insulin-like activity after pancreatectomy and normalization by insulin therapy. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1977. 85:818–822.
Article16. Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:Suppl 1. S5–S20.17. Fryburg DA. Insulin-like growth factor I exerts growth hormone- and insulin-like actions on human muscle protein metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1994. 267(2 Pt 1):E331–E336.
Article18. Frystyk J, Baxter RC. Competitive binding assay for determination of rat insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3. Endocrinology. 1998. 139:1454–1457.
Article19. Kratzsch J, Keliner K, Zilkens T, Schmidt-Gayk H, Selisko T, Scholz GH. Growth hormone-binding protein related immunoreactivity is regulated by the degree of insulinopenia in diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1996. 44:673–678.
Article20. Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970. 227:680–685.
Article21. Laronga C, Becker S, Watson P, Gregory B, Cazares L, Lynch H, Perry RR, Wright GL Jr, Drake RR, Semmes OJ. SELDI-TOF serum profiling for prognostic and diagnostic classification of breast cancers. Dis Markers. 2003-2004. 19:229–238.
Article22. Lewitt MS, Hazel SJ, Church DB, Watson ADJ, Powell SE, Tan K. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 ternary complex in feline diabetes mellitus. J Endocrinol. 2000. 166:21–27.
Article23. Löfqvist C, Andersson E, Gelander L, Rosberg S, Hulthen L, Blum WF, Wikland KA. Reference values for insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and the ratio of insulin-like growth factor-I to IGFBP-3 throughout childhood and adolescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 90:1420–1427.
Article24. Massa R, Bantar C, Lopardo H, Vay C, Gutkind G. Whole-cell protein profiles are useful for distinguishing enterococcal species recovered from clinical specimens. Rev Argent Microbiol. 2007. 39:199–203.25. Maxwell A, Butterwick R, Batt RM, Camacho-Hübner C. Serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I concentrations are reduced by short-term dietary restriction and restored by refeeding in domestic cats (Felis catus). J Nutr. 1999. 129:1879–1884.
Article26. McMillan DE. Increased levels of acute-phase serum proteins in diabetes. Metabolism. 1989. 38:1042–1046.
Article27. Myers MG Jr, Sun XJ, Cheatham B, Jachna BR, Glasheen EM, Backer JM, White MF. IRS-1 is a common element in insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I signaling to the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. Endocrinology. 1993. 132:1421–1430.
Article28. O'Connell TX, Horita TJ, Kasravi B. Understanding and interpreting serum protein electrophoresis. Am Fam Physician. 2005. 71:105–112.29. Okumuş Z. Diabetes mellitus in dogs and cats Part 1: Etyology, pathogenesis and treatment. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg. 1999. 5:223–231.30. Rand JS, Fleeman LM, Farrow HA, Appleton DJ, Lederer R. Canine and feline diabetes mellitus: nature or nurture? J Nutr. 2004. 134:8 Suppl. 2072S–2080S.
Article31. Rand JS, Marshall RD. Diabetes Mellitus in Cats. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2005. 35:211–224.
Article32. Raynaud-Simon A, Perin L, Meaume S, Lesourd B, Moulias R, Postel-Vinay MC, Le Bouc Y. IGF-I, IGF-I-binding proteins and GH-binding protein in malnourished elderly patients with inflammation receiving refeeding therapy. Eur J Endocrinol. 2002. 146:657–665.
Article33. Reusch CE, Kley S, Casella M, Nelson RW, Mol J, Zapf J. Measurements of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 in cats with diabetes mellitus. Vet Rec. 2006. 158:195–200.
Article34. Rinderknecht E, Humbel RE. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978. 253:2769–2776.
Article35. Rosenfeld RG, Lamson G, Pham H, Oh Y, Conover C, De Leon DD, Donovan SM, Ocrant I, Giudice L. Insulinlike growth factor-binding proteins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1990. 46:99–159.
Article36. Russell-Jones DL, Umpleby AM, Hennessy TR, Bowes SB, Shojaee-Moradie F, Hopkins KD, Jackson NC, Kelly JM, Jones RH, Sönksen PH. Use of a leucine clamp to demonstrate that IGF-I actively stimulates protein synthesis in normal humans. Am J Physiol. 1994. 267(4 Pt 1):E591–E598.
Article37. Russell-Jones DL, Bates AT, Umpleby AM, Hennessy TR, Bowes SB, Hopkins KD, Jackson N, Kelly J, Shojaee-Moradie F, Jones RH, Sonksen PH. A comparison of the effects of IGF-I and insulin on glucose metabolism, fat metabolism and the cardiovascular system in normal human volunteers. Eur J Clin Invest. 1995. 25:403–411.
Article38. Scheiwiller E, Guler HP, Merryweather J, Scandella C, Maerki W, Zapf J, Froesch ER. Growth restoration of insulin-deficient diabetic rats by recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I. Nature. 1986. 323:169–171.
Article39. Simpson HL, Jackson NC, Shojaee-Moradie F, Jones RH, Russell-Jones DL, Sönksen PH, Dunger DB, Umpleby AM. Insulin-like growth factor I has a direct effect on glucose and protein metabolism, but no effect on lipid metabolism in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. 89:425–432.
Article40. Sjögren K, Wallenius K, Liu JL, Bohlooly-Y M, Pacini G, Svensson L, Törnell J, Isaksson OG, Ahrén B, Jansson JO, Ohlsson C. Liver-derived IGF-I is of importance for normal carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Diabetes. 2001. 50:1539–1545.
Article41. Sönksen PH, Russell-Jones D, Jones RH. Growth hormone and diabetes mellitus. A review of sixty-three years of medical research and a glimpse into the future? Horm Res. 1993. 40:68–79.42. Starkey SR, Tan K, Church DB. Investigation of serum IGF-I levels amongst diabetic and non-diabetic cats. J Feline Med Surg. 2004. 6:149–155.
Article43. Struble AL, Nelson RW. Non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in cats and humans. Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet. 1997. 19:935–944.44. Stogdale L. Definition of diabetes mellitus. Cornell Vet. 1986. 76:156–174.45. Townsend JC. Increased albumin excretion in diabetes. J Clin Pathol. 1990. 43:3–8.
Article46. Wa C, Cerny RL, Clarke WA, Hage DS. Characterization of glycation adducts on human serum albumin by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2007. 385:48–60.
Article47. Zerbé CA. What is so Special about Feline Diabetes Mellitus? J Feline Med Surg. 2001. 3:99–103.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of circulating IGF-I and IGFBP-3 as biomarkers for tumors in dogs
- Characteristics of Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor ( IGF ) and IGF-Bindign Protein-3 during Pregnancy
- Normative Data on Serum Levels of IGF-I, IGFBP-3 in Healthy Korean Children: Effect of Age, Sex, Height, Body Mass Index, and Pubertal Maturation on the Serum Levels
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding proteins axis in diabetes mellitus
- Serum levels of free insulin-like growth factor-I and clinical value in healthy children