Yonsei Med J.
2010 Mar;51(2):202-205. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.2.202.
A Single Center Experience of Self-Bougienage on Stricture Recurrence after Surgery for Corrosive Esophageal Strictures in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Masan Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Masan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. i101016@skku.edu
- 3Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1126018
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.2.202
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was undertaken to evaluate the long-term treatment of esophageal strictures in children with corrosive esophagitis and to determine the effect of self-bougienage on recurrent strictures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the medical records of nine children that were treated for corrosive esophageal strictures from May 2000 to May 2008. Six males and three females were included and their average age was 30 months. Six patients had ingested acids, two patents had ingested alkali, and one ingested an unknown agent.
RESULTS
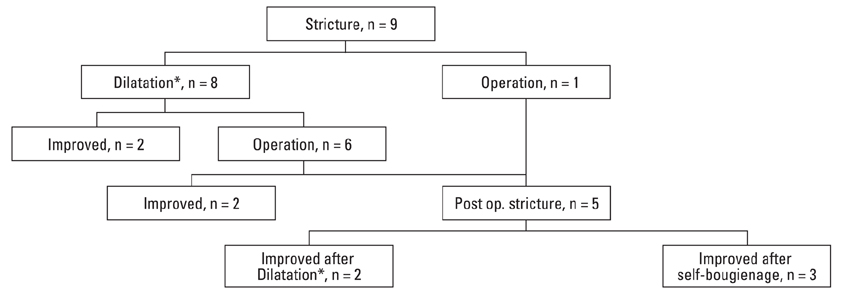
The interval between caustic ingestion and esophageal stricture ranged from one to eight weeks. The average length of the esophageal strictures was 3.8 cm (range, 1 to 9.2 cm). Four patients had a long segment stricture (longer than 5 cm) and one patient had multiple strictures. The most common site of involvement was the upper third followed by the mid third of the esophagus. Eight patients received repeated dilatation using a balloon catheter or bougie dilator. Among the eight patients, two patients had complete resolution of symptoms and six patients required surgery. Among five patients that developed restenosis of the esophageal anastomosis site, three patients had improved symptoms after self-bougienage and two patients had improved symptoms with repeated balloon dilatation or endoscopic bougienage. There were no complications in these patients.
CONCLUSION
Although a small number of patients were studied, self-bougienage was safe, less invasive, and effective for the management of esophageal restenosis in patients who required frequent dilation after surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arévalo-Silva C, Eliashar R, Wohlgelernter J, Elidan J, Gross M. Ingestion of caustic substances: a 15-year experience. Laryngoscope. 2006. 116:1422–1426.
Article2. Doğan Y, Erkan T, Cokuğras FC, Kutlu T. Caustic gastroesophageal lesions in childhood: an analysis of 473 cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2006. 45:435–438.
Article3. Ferguson DD. Evaluation and management of benign esophageal strictures. Dis Esophagus. 2005. 18:359–364.
Article4. Genç A, Mutaf O. Esophageal motility changes in acute and late periods of caustic esophageal burns and their relation to prognosis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2002. 37:1526–1528.5. Kruger FC. Caustic injury to the upper GI tract. SADJ. 2004. 59:335.6. Gün F, Abbasoğlu L, Celik A, Salman ET. Early and late term management in caustic ingestion in children: a 16-year experience. Acta Chir Belg. 2007. 107:49–52.
Article7. Han Y, Cheng QS, Li XF, Wang XP. Surgical management of esophageal strictures after caustic burns: a 30 years of experience. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. 10:2846–2849.8. Grobe JL, Kozarek RA, Sanowski RA. Self-bougienage in the treatment of benign esophageal stricture. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1984. 6:109–112.9. Kim CH, Groskreutz JL, Gehrking SJ. Recurrent benign esophageal strictures treated with self-bougienage: report of seven cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1990. 65:799–803.
Article10. Gündoğdu HZ, Tanyel FC, Büyükpamukçu N, Hiçsönmez A. Conservative treatment of caustic esophageal strictures in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1992. 27:767–770.
Article11. Gilmore IT, Sheers R. Oesophageal self-bougienage. Lancet. 1982. 1:620–621.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Affecting the Response to Endoscopic Dilatation Therapy for Benign Esophageal Stricture
- Balloon catheter dilatation of esophageal strictures in children and an infant
- Difficulty of balloon dilatation in corrosive esophageal strictures
- The Role of Endoscopic Balloon Dilation in the Treatment of Esophageal Strictures
- Balloon Dilatation and Bougienage of Post-operative Anastomotic Site Stricture of Upper G-I Tract