Yonsei Med J.
2008 Apr;49(2):337-340. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.337.
A New Method for Investigation of the Hair Shaft: Hard X-Ray Microscopy with a 90-nm Spatial Resolution
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology and Institute of Hair and Cosmetic Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. leewonsoo@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, Korea.
- KMID: 1084511
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.337
Abstract
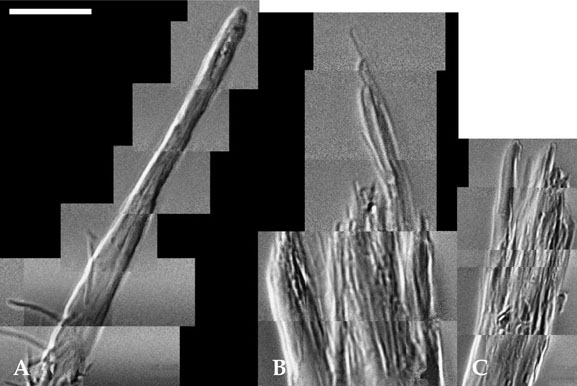
- Various methods have been used to investigate the hair shaft. In the ultrastructural hair field, scanning and transmission electron microscopies are widely used investigative methods, but they have some technical limitations. Recently, X-ray microscopes with sub-micron spatial resolution have emerged as useful instruments because they offer a unique opportunity to observe the interior of an undamaged sample in greater detail. In this report, we examined damaged hair shaft tips using hard X-ray microscopy with a 90 nm spatial resolution. The results of this study suggest that hard X-ray microscopy is an alternative investigative method for hair morphology studies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wolfram LJ. Human hair: A unique physicochemical composite. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003. 48:Suppl 1. S106–S114.
Article2. Chao W, Anderson E, Denbeaux GP, Harteneck B, Liddle JA, Olynick DL, et al. 20-nm resolution x-ray microscopy demonstrated by use of multilayer test structures[corrected]. Opt Lett. 2003. 28:2019–2021.
Article3. Hadjur C, Daty G, Madry G, Corcuff P. Cosmetic assessment of the human hair by confocal microscopy. Scanning. 2002. 24:59–64.
Article4. Baltenneck F, Bernard , Garson JC, Engström P, Riekel C, Leroy F, et al. Study of the keratinization process in human hair follicle by X-ray microdiffraction. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2000. 46:1017–1024.5. James V, Corino G, Robertson T, Dutton N, Halas D, Boyd A, et al. Early diagnosis of breast cancer by hair diffraction. Int J Cancer. 2005. 114:969–972.
Article6. Rogers KD, Hall CJ, Hufton A, Wess TJ, Pinder SE, Siu K. Reproducibility of cancer diagnosis using hair. Int J Cancer. 2006. 118:1060.
Article7. Jung H, Kim HJ, Kim EK, Hong JO, Je JH, Hwu Y, et al. Comparison of unmonochromatized synchrotron radiation and conventional X-rays in the imaging of mammographic phantom and human breast specimens: a preliminary result. Yonsei Med J. 2005. 46:95–103.
Article8. Hwu Y, Tsai WL, Je JH, Seol SK, Kim B, Groso A, et al. Synchrotron microangiography with no contrast agent. Phys Med Biol. 2004. 49:501–508.
Article9. Neuhäusler U, Schneider G, Ludwig W, Meyer MA, Zschech E, Hambach D. X-ray microscopy in Zernike phase contrast mode at 4keV photon energy with 60 nm resolution. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2003. 36:A79–A82.10. Youn HS, Baik SY, Chang CH. Hard x-ray microscopy with a 130 nm spatial resolution. Rev Sci Instrum. 2005. 76:023702. 1-4.11. Youn HS, Jung SW. Observations of human hair shaft with an x-ray microscope. Phys Med Biol. 2005. 50:5417–5420.12. Kim BJ, Kwon OS, Park WS, Youn HS, Choi CW, Kim KH, et al. Non-invasive evaluation of hair interior morphology by X-ray microscope. J Dermatol. 2006. 33:759–764.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Synchrotron Radiation Imaging of Breast Tissue Using a Phase-contrast Hard X-ray Microscope
- Four Cases of Hair Shaft Breakage Caused by Hair Care Cosmetics
- Central Trichoptilosis Associated with Trichorrhexis Nodosa and Pili Torti
- Scanning Electron Microscopic Findings of Hair Anomalies
- Isolation and Quantification of Glycosaminoglycans from Human Hair Shaft