Korean J Lab Med.
2007 Oct;27(5):360-368. 10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.5.360.
Evaluation of BioSewoom(TM) HLA-A, -B, -C PCR/SSP Kit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hboh@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1781536
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.5.360
Abstract
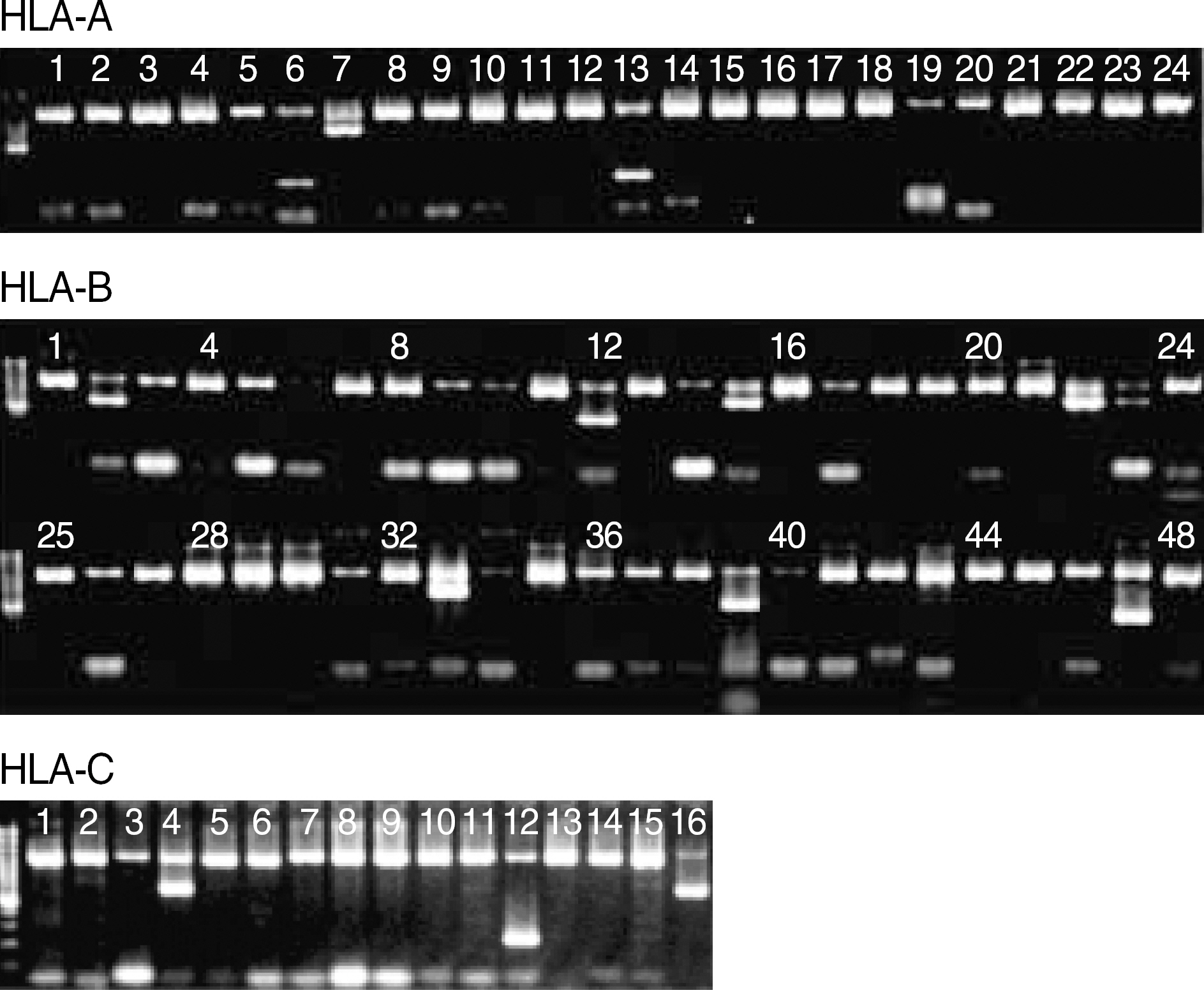
- BACKGROUND: Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is rapidly replacing the conventional serological method. This study was intended to evaluate Bio- SewoomTM HLA-A, -B, -C PCR/SSP kit (BioSewoom SSP) which had recently been developed in Korea. METHODS: A total of 158 samples from domestic (21) and international (137) HLA proficiency testing (PT) were genotyped with BioSewoom SSP, and its results were compared to consensus results. For comparison with INNO-LiPA HLA-A, -B, -C Typing Kit (INNO-LiPA, Innogenetics, Belgium), 20 samples of Koreans were genotyped with both kits for each HLA-A, -B, -C locus. RESULTS: Among the 21 samples of domestic PT, BioSewoom SSP showed ambiguities as follows: 4 samples (19.0%) in HLA-A, 6 (28.6%) in HLA-B, and 1 (4.8%) in HLA-C. The ambiguities could be resolved by considering the allele distribution of Koreans. Among the 137 samples from international PT, BioSewoom SSP also showed ambiguities as follows: 12 samples (8.8%) in HLA-A, 26 (19.0%) in HLA-B and 6 (4.4%) in HLA-C. Considering the allele distribution of Koreans, the serologic equivalents obtained from BioSewoom SSP showed a full agreement with those of INNO-LiPA in all the loci tested. Twelve (0.007%) among 1,760 PCR reactions from the 21 samples of domestic PT and 20 patient samples produced faint nonspecific bands, but it was negligible. PCR failure of internal control just barely occurred (15 PCR reactions, 0.009%), but it had no bearing on allele assignment. CONCLUSIONS: The performance of BioSewoom SSP was comparable to that of INNO-LiPA. All the ambiguities could be resolved by considering the allele distribution of Koreans. It is concluded that BioSewoom SSP has good performance to be used in routine HLA laboratories.
Keyword
- HLA; SSP; DNA typing
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Middleton D., Williams F. A history of DNA typing for HLA. Terasaki PI, Gjertson DW, editors. HLA 1997. Los Angeles: UCLA Tissue Typing Laboratory;1997. p. 61–84.2.Hurley CK., Cao K., Tang T., Steiner N., Lazaro AM., Howard A, et al. Molecular methods: HLA alleles. Detrick B, Hamilton RG, editors. , eds.Manual of molecular and clinical laboratory immunology. 7th ed.Washington, DC: ASM Press;2006. p. 1198–214.3.Yang YS., Kim DW. Evaluation of a commercial kit “INNOLiPA HLA DRB” for HLA-DR genotyping. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1996. 16:228–37. (양윤선 및 김대원. HLA-DR Genotyping 키트 “INNO-LiPA HLA DRB”의 평가. 대한임상병리학회지 1996;16: 228-37.).4.Bunce M., Welsh K. PCR-SSP typing of HLA class I and class II alleles. Hahn AB, Land GA, editors. , eds.ASHI laboratory manual. 4th ed.American Society for Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics;2000. :V.C.1.5.Lee KW., Jeon H., Park JY., Cho HC. Establishment of HLA-B∗15 supplementary DNA typing for Korean samples. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2000. 20:576–82. (이경화, 전현배, 박지영, 조현찬. HLA-B*15 대립유전자구별용보조 DNA 검사법확립: 한국인검체용. 대한임상병리학회지 2000;20: 576-82.).6.Olerup O., Zetterquist H. HLA-DR typing by PCR amplification with sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP) in 2 hours: an alternative to serological DR typing in clinical practice including donor-recipient matching in cadaveric transplantation. Tissue Antigens. 1992. 39:225–35.
Article7.Oh J., Kim T. Rapid HLA-DR DNA typying using the Biotest HLA-DRB SSP kit. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1996. 16:751–9. (오지하및김신규. PCR-SSP법에의한HLA-DR DNA typing. 대한임상병리학회지 1996;16: 751-9.).8.Choi SJ., Won CY., Oh HB. HLA-DR typing with PEL-FREEZ DR4 TEST-SSP UNITRAY. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 1999. 21:237–42. (최수진, 원진연, 오흥범. PEL-FREEZ DR4 TEST-SSP UNITRAY를이용한 HLA-DR 검사. 임상검사와정도관리 1999;21: 237-42.).9.Song EY., Park H., Park MH. Evaulation of the NeoDin SSP™ HLA-DR Typing Kit. Korean J Lab Med. 2003. 23:345–51. (송은영, 박혜진, 박명희. HLA-DR DNA 검사용시약 NeoDin SSPTM HLA-DR Typing Kit의평가. 대한진단검사의학회지 2003;23: 345-51.).10.Hwang SH., Oh HB., Yang JH., Kwon OJ., Shin ES. Distribution of HLA-A, B, C allele and haplotype frequencies in Koreans. Korean J Lab Med. 2004. 24:396–404. (황상현, 오흥범, 양진혁, 권오중, 신은순. 한국인의 HLA-A, -B, -C 대립유전자와일배체형분포. 대한진단검사의학회지 2004;24: 396-404.).11.QC Committee KSLM. Results of the 17th HLA typing proficiency survey in Korea: Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine. 2006. 1–29. 대한진단검사의학회정도관리위원회. 제 17차 HLA 검사신빙도조사분석결과: 대한진단검사의학회. 2006:1–29. ).12.QC Committee K. Results of the 18th HLA typing proficiency survey in Korea: Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine. 2006. 1–30. (대한진단검사의학회 정도관리위원회. 제 18차 HLA 검사 신빙도조사분석결과: 대한진단검사의학회. 2006:1–30. ).13.Bozon MV., Delgado JC., Turbay D., Salazar M., Granja CB., Alosco SM, et al. Comparison of HLA-A antigen typing by serology with two polymerase chain reaction based DNA typing methods: implications for proficiency testing. Tissue Antigens. 1996. 47:512–8.14.Yu N., Ohashi M., Alosco S., Granja C., Salazar M., Hegland J, et al. Accurate typing of HLA-A antigens and analysis of serological deficiencies. Tissue Antigens. 1997. 50:380–6.
Article15.Mytilineos J., Lempert M., Middleton D., Williams F., Cullen C., Scherer S, et al. HLA class I DNA typing of 215 “HLA-A, -B, -DR zero mismatched” kidney transplants. Tissue Antigens. 1997. 50:355–8.
Article16.Mytilineos J., Lempert M., Scherer S., Schwarz V., Opelz G. Comparison of serological and DNA PCR-SSP typing results for HLA-A and HLA-B in 421 Black individuals: a Collaborative Transplant Study report. Hum Immunol. 1998. 59:512–7.17.Bunce M., Fanning GC., Welsh KI. Comprehensive, serologically equivalent DNA typing for HLA-B by PCR using sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP). Tissue Antigens. 1995. 45:81–90.
Article18.Lorentzen DF., Iwanaga KK., Meuer KJ., Moritz TL., Watkins DI. A 25% error rate in serologic typing of HLA-B homozygotes. Tissue Antigens. 1997. 50:359–65.
Article19.Bozon MV., Delgado JC., Selvakumar A., Clavijo OP., Salazar M., Ohashi M, et al. Error rate for HLA-B antigen assignment by serology: implications for proficiency testing and utilization of DNA-based methods. Tissue Antigens. 1997. 50:387–94.20.Bunce M., Barnardo MC., Procter J., Marsh SG., Vilches C., Welsh KI. High resolution HLA-C typing by PCR-SSP: identification of allelic frequencies and linkage disequilibria in 604 unrelated random UK Caucasoids and a comparison with serology. Tissue Antigens. 1997. 50:100–11.
Article21.Mytilineos J., Christ U., Lempert M., Opelz G. Comparison of typing results by serology and polymerase chain reaction with sequence-specific primers for HLA-Cw in 650 individuals. Tissue Antigens. 1997. 50:395–400.
Article22.Lee YW., Yang YS. Comparison of HLA-Cw typing by serology and PCR-SSP in the Korean population. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1999. 19:239–45. (이용화및양윤선. 한국인에서혈청학적방법과 PCR-SSP로실시한 HLA-Cw 형별검사의 비교. 대한임상병리학회지 1999;19: 239-45.).23.Park MH., Kim BC., Han BY. Results of the HLA typing proficiency survey in Korea, 2000-2002. Korean J Lab Med. 2005. 25:329–39. (박명희, 김병철, 한복연. HLA 검사신빙도조사결과(2000-2002년). 대한진단검사의학회지 2005;25: 329-39.).24.De Vreese K., Barylski R., Pughe F., Blaser M., Evans C., Norton J, et al. Performance characteristics of updated INNO-LiPA assays for molecular typing of human leukocyte antigen A (HLA-A), HLA-B, and HLA-DQB1 alleles. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. 11:430–2.
Article25.Lim JH., Hwang SH., Oh HB. HLA Typing Proficiency Survey in Korea, 2003-2004. Korean J Lab Med. 2005. 25:434–41. (임지훈, 황상현, 오흥범. HLA 검사신빙도조사결과(2003-2004년). 대한진단검사의학회지 2005;25: 434-41.).26.The Anthony Nolan Research Institute. http://www.anthonynolan.org.uk/HIG. (Updated on Jan. 2007.27.Marsh SG., Albert ED., Bodmer WF., Bontrop RE., Dupont B., Erlich HA, et al. Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system, 2004. Tissue Antigens. 2005. 65:301–69.
Article28.Lee KW., Oh DH., Lee C., Yang SY. Allelic and haplotypic diversity of HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, and -DQB1 genes in the Korean population. Tissue Antigens. 2005. 65:437–47.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Two Commercial HLA-B27 Real-Time PCR Kits
- Evaluation of the NeoDin SSP(TM) HLA-DR Typing Kit
- HLA-DR Typing with PEL-FREEZ(R) DR4 TEST-SSP UNITRAY(TM)
- Usefulness of PCR-SSP Method for Detection of HLA-DRB1*0405
- Utility of In-House PCR for HLA-B27 Typing: Comparison of Concordance Rate between PCR Kit and In-House PCR