Korean J Ophthalmol.
2006 Dec;20(4):234-237. 10.3341/kjo.2006.20.4.234.
A Case of Orbital Abscess following Porous Orbital Implant Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. swyang @catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 754589
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2006.20.4.234
Abstract
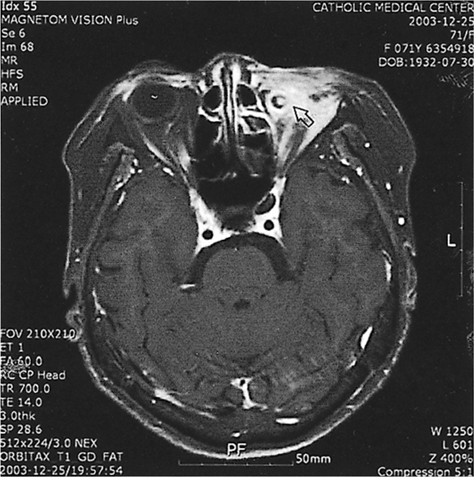
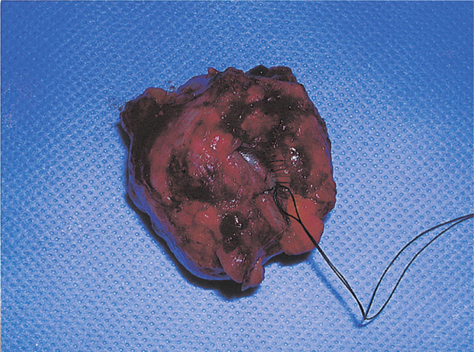
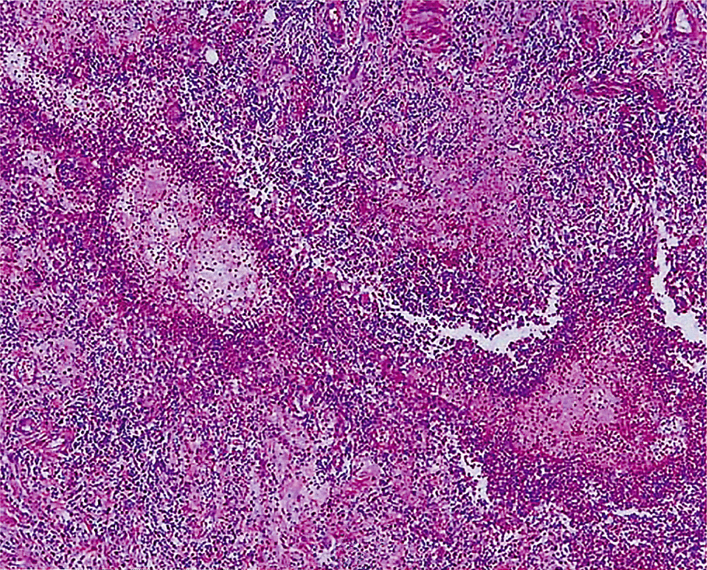
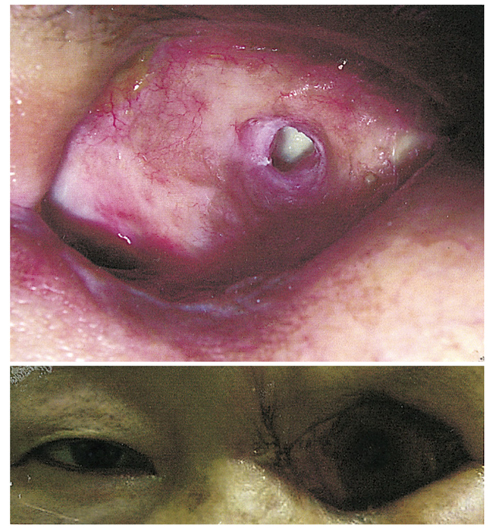
- PURPOSE: We present a case of orbital abscess following porous orbital implant infection in a 73-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis. METHODS: Just one month after a seemingly uncomplicated enucleation and porous polyethylene (Medpor(R)) orbital implant surgery, implant exposure developed with profuse pus discharge. The patient was unresponsive to implant removal and MRI confirmed the presence of an orbital pus pocket. Despite extirpation of the four rectus muscles, inflammatory granulation debridement and abscess drainage, another new pus pocket developed. RESULTS: After partial orbital exenteration, the wound finally healed well without any additional abscess formation. CONCLUSIONS: A patient who has risk factors for delayed wound healing must be examined thoroughly and extreme care such as exenteration must be taken if there is persistent infection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goldberg RA, Holds JB, Ebrahimpour J. Exposed hydroxyapatite orbital implants. Ophthalmology. 1992. 95:831–836.2. Ainbinder DJ, Haik BG, Tellado M. Hydroxyapatitie orbital implant abscess: histopathologic correlation of an infected implant following evisceration. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994. 10:267–270.3. Jordan DR, Brownstein S, Jolly SS. Abscessed hydroxyapatite orbital implants- a report of two cases. Ophthalmology. 1996. 103:1784–1787.4. Oestreicher JH, Bashour M, Jong R, et al. Aspergillus Mycetoma in a secondary hydroxyapatite orbital implant - a case report and literature review. Ophthalmology. 1999. 106:987–991.5. Kim YD, Goldberg RA, Shorr N, et al. Management of exposed hydroxyapatite orbital implants. Ophthalmology. 1994. 101:1709–1715.6. Jordan DR, Brownstein S, Faraji H. Clinicopathologic analysis of 15 explanted hydroxyapatite implants. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. 20:285–290.7. Zegans ME, Becker HI, Budzik J, et al. The role of bacterial biofilms in ocular infections. DNA Cell Biol. 2002. 21:415–420.8. You SJ, Yang HW, Lee HC, Kim SJ. 5 cases of infected hydroxyapatite orbital implant. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002. 43:1553–1557.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Medpor(R) Orbital Implant Infection
- Scleral Eversion Technique for Porous Polyethylene Orbital Implant after Evisceration
- Two Cases of Actinomyces Infection in a Hydroxyapatite Orbital Implant with a Motility Peg
- Management of Exposed Porous Orbital Implants
- Clinical Effect of Porous Polyethylene (Medpor(r))Orbital Implant