Korean J Radiol.
2002 Sep;3(3):194-198. 10.3348/kjr.2002.3.3.194.
Gene Delivery to the Rat Liver Using Cationic Lipid Emulsion/DNA Complex: Comparison between Intra-arterial, Intraportal and Intravenous Administration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chungjw@radcom.snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, SNUMRC, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Biomedical Research Center, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 754062
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2002.3.3.194
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare the efficiency of intra-arterial, intraportal, and intravenous administration of cationic lipid emulsion/DNA complex, as used for gene transfer to rat liver.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
DNA-carrier complex for the in-vivo experiment was prepared by mixing DNA and a cationic lipid emulsion. According to the administration route used (intra-arterial, intraportal, or intravenous), the animals were assigned to one of three groups. The heart, lung, liver, spleen and kidneys were removed and assayed for total protein and luciferase concentration.
RESULTS
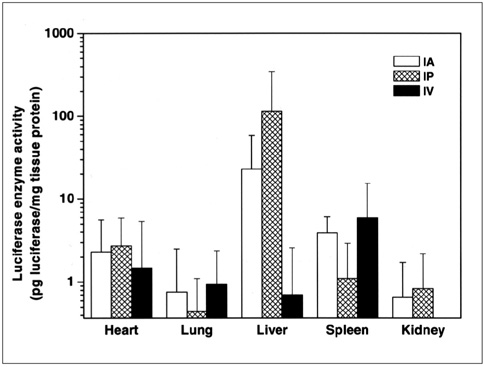
The cationic lipid emulsion/DNA complex used successfully transfected the various organs via the different administration routes employed. Luciferase activity in each organ of untreated animals was negligible. Liver luciferase values were significantly higher in the groups in which intra-arterial or intraportal administration was used.
CONCLUSION
The intra-arterial or intraportal administration of cationic lipid emulsion/DNA complex is superior to intravenous administration and allows selective gene transfer to the liver.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Voss SD, Kruskal JB. Gene therapy: a primer for radiologists. RadioGraphics. 1998. 18:1343–1372.2. Barron LG, Uyechi LS, Szoka FC. Cationic lipids are essential for gene delivery mediated by intravenous administration of lipoplexes. Gene Ther. 1999. 6:1179–1183.3. Wilson JM. Adenoviruses as gene-delivery vehicles. Mol Med. 1996. 18:1185–1187.4. Kim TW, Chung H, Kwon IC, Sung HC, Jeong SY. In vivo gene transfer to the mouse nasal cavity mucosa using a stable cationic lipid emulsion. Mol Cells. 2000. 2:142–147.5. Anderson SC, Johnson DE, Harris MP, et al. p53 gene therapy in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma: intra-arterial delivery of a recombinant adenovirus. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. 4:1649–1659.6. Kim TW, Chung H, Kwon IC, et al. Optimization of lipid composition in cationic emulsion as in vitro and in vivo transfection agents. Pharm Res. 2001. 18:54–60.7. Grossman M, Rader D, Muller D, et al. A pilot study of ex vivo gene therapy for homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Nat Med. 1995. 1:1148–1154.8. Ye X, Robinson M, Batshaw M, et al. Prolonged metabolic correction in adult ornithine transcarbamylase-deficient mice with adenoviral vectors. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:3639–3646.9. Wang L, Nichols TC, Read MS, Bellinger DA, Verma IM. Sustained expression of therapeutic level of factor IX in hemophilia-B dogs by AAV-mediated gene therapy in liver. Mol Ther. 2000. 1:154–158.10. Nunes FA, Raper SE. Liver-directed gene therapy. Med Clin North Am. 1996. 80:1201–1213.11. Gnant MFX, Puhlmann M, Barlett DL, Alexander R Jr. Regional versus systemic delivery of recombinant vaccinia virus as suicide gene therapy for murine liver metastases. Ann Surg. 1999. 230:352–361.12. Liu F, Yang J, Huang L, Liu D. Effect of non-ionic surfactants on the formation of DNA/emulsion complexes and emulsion-mediated gene transfer. Pharm Res. 1996. 13:1642–1646.13. Ghosh SS, Takahashi M, Thummala NR, et al. Liver-directed gene therapy: promises, problems and prospects at the turn of the century. J Hepatol. 2000. 32:238–252.14. Kawakami S, Fumoto S, Nishikawa M, et al. In vivo gene delivery to the liver using novel galactosylated cationic liposomes. Pharm Res. 2000. 17:306–313.15. Mahato RI, Kawabata K, Nomura T, et al. Physicochemical and pharmacokinetic characteristics of plasmid DNA/cationic liposome complexes. J Pharm Sci. 1995. 84:1267–1271.16. Yi SW, Yun TY, Kim TW, et al. A cationic lipid emulsion/DNA complex as a physically stable and serum-resistant gene delivery system. Pharm Res. 2000. 17:314–320.17. Litzinger DC, Brown JM, Wala I, et al. Fate of cationic liposomes and their complex with oligonucleotide in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996. 1281:139–149.18. Hofland HEJ, Shephard L, Sullivan SM. Formation of stable cationic lipid/DNA complexes for gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. 93:7305–7309.19. Zelphati O, Uyechi LS, Barron LG, Szoka FC. Effect of serum components on the physico-chemical properties of cationic lipid/oligonucleotide complexes and on their interactions with cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994. 1189:195–203.20. Chung H, Kim TW, Kwon M, et al. Oil components modulate physical characteristics and function of the natural oil emulsion as drug or gene delivery system. J Control Rel. 2001. 71:339–350.21. Templeton NS, Lasic DD, Frederik PM, Strey HH, Roberts DD, Pavlakis GN. Improved DNA:liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery and gene expression. Nat Biotechnol. 1997. 15:647–652.22. Mahato RI, Kawabata K, Nomura T, Takakura Y, Hashida M. Physicochemical and pharmacokinetic characteristics of plasmid DNA/cationic liposome complexes. J Pharm Sci. 1995. 84:1267–1271.23. Kim TW, Chung H, Kwon IC, Sung HC, Jeong SY. Optimization of lipid composition in cationic emulsion as in vitro and in vivo transfection agents. Pharm Res. 2000. 18:54–60.24. Wu J, Zern MA. Modification of liposomes for liver targeting. J Hepatol. 1996. 24:757–763.25. Litzinger DC, Buiting AMJ, Rooijen AV, Huang L. Effect of liposome size on the circulation time and intraorgan distribution of amphipathic polyethylene glycol-containing liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994. 1190:99–107.26. Seol JG, Heo DS, Kim HK, et al. Selective gene expression in hepatic tumor with transarterial delivery of DNA/liposome/transferrin complex. In vivo. 2000. 14:513–517.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Enhanced Expressions and Histological Characteristics of Intravenously Administered Plasmid DNA in Rat Lung
- Experimental Study on in Vivo Gene Transfer to Kidney Tumor Using Intrarenal-arterial Administration of Plasmid DNA in Complex with Cationic Polyliposome
- Lipid Emulsion in the Successful Resuscitation of Local Anesthetic Toxicity after Ankle Block
- The Effect of Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in a Rat Model of Verapamil Toxicity
- Lipid-Emulsion Propofol Less Attenuates the Regulation of Body Temperature than Micro-Emulsion Propofol or Sevoflurane in the Elderly