Korean J Radiol.
2006 Mar;7(1):28-34. 10.3348/kjr.2006.7.1.28.
Interventional Procedures in Superficial Lesions: The Value of 2D with Additional Coronal Reformatted 4D Ultrasonography Guidance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital and School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan. cmychang@vghtpe.gov.tw
- 2Department of Orthopedics, Taipei Veterans General Hospital and School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan.
- KMID: 753913
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2006.7.1.28
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
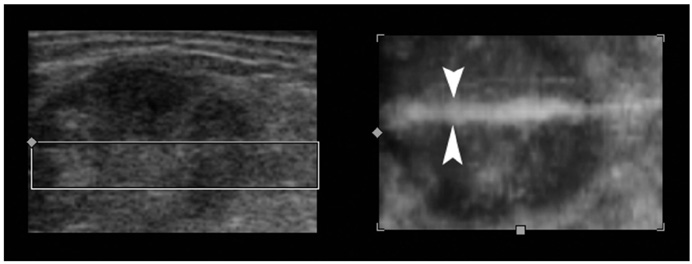
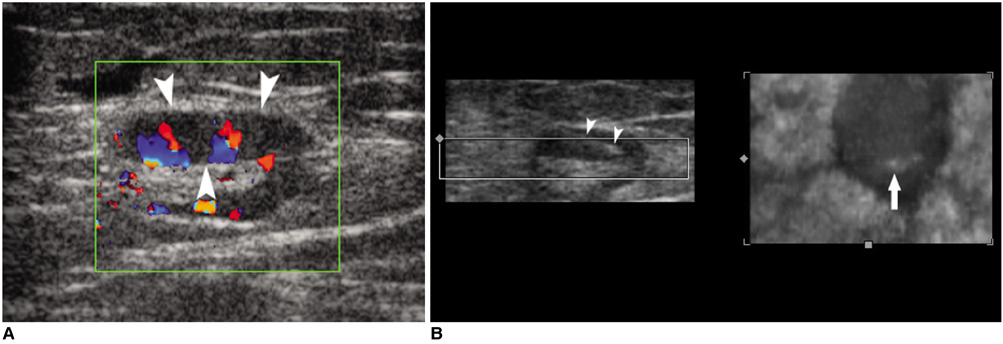
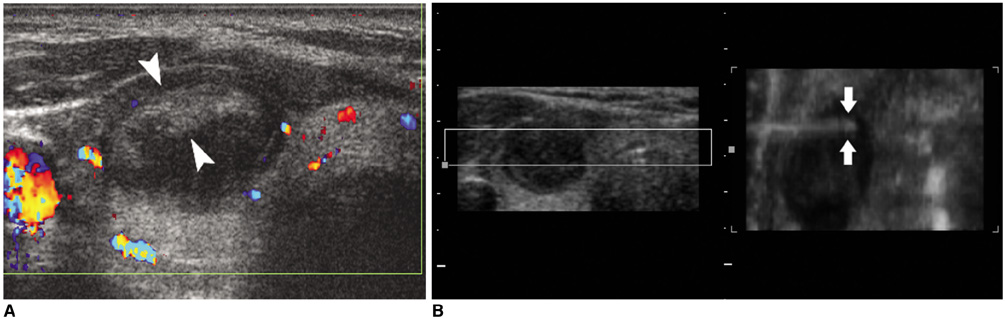
We wanted to assess the usefulness of four-dimensional (4D) ultrasonography (US), i.e., real-time three-dimensional US, as an adjunct for performing various US-guided interventional procedures in superficial lesions. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirty-three patients were referred for US-guided interventional procedures for superficial lesions, including core biopsy in 19, fine-needle aspiration in eight, therapeutic drug injection in four and needle puncture in two. The procedures were performed under 4D US guidance. We reviewed the pathologic/cytologic results of the core biopsies or needle aspirations, and also the outcomes of drug injection or needle puncture. RESULTS: For all the patients who underwent 4D US-guided core biopsy, the specimens were adequate for making the pathological diagnosis, and specimens were successfully obtained for those patients who underwent 4D US-guided aspiration. The patients treated with 4D US-guided therapeutic drug injection or needle puncture had a good response. No major procedure-related complications occurred. The procedural times were similar to those procedural times with using two-dimensional US. CONCLUSION: Combining the two dimensional and 4D US techniques aids the physician when performing US-guided interventional procedures for the superficial lesions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cho N, Moon WK, Cha JH. Sonographically guided core biopsy of the breast: comparison of 14-gauge automated gun and 11-gauge directional vacuum-assisted biopsy methods. Korean J Radiol. 2005. 6:102–109.2. Lim HK. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas. Korean J Radiol. 2000. 1:175–184.3. Lees W. Ultrasound imaging in three and four dimensions. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2001. 22:85–105.4. Downey DB, Fenster A, Williams JC. Clinical utility of three-dimensional US. RadioGraphics. 2000. 20:559–571.5. Rose SC, Pretorius DH, Nelson TR, Kinney TB, Huynh TV, Roberts AC, et al. Adjunctive 3D US for achieving portal vein access during transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000. 11:611–621.6. Rose SC, Roberts AC, Kinney TB, Pretorius DH, Nelson TR. Three-dimensional ultrasonography for planning percutaneous drainage of complex abdominal fluid collections. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003. 14:451–459.7. Smith WL, Surry KJ, Mills GR, Downey DB, Fenster A. Three-dimensional ultrasound-guided core needle breast biopsy. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2001. 27:1025–1034.8. Rose SC, Hassanein TI, Easter DW, Gamagami RA, Bouvet M, Pretorius DH, et al. Value of three-dimensional US for optimizing guidance for ablating focal liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001. 12:507–515.9. Strasser H, Janetschek G, Horninger W, Bartsch G. Three-dimensional sonographic guidance for interstitial laser therapy in benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Endourol. 1995. 9:497–501.10. Weismann CF, Forstner R, Prokop E, Rettenbacher T. Three-dimensional targeting: a new three-dimensional ultrasound technique to evaluate needle position during breast biopsy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2000. 16:359–364.11. Chin JL, Downey DB, Mulligan M, Fenster A. Three-dimensional transrectal ultrasound guided cryoablation for localized prostate cancer in nonsurgical candidates: a feasibility study and report of early results. J Urol. 1998. 159:910–914.12. Won HJ, Han JK, Do KH, Lee KH, Kim KW, Kim SH, et al. Value of four-dimensional ultrasonography in ultrasonographically guided biopsy of hepatic masses. J Ultrasound Med. 2003. 22:215–220.13. Liu JC, Chiou HJ, Chen WM, Chou YH, Chen TH, Chen W, et al. Sonographically guided core needle biopsy of soft tissue neoplasms. J Clin Ultrasound. 2004. 32:294–298.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-guided genitourinary interventions: principles and techniques
- Is the Index Finger and Ring Finger Ratio (2D:4D) Reliable Predictor of Semen Quality?
- A Relationship between 2nd to 4th Digit Length Ratio and Aggression Related-Sports Entries Characteristics in Female Athletics of Korean National Teams
- Value of Coronal Reformatted Images Using Multi-detector Computed Tomography for Nodal Staging in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Cases
- The Study on The Near Point in Koreans